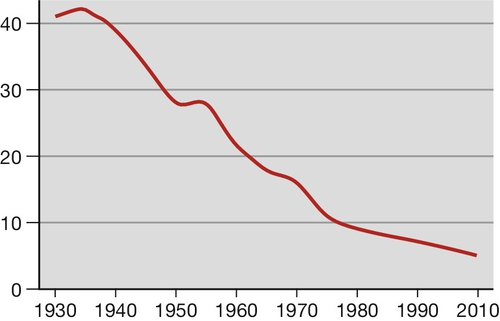
48 To suffer the loss of a baby before or shortly after birth is one of the most profoundly distressing experiences, one that affects a wide community of parents and siblings, relatives and friends, for most of whom the emotional upheaval is never resolved fully. Stillbirths, babies born with no signs of life after the end of the 24th week (24 + 0), are classified as deaths before the onset of labour (late fetal death) and deaths in labour (intrapartum stillbirth). Intrapartum deaths account for about 10% of all stillbirths in the UK. The UK stillbirth rate fell greatly across the second half of the 20th century (Fig. 48.1), mainly because of improved general health, better nutrition and wider education, probably more so than the consequence of any change in antenatal care per se. Despite this large fall, about 1 in 200 maternities in developed countries still end in stillbirth, 50 times the rate of sudden unexplained deaths in infancy (SUDI). In 2010, 3710 babies were stillborn in England and Wales, more than 10 each day, on average. There are a total of 3 million stillbirths each year worldwide and in the developing world, the stillbirth rate remains high, approximately 10-fold greater than for countries with advanced healthcare systems. There are many causes (see below) but as with almost half of affected pregnancies in the UK, no adequate explanation can be provided for the parents. Neonatal mortality, defined as death in the first 28 days of life, is divided into early deaths within the first 7 days and late deaths beyond 7 days. In 2010, there were 1657 deaths at age under 7 days in England and Wales. In developed countries, the large majority is associated with pre-term birth, which can be the result of spontaneous labour or be the consequence of elective birth because of maternal or fetal conditions. The rate of survival varies with gestation at birth and the underlying cause. As with stillbirths, there is great variation in causes and rates across the globe. Overall, the perinatal mortality rate for England and Wales is about 7/1000 total births. This chapter provides definitions for these birth statistics as well as considering the causes, complications and comprehensive care for parents whose baby dies before or shortly after birth. The definitions of commonly used birth statistics are presented in Table 48.1. Perinatal mortality rate (PNMR) has been seen as a broad indicator of the quality of maternity and neonatal services, often adjusted to exclude deaths related to lethal congenital malformations that cannot be avoided. In truth, even the adjusted PNMR is of relatively limited value for clinicians interested in quality improvement. For individual units, comparisons with other units are clouded by variations in societal differences and case mix. Table 48.1 Definitions of stillbirth and deaths in infancy a Some authorities also exclude babies below a certain weight. Even international comparisons of PNMR of whole populations can be misleading, as there can be: The PNMR is perhaps of most value for monitoring progress of major health initiatives in individual countries with very poor outcomes. The loss of a baby in late pregnancy or during the early neonatal period is nearly always accompanied by profound distress for parents and siblings, relatives and friends. For the mother especially, the feelings of loss can be compounded by vulnerability, depression and post-traumatic stress. Emotional reactions can be further heightened by prior suboptimal treatment, traumatic birth or a period of intensive critical care after the delivery. Any resolution of these feelings can be delayed by a later inability to explain the death. For carers, stillbirth and neonatal death can engender feelings that range from deep sadness, through anxiety and loss of confidence, to a sense of personal failure. All of this must be taken into full account when accompanying the parents on the journey that starts with the realization of their loss, and also when supporting staff. Higher maternal age and maternal obesity are the two commonest associations. The prevalence of these factors is rising, which might explain why the stillbirth rate is no longer falling. Other associations include smoking, illicit drug use, teenage pregnancy and maternal disease, many of which are also rising in frequency. It is not always possible to define a disease process and so descriptive categories have been identified, of which there are several classifications. The commonest method still in use is Wigglesworth’s classification, which is summarized in Table 48.2. Many categories simply describe the mode of death rather than the true underlying cause, for example hypoxia and growth restriction. Hypoxia may be chronic, in relation to placental disease, or acute such as placental abruption, cord prolapse or cord entanglement, but often the precise cause is unknown. For more details on specific causes such as antepartum haemorrhage, hypertension, medical disorders and isoimmunization, see the relevant individual chapters. A more detailed system is the ReCoDe (Relevant Condition at Death) classification developed in the West Midlands (Table 48.3). Clinicians have to be aware that the presence of a condition does not necessarily mean it is the cause of death and the authors of the ReCoDe system emphasize that. Table 48.2 Wigglesworth’s classification of stillbirths Table 48.3 ReCoDe classification of stillbirths a < 10th customized weight for gestational age centile. b If severe enough to be considered relevant. c Histological diagnosis. Isoimmunization was previously a common cause of stillbirth with severe fetal anaemia but the introduction of anti-Rh(D) gammaglobulin prophylaxis in 1971 steadily reduced the number of women with anti-red cell antibodies. For those that do have isoimmunization, intrauterine treatments have reduced the chance of affected pregnancies ending in fetal death. Before 1970, babies with severe congenital abnormalities also formed a much larger proportion of stillbirths. With the advent and steady improvement of prenatal ultrasound, more of these are diagnosed between 12 and 20 weeks’ gestation (Table 48.4). Many women choose termination of pregnancy when faced with such a diagnosis, which subsequently reduces the numbers that end as late fetal death or neonatal death; this represents a change in the statistic, but not the sense of loss for the mother. The widespread use of folic acid supplementation has also reduced the number of pregnancies affected by neural tube defects. Table 48.4 Examples of lethal or potentially lethal congenital malformations by system a Early usually means 12 weeks’ gestation; late usually means 20 weeks’ gestation. Most women attend with reduced or absent fetal movement, bleeding or pain, but for some the absence of heart activity is an unanticipated finding at a routine antenatal clinic or midwife visit. Fetal death may be diagnosed during labour or even at the moment of birth.
