Trans-Spatial Mass
Bernadette L. Koch, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Abscess
Lymphatic Malformation
Venous Malformation
Infantile Hemangioma
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Less Common
Lipoma
Thymic Cyst
4th Branchial Anomaly
Rare but Important
Teratoma
Fibromatosis
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Trans-spatial: Multiple contiguous spaces
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Abscess
Key facts
Signs and symptoms of infection
May be in deep soft tissues of neck
May present with airway impingement
75% drainable pus; 25% phlegmonous, nondrainable inflammatory tissue
Imaging
Low-attenuation, rim-enhancing mass
Retropharyngeal edema common
May extend via danger space into mediastinum
Lymphatic Malformation
Key facts
Most common cystic neck mass with spontaneous hemorrhage
Sudden increase in size secondary to hemorrhage or viral respiratory infection
Imaging
Unilocular or multilocular; macrocystic or microcystic; 1 space or trans-spatial
Insinuates morphology
Only septations enhance, unless associated with venous malformation
Lack high-flow vessels on flow-sensitive MR sequences and angiography
Fluid-fluid levels secondary to intralesional hemorrhage common
Venous Malformation
Key facts
Lobulated soft tissue mass; variably sized venous channels with phleboliths
Mass increases in size with Valsalva, crying, or bending over
Imaging
Intermediate attenuation/hyperintense T2 with variable contrast enhancement
No high flow vessels
Infantile Hemangioma
Key facts
Neoplasm with spontaneous proliferation and involution
Present within 1st few weeks of life; usually not present at birth
May be multiple (PHACES syndrome)
Imaging
Lobulated mass, intense enhancement
High-flow intralesional vessels
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Key facts
Localized neurofibroma (NF), diffuse NF, plexiform NF (PNF), or malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (PNST)
If multiple or plexiform, think NF1
Imaging
May be hypoattenuating on CT
Localized: Well-circumscribed, fusiform, solid masses and moderate enhancement ± dumbbell-shaped extension into neural foramina
Diffuse NF: Plaque-like subcutaneous lesion with poorly defined infiltrating margins, moderate enhancement
Plexiform NF: Lobulated, tortuous, rope-like enlargement in major nerve distribution; resembles “tangle of worms”
Malignant PNST: Benign vs. malignant difficult to differentiate on imaging; consider malignant if ≥ 5 cm, intensely enhancing with infiltrative margins
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Key facts
Sites: Orbit, nasopharynx, temporal bone, sinonasal, cervical neck
Imaging
Soft tissue mass with variable contrast enhancement ± bone erosion
Coronal post-contrast fat-saturated T1 images best for intracranial extension
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Lipoma
Key facts
Benign neoplasm, mature fat
Imaging
Well-circumscribed homogeneous mass of fat attenuation and signal intensity
Small minority of lesions will have a nonfatty soft tissue component
Any space of neck
Single space or trans-spatial
Imaging cannot differentiate between lipoma and low-grade liposarcoma
Thymic Cyst
Key facts
Remnant of thymopharyngeal duct, 3rd branchial pouch remnant
Wall contains Hassall corpuscles
Imaging
Cystic neck mass along course of thymopharyngeal duct ± solid enhancing thymic tissue
Close association with carotid sheath
May be connected to mediastinal thymus directly or by fibrous cord
Rarely extends to skull base; may rupture into parapharyngeal space
4th Branchial Anomaly
Key facts
Presents with recurrent thyroiditis or anterior neck abscess secondary to sinus tract extending from apex of pyriform sinus to lower anterior neck
Imaging
Cyst or abscess anterior to left thyroid lobe with associated thyroiditis
Barium swallow or post barium swallow CT may show sinus tract extending from apex of pyriform sinus to anterior lower neck
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Teratoma
Key facts
All 3 germ cell lines
Mature, immature, and malignant
Imaging
Fat, calcium, cyst, and solid components
Fibromatosis
Key facts
Synonyms: Desmoid fibromatosis, extraabdominal desmoid fibromatosis, infantile fibromatosis
Histologically benign fibroproliferative disorder with potentially aggressive clinical course and invasive growth
Associated with Gardner syndrome
Imaging
Poorly marginated trans-spatial mass
Moderate post-contrast enhancement
± bone erosion or invasion
Image Gallery
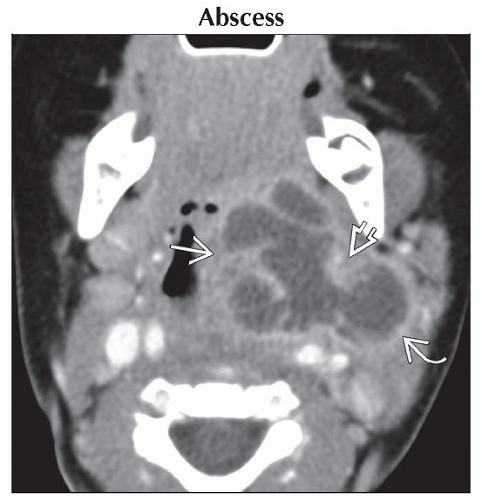 Axial CECT shows a large, multilobulated, rim-enhancing abscess arising from the left palatine tonsil
 , spreading into the parapharyngeal space , spreading into the parapharyngeal space  with extension to the deep parotid space with extension to the deep parotid space  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|