Skull Base Foraminal or Fissural Variants
Christine M. Glastonbury, MBBS
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Jugular Foramen Asymmetry
Glossopharyngeal Canal
Less Common
Petromastoid Canal
Asymmetric Sphenoidal Emissary Vein (of Vesalius)
Persistent Craniopharyngeal Canal
Medial Basal Canal (Basilaris Medianus)
Internal Auditory Canal Hypoplasia
Enlarged Emissary Vein, Transmastoid
Asymmetric Posterior Condylar Vein
Rare but Important
Enlarged Inferior Tympanic Canaliculus
Absent Foramen Spinosum
Innominate Canal
Accessory Foramen Ovale
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Normal variants may be uni- or bilateral
When normal structures are asymmetric, this may be normal variation or sign of pathology
Many are incidental findings
Imaging strategy
CT: Best defines or clarifies variants
MR: Often source of pitfalls
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Jugular Foramen Asymmetry
Key facts
Common developmental asymmetry of jugular foramen
Imaging
CT: Smooth cortical bone surrounds enlarged jugular foramen
MR: Various flow phenomena may result in misinterpretation of mass lesion
Glossopharyngeal Canal
Key facts
30% have partial or complete canal
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN9) enters canal prior to jugular foramen
Imaging
CT: Small funnel-shaped canal leading to anterior portion of jugular foramen (pars nervosa)
MR: High-resolution T2 may show CN9
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Petromastoid Canal
Key facts
Synonyms: Subarcuate canaliculus
From posterior CPA to mastoid air cells
Canal passes between and below crura of superior semicircular canal
Vestige of neonatal subarcuate fossa
Contents: Subarcuate artery and vein; branch of AICA or labyrinthine artery
In infant, subarcuate artery pseudolesion may confound radiologist
Imaging
If seen in adult: ≤ 1 mm curvilinear canal below superior semicircular canal
May be ≥ 2 mm in young children; subarachnoid space association may mimic lesion
Asymmetric Sphenoidal Emissary Vein (of Vesalius)
Key facts
Transmits emissary vein from cavernous sinus to pterygoid venous plexus
May enlarge with ↑ venous flow from caroticocavernous fistula
Imaging
Located medial to anterior aspect of foramen ovale; usually < 2 mm
May be partially assimilated with ovale or may be duplicated
Persistent Craniopharyngeal Canal
Key facts
Synonym: Trans-sphenoidal canal; persistent hypophyseal canal
Considered embryologic remnant of vascular channel
Site of trans-sphenoidal cephalocele
Imaging
Bone CT: Midline sphenoid, < 1.5 mm
Anterior to sphenooccipital synchondrosis
Medial Basal Canal (Basilaris Medianus)
Key facts
Considered remnant of cephalic end of notochord
Rarely enlarged to form basal cephalocele
Imaging
Midline sphenoid; < 1.5 mm
Posterior to sphenooccipital synchondrosis
Internal Auditory Canal Hypoplasia
Key facts
Contents: CN7 and CN8
Hypoplasia from congenital absence or deficiency of CN8
Associated with inner ear malformations
Normal canal diameter: 4-8 mm
Imaging
CT: Small caliber IAC, < 4 mm
MR: High-resolution imaging may show deficient CN8
Enlarged Emissary Vein, Transmastoid
Key facts
Connects transverse sinus to posterior auricular or occipital veins
Enlargement may be associated with small jugular foramen (JF)
Imaging
Horizontal canal through posteromedial mastoid bone adjacent to occipital suture
Asymmetric Posterior Condylar Vein
Key facts
Contents: Emissary vein from sigmoid sinus to suboccipital veins; meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery
Enlargement associated with small JF
Imaging
Well-corticated curvilinear channel
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Enlarged Inferior Tympanic Canaliculus
Key facts
Normally transmits Jacobsen nerve (inferior tympanic branch of CN9)
Aberrant internal carotid artery (ICA) enters middle ear through this
Imaging
Aberrant ICA widens canaliculus to reach cochlear promontory
CTA or MRA to confirm aberrant ICA
Absent Foramen Spinosum
Key facts
Normally transmits middle meningeal artery (MMA)
May be absent if MMA arises from ophthalmic artery or replaced by persistent stapedial artery (PSA)
Foramen rarely duplicated when MMA has anterior and posterior branches
Imaging
Foramen normally < 3 mm
Posterolateral to foramen ovale
Look for PSA and aberrant ICA
Innominate Canal
Key facts
Synonym: Canal of Arnold
Contains lesser petrosal nerve
Imaging
Between foramen ovale and spinosum
Usually ≤ 2 mm
Accessory Foramen Ovale
Key facts
Contains accessory meningeal artery
Imaging
Lateral to foramen ovale; < 2 mm
May be partially assimilated with ovale resulting in posterolateral groove
Image Gallery
 Axial bone CT through the low skull base demonstrates asymmetry of jugular foramina with the left foramen
 much smaller compared to the right much smaller compared to the right 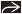 . This is a normal finding and does not indicate pathology. . This is a normal finding and does not indicate pathology.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|