When a baby dies
stillbirth and neonatal death
Introduction
Statistics of adverse perinatal outcomes
Stillbirth (rate)
Any fetus born without signs of life, after 24 completed weeks of pregnancy (excepting fetuses that clearly died before 24 weeks, e.g. fetus papyraceous) (/1000 total births)
Early neonatal death (rate)
Death in the first seven days of life (/1000 live births)
Late neonatal death
Deaths from age 7 days to 28 completed days of life (/1000 live
births)
Perinatal mortality (rate, PNMR)
Stillbirth or neonatal death in first week of life (combined/1000 total births)
Adjusted PNMR
Number of deaths/1000 live and stillbirths, excluding lethal
congenital malformationsa
Post-neonatal death
Deaths beyond 28 days, but under 1 year of age
Infant death
All deaths at age under 1 year of age
![]() differences in the way statistics are collected
differences in the way statistics are collected
![]() differences in how gestational age is calculated
differences in how gestational age is calculated
![]() differences in social conditions that probably have more influence than health care
differences in social conditions that probably have more influence than health care
![]() differences in reproductive patterns such as the one-child policy in China
differences in reproductive patterns such as the one-child policy in China
![]() cultural infanticide of baby girls in some countries.
cultural infanticide of baby girls in some countries.
Emotional effects of perinatal death
Common associations and causes of stillbirth
Category
Comment
Unexplained
Largest single category
Mostly normally-grown babies at term
Malformations
Lethal or severe
Intrapartum asphyxia or trauma
Related to abruptions, cord prolapse, shoulder dystocia, etc.
Immaturity
More usually a cause of neonatal death
Fetal infection
May be acute bacterial or chronic viral, protozoal, etc.
Other causes
Twin-to-twin transfusion, tumours, isoimmunization
Group
Subgroups
Fetal
Lethal congenital anomaly
Infection
Non-immune hydrops
Isoimmunization
Fetomaternal haemorrhage
Twin–twin transfusion
Fetal growth restrictiona
Umbilical cord
Cord prolapse
Constricting loop or knotb
Velamentous insertion
Other
Placenta
Placental abruption
Placenta praevia
Vasa praevia
Other ‘placental insufficiency’c
Other
Uterus
Rupture
Anomalies
Other
Amniotic fluid
Chorioamnionitis
Oligohydramniosb
Polyhydramniosb
Other
Mother
Diabetes and thyroid diseases
Essential hypertension and hypertensive diseases in pregnancy
Lupus or antiphospholipid syndrome
Cholestasis
Drug misuse
Other
Intrapartum
Asphyxia
Trauma
Trauma
External
Iatrogenic
Unclassified
No cause evident
No information
System
Examples
Diagnostic test
CNS
Anencephaly
Early ultrasound scana
Cardiovascular
Single ventricle, hypoplastic left heart
Late ultrasound scana
Renal
Renal agenesis, urethral atresia
Late ultrasound scan
Gastrointestinal
Diaphragmatic hernia, exomphalos
Late ultrasound scan
Chromosomal
Edwards syndrome (47 + 18)
Patau syndrome (47 + 13)
Early combined serum/ultrasound screening or later 20-week ultrasound, prompting invasive diagnostic testing
Musculoskeletal
Thanatophoric dysplasia, achondrogenesis
Some types of osteogenesis imperfecta
Late ultrasound scan
Stillbirth
Clinical aspects of stillbirth care
Presentation
Diagnosis of death
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree