Sinonasal Anatomic Variants
Michelle A. Michel, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Nasal Septal Deviation
Agger Nasi Cell
Nasal Septal Spur
Concha Bullosa
Infraorbital Ethmoid (Haller) Cell
Paradoxical Middle Turbinate
Less Common
Pneumatized Anterior Clinoid Process
Fovea Ethmoidalis, Asymmetric (Low)
Pneumatized Uncinate Process
Frontal Cells
Pneumatized Crista Galli
Supraorbital Ethmoid Cell
Dehiscent Lamina Papyracea
Rare but Important
Sphenoethmoidal (Onodi) Cell
Carotid Artery, Sphenoid Dehiscence
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Anatomic variants are rule rather than exception
Multiple variants often present in same patient, so identify and report them!
Variants may make patients prone to recurrent inflammatory disease and may increase risk of complications during functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Nasal Septal Deviation
Most common variant; often associated with previous trauma
Deviates from midline or S-shaped
Impact on nasal airway patency depends on overall nasal cavity width
Measure maximum deviation from midline
Agger Nasi Cell
Present in > 85% (really a variant?); most anterior extramural ethmoid air cell
Located anterior to frontal recess; at level of lacrimal sac or head of middle turbinate on coronal CT
Nasal Septal Spur
Nearly always associated with septal deviation; often at ethmoid-vomer junction
Document direction and length of spur; bony or cartilaginous; contact with lateral nasal wall structures or septum?
Concha Bullosa
Pneumatization of conchal turn of middle turbinate; may narrow middle meatus
Can be diseased with mucosal thickening, fluid, retention cysts, osteoma
Inferior pneumatization is uncommon
Infraorbital Ethmoid (Haller) Cell
Air cell located along inferior surface of orbital floor (antral roof)
↑ risk of orbital injury during FESS
Variable size; often bilateral; can narrow infundibulum and be diseased
Paradoxical Middle Turbinate
Concavity of turbinate concha directed toward septum
Diffuse or focal; variable size; often club-shaped
Can narrow middle meatus and be diseased
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Pneumatized Anterior Clinoid Process
Position lateral to optic nerve ↑ risk of injury during sphenoid surgery
Fovea Ethmoidalis, Asymmetric (Low)
Low position ↑ risk of skull base complication during ethmoidectomy
Resulting in CSF leak
Encephalocele
Parenchymal brain injury
Report measurement of asymmetry in millimeters in dictation
Pneumatized Uncinate Process
May narrow either infundibulum or middle meatus
Frontal Cells
Located anterior to frontal recess (above agger nasi cell) or within frontal sinus; 4 types (Bent classification); ↑ incidence of these cells with other variants (concha bullosa); types 3 and 4 may be associated with ↑ disease in frontal sinus
Type 1: Single cell above agger nasi
Type 2: Tier of 2 or more cells above agger nasi
Type 3: Single large cell above agger nasi that extends superiorly into frontal recess
Type 4: Cell located completely within frontal sinus
Pneumatized Crista Galli
Drains into 1 of frontal sinuses or frontal recess; mucocele formation and subsequent infection (mucopyocele)
↑ risk of anterior cranial fossa infection
Supraorbital Ethmoid Cell
Cell within orbital plate of frontal bone; posterior to frontal sinus and frontal recess
Best delineated on axial imaging
Dehiscent Lamina Papyracea
Post-traumatic or congenital
Orbital fat or medial rectus muscle may herniate into ethmoid labyrinth
↑ risk for orbital injury during FESS
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Sphenoethmoidal (Onodi) Cell
Pneumatization of posterior ethmoid cell superior to optic nerve
Optic nerve at ↑ risk during posterior ethmoidectomy
Best seen on axial imaging
Look for horizontal septation on coronal images between this cell superiorly and sphenoid sinus inferiorly
Carotid Artery, Sphenoid Dehiscence
Absence of bony covering over internal carotid artery; artery bulges into sphenoid sinus lumen; artery at ↑ risk for injury during sphenoid sinus surgery
Better delineated on axial imaging
Other Essential Information
Anatomic variations can also be categorized based on location or anatomic structure involved
Frontal region variants
Ethmoid region variants
Middle turbinate variants
Uncinate variants
Sphenoethmoidal region variants
Nasal septal variants
Additional variants not mentioned above
Variable pneumatization
Aplasia, hypoplasia, hyperpneumatization
Intersinus septal cell
Located within septum between frontal sinuses
Fusion of uncinate to middle turbinate, lamina papyracea, or skull base
Pneumatization of vertical lamella of middle turbinate
Septal recess
Cell within posterior nasal septum
Sphenoid sinus septations inserting on carotid canal
Pneumatization of dorsum sella
Image Gallery
 Coronal bone CT shows deviation of the nasal septum to the right with a small bony spur
 . Also note the paradoxical curvature of the middle turbinate . Also note the paradoxical curvature of the middle turbinate 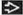 on the left side. on the left side.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|