Fig. 72.1
Clinical photographs showing epispadias. Note the extent of the epispadias groove in (a) (glandular) and the dorsal chordee in (b)
The symphysis pubis is generally widened.
The rectus muscles are divergent distally.
In males:
◦ The phallus is short and broad with upward chordee.
◦ The urethral meatus is located on the dorsal penile shaft and can be limited to the glans penis or extends the whole length of the penis.
◦ The glans penis lies open and flat .
In females:
◦ The clitoris is bifid with divergent labia superiorly.
◦ The dorsal aspect of the urethra is open distally.
◦ The urethra and bladder neck are patulous and may allow visualization of bladder.
◦ Bladder mucosa may prolapse through the bladder neck .
In cloacal exstrophy (covered in detail in a separate chapter; Fig. 72.2) :
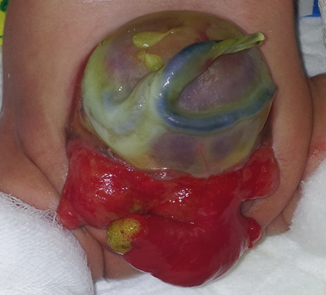
Fig. 72.2
A clinical photograph showing classic cloacal exstrophy. Note the omphalocele, the open urinary bladder, and the open trunk of bowel onto the cecal plate
Nearly all patients have an associated omphalocele.
The bladder is open and separated into two halves, with the exposed interior of the cecum between them.
The cecal plate contains openings to the remainder of the hindgut and to one or two appendices.
The terminal ileum may prolapse as a “trunk” of bowel onto the cecal plate.
The penis is generally small and bifid, with a hemi-glans located just caudal to each hemi-bladder.
Infrequently, the phallus may be intact in the midline.
In females, the clitoris is bifid and two vaginas are present.
The anus is absent.
Sixty-five percent of patients have a clubfoot or major deformity of a lower extremity.
Eighty percent of patients have vertebral anomalies.
Ninety-five percent of patients have myelodysplasia, which may include myelomeningocele, lipomeningocele, meningocele, or other forms of occult dysraphism.
These patients are at risk of neurologic deterioration, and they should be observed closely .
Early neurosurgical consultation is recommended if a radiographic abnormality of the spinal cord or canal is observed .
In exstrophy variants :
The symphysis pubis is widely separated, and rectus muscles diverge distally.
The umbilicus is low in position or elongated.
A small superior bladder opening or a patch of isolated bladder mucosa may be present.
The intact bladder may be externally covered by only a thin membrane.
Isolated ectopic bowel segments have been reported.
Genitalia generally are intact, though epispadias can occur.
In the split-symphysis variants of exstrophy, the symphysis pubis is widely separated, and the rectus muscles are divergent .
Isolated Epispadias
Introduction
Epispadias as an isolated malformation is very rare.
It is an uncommon congenital malformation of the penis and more commonly seen as part of the epispadias–exstrophy malformation.
Epispadias occurs more commonly in males than in females. The male to female ratio is 2.3:1.
It occurs in around 1 in 50,000 to 1 in 120,000 male and 1 in 400,000 to 1 in 500,000 female live births.
The extent of the defect can vary from a mild glandular defect to complete defects involving the whole length of the phallus.
Evaluation of the bladder neck and proximal urethra is recommended in patients with epispadias in order to plan surgical management
Embryology
Epispadias results from defective migration of the paired primordial genital tubercle that fuse on the midline to form the genital tubercle at the fifth week of embryologic development .
Epispadias and exstrophy of the bladder are considered varying degrees of a single disorder.
The extent of epispadias varies in severity depending on the time of the insult during embryologic development .
Classification
Epispadias is classified into :
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Glandular (Fig. 72.3)
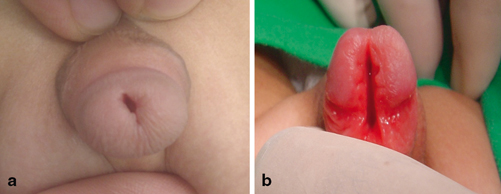
Fig. 72.3
a and b Clinical photographs showing mild glandular epispadias and full glandular epispadias
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


