KEY QUESTIONS FROM THE HISTORY
Breathlessness
- Consider the severity of breathing problems with activities
- Poor weight gain in infancy (a sign of respiratory distress)
Cough
- Chronology—any link to time of day/activity/environment
- Nature of cough: dry (viral), loose (productive), barking (croup), paradoxical (forced repetitive cough with difficult inspiration, seen in whooping cough)
Feeding in Infancy
- Choking (gastro-oesophageal reflux)
- Symptoms with introduction of formula milk (cow’s milk protein allergy)
Fever
Noisy Breathing
- Noise in expiration (wheeze = lower airway obstruction)
- Noise in inspiration (stridor = upper airway obstruction)
Cough, Wheeze or Stridor in a Young Child
- If sudden onset, is there a history of inhaled foreign body or choking?
Ear, Nose and Throat
- Child pulling at their ears (middle ear infection)
- Difficulty in swallowing (tonsillitis or epiglottitis)
- Offensive odour breath (bacterial infection)
- Nasal secretions, bleeding
Family History
- Family history of respiratory problems (asthma, cystic fibrosis)
- Asthma, eczema, hay fever in close relative (atopy)
- Any smokers or pet animals in household?
- Travel to area of high tuberculosis prevalence, or contact with infected relative?
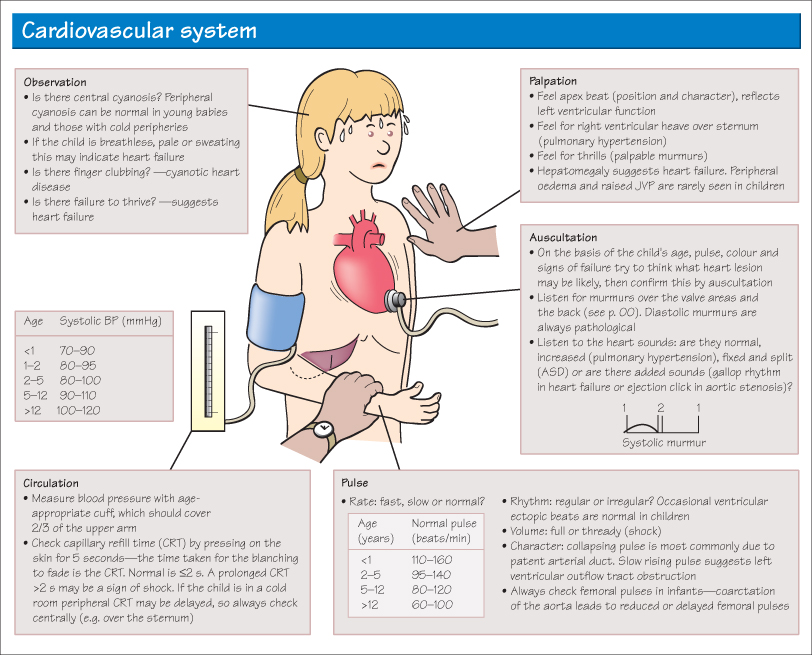
KEY QUESTIONS FROM THE HISTORY
Medical Condition Associated with Cardiovascular Problems
- Genetic syndromes involving structural heart defects (e.g. Down’s, Turner’s, Marfan’s syndromes)
- Renal problems (hypertension)
- Chemotherapy (some drugs cardiotoxic)
Breathlessness
- Breathing difficulties without signs of acute infection (consider cardiac disease)
Exercise
- Exercise limited by shortness of breath, palpitations or chest pain
- Competitive sports—rarely these may need to be limited with some cardiac defects
Colour Change
- Cyanosis—central (tongue) or peripheral (hands and feet)
- Pale and sweaty, poor perfusion (sign of cardiac failure or an arrhythmia)
Growth
- Feeding problems in babies (breathlessness impairs feeding)
- Poor weight gain on growth chart
Syncope
- Unexplained collapse or fainting
- Collapse linked with exercise
- Palpitations
- Ask the parents to demonstrate rate/rhythm by tapping with their hand
Murmurs
- Previously noted heart murmur (physiological flow murmurs sometimes audible only at times of illness or after exercise)
Family History
- Family history of congenital heart disease
- Sudden death in early adulthood (congenital cardiomyopathy)
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue



