Least resistance
Nerves, blood, mucous membranes, muscles, amniotic fluid
Intermediate resistance
Dry skin
Most resistance
Tendons, fat, bones
Voltage
Voltage is the measure of difference in electrical potential between two points and is determined by the electrical source. Electrical injuries are divided into high or low voltage using 500 or 1000 V as dividing lines. No death is recorded from contact with low-voltage telephone line (65 V).
Amperage (Strength of Current in Amperes)
Current is expressed in amperes, which is a measure of amount of energy that flows through an object.
Physical effects of different amperage levels at 50–60 Hz:
Physical effect | Milliamperes (mA) |
|---|---|
Tingling sensation | 1–4 |
Let-go current (muscular tetany preventing release of grip from current source) | |
(a) Children | 4 |
(b) Women | 7 |
(c) Men | 9 |
Freezing to circuit | 10–20 |
Respiratory arrest from thoracic muscle tetany | 20–50 |
Ventricular fibrillation | 60–120 |
Asystole | >2 A |
The Pathway of Current
In most of the cases, the current passes from hand to hand (Figs. 28.1 and 28.2), and it does not have effect on the foetus if the duration and strength of current is less. From hand to foot (Fig. 28.3) transmission, the current passes through the uterus and is associated with high incidence of foetal mortality and morbidity [2].
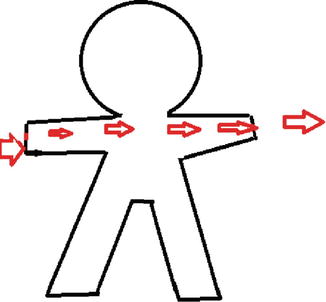
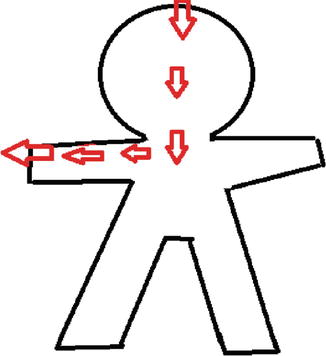
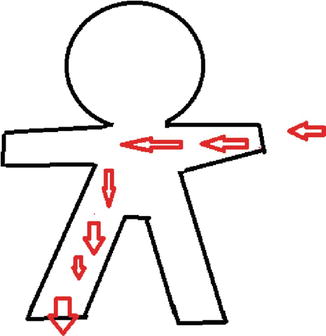

Fig. 28.1
Hand to hand

Fig. 28.2
Head to hand

Fig. 28.3
Hand to foot
Hands are commonest site for contact with an AC electrical source, and the contractions of the wrist can pull the AC source closer to body [6]. Current passing through the thorax or heart can cause cardiac dysrhythmias or direct myocardial damage. Current passing through the brain can result in respiratory arrest, seizures and paralysis (Fig. 28.4).
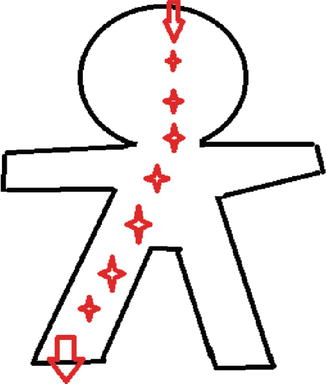

Fig. 28.4
Head to foot
Electrical Shock in Pregnancy
The amount of current which will cause minimal injury to the mother may cause grievous injury to the foetus as the foetal skin is 200 times less resistant than the skin postnatal. So less current is more lethal to the foetus. The pathway of current is also very important; if the pathway is through the uterus, the foetus is seriously injured [7].
Foetal Outcome
The foetus can have cardiac arrest, foetal complications like intrauterine growth retardation, oligohydramnios and reduced foetal movements to spontaneous abortions [7].
Lightning
Flash or bolt of lightning is due to an electrical discharge from a cloud to the earth. The electric current is direct with a potential of 1000 million volts or more. Lightning is neither a direct current nor an alternating current. It is best regarded as unidirectional massive current impulse; thus, it is classed as a phenomenon of current. A lightning bolt may injure or kill a person by a direct strike, a side flash or conduction through another object (ground current or step voltage) and last but not the least by blunt trauma. After lightning meets the body, current is initially transmitted internally, and then there is skin breakdown, and ultimately external flashover occurs.
Thus, burns and myoglobinuric renal failure are not common injuries in lightning. The injuries which occur are cardiac or respiratory arrest, vascular spasm, neurologic damage and autonomic instability. Lightning causes asystole rather than ventricular fibrillation.
Prehospital Management
Immediately turn off the electrical supply, if possible, and separate the patient from the source using non-conducting instrument (e.g. rubber, wood). It should be made a principle to not to touch the patient before the power is turned off.
Start with cardiopulmonary resuscitation immediately.
As the most common cause is arrhythmia, start early defibrillation.
Basic trauma care is also mandatory because these patients often suffer blunt injuries and burns.
All patients with conductive injury should have at least one large-bore intravenous (IV) line established.
An electrical injury should be treated like a crush injury rather than like a thermal burn.
Management
Once the pregnant woman is received in the hospital, trauma team must emphasise on the assessment and resuscitation of mother. A short history should be asked regarding:
1.
Source of shock
2.
Voltage
3.
Environment
4.
Presence of tetany
5.
Loss of consciousness



