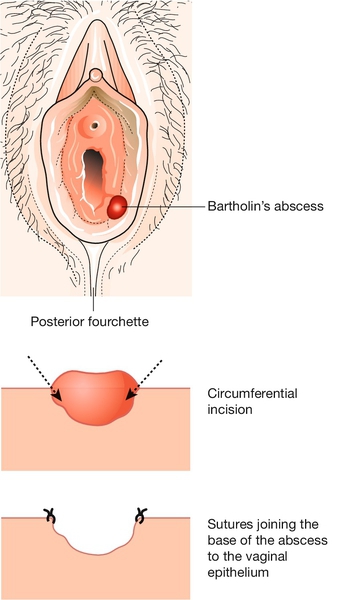
22 The vulva consists of the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris and the vestibule (see Fig. 3.1). It is covered with keratinizing squamous epithelium, unlike the vaginal mucosa, which is covered with non-keratinizing squamous epithelium. The labia majora are hair-bearing and contain sweat and sebaceous glands: from an embryological viewpoint, they are analogous to the scrotum. Bartholin’s glands are situated in the posterior part of the labia, one on each side of the vestibule. The lymphatics of the vulva drain to the inguinal nodes and then to the external iliac nodes. The area is richly supplied with blood vessels. Before direct examination of the vulva, a general dermatological examination may be useful, particularly: The vulva may than be inspected under a good light, as described on page 29. If necessary, closer inspection is possible using a colposcope. A urethral caruncle is a polypoidal outgrowth from the edge of the urethra, which is most commonly seen after the menopause. The tissue is soft, red and smooth and appears as an eversion of the urethral mucosa. Most women are asymptomatic, but others experience dysuria, frequency, urgency and focal tenderness. If there are any suspicious features, an excision and biopsy may be required to exclude the very rare possibility of a urethral carcinoma. The greater vestibular, or Bartholin’s, glands lie in the subcutaneous tissue below the lower third of the labium majus and open via ducts to the vestibule between the hymenal orifice and the labia minora. They secrete mucus, particularly at the time of intercourse. If the duct becomes blocked, a tense retention cyst forms, and if there is super-added infection, a painful abscess develops. The abscess can be incised and drained, usually under general anaesthesia, with the incision on the inner aspect of the labium so that secretions bathe the introitus rather than the outside of the vulva. To prevent the cyst reforming, the fistula is kept open by suturing its edges to the surrounding skin, a procedure known as marsupialization (Fig. 22.1). Bartholin’s gland carcinoma is rare. The lower part of the abscess cavity granulates and heals during the subsequent weeks. The commonest small vulval cysts are usually either inclusion cysts or sebaceous cysts. Inclusion cysts form because epithelium is trapped in the epidermis, usually following obstetric trauma or episiotomy. They are usually asymptomatic and need no treatment. Sebaceous cysts are usually multiple, mobile, non-tender, white or yellow, filled with a cottage cheese-like substance and more common in the anterior half of the vulva. Excision may be requested by the patient. Cysts in an episiotomy scar can be tender and need excision. Infected cysts need to be excised and drained, and recurrent infections should be treated by excision in their non-acute phase. Vulval moles are usually asymptomatic but become more pigmented at puberty. Any other change in a vulval naevus is an indication for removal. There is a good case to be made for removing all vulval moles, as approximately 2% of malignant melanomas in women arise from the vulva. Fibromas and lipomas are benign, mobile tumours of fibrous tissue and fat, respectively. Hidradenomas are rare tumours of sweat glands near the surface of the labia. All are benign, but the diagnosis is usually only made once they have been excised. The commonest cause of a vulval haematoma is vaginal delivery. It may also occur following any vulval operation, or by ‘falling astride’ accidents, particularly in children. The possibility of sexual assault should be borne in mind in this situation. Vulval haematomas usually present with severe pain, and evacuation under general anaesthesia is often required. Elderly women develop vaginal, vulval and clitoral atrophy as part of the normal ageing process of skin. In severe cases, the thin vulval skin, terminal urethra and fourchette cause dysuria and superficial dyspareunia, the labia minora may fuse and bury the clitoris. Introital stenoses can make coitus impossible. A simple effective moisturizer rubbed into the vulva is effective, although some advocate topical oestrogen replacement. There is a small amount of systemic absorption with topical oestrogen therapy, and, if this route is chosen, treatment should be for no more than 2 or 3 months without either a break or a short course of progesterone to prevent endometrial stimulation. These may be: Treatment depends on the cause. The management of Behçet syndrome is difficult, but the combined oral contraceptive or topical steroids may be tried.
Disorders of the vulva
Introduction
Examination of the vulva
![]() the nail beds for signs of pitting (found in psoriasis)
the nail beds for signs of pitting (found in psoriasis)
![]() the extensor surfaces (elbows and knees) also for features of psoriasis
the extensor surfaces (elbows and knees) also for features of psoriasis
![]() the flexor surfaces for lichen planus and dermatitis
the flexor surfaces for lichen planus and dermatitis
![]() the mouth for other features of lichen planus.
the mouth for other features of lichen planus.
Simple vulval conditions
Urethral caruncle
Bartholin’s cysts
Small cysts
Moles
Fibroma, lipoma, hidradenoma
Haematoma
Simple atrophy
Ulcers
![]() aphthous (yellow base)
aphthous (yellow base)
![]() herpetic (exquisitely painful multiple ulceration, pp. 180, 186)
herpetic (exquisitely painful multiple ulceration, pp. 180, 186)
![]() syphilitic (indurated and painless, p. 188)
syphilitic (indurated and painless, p. 188)
![]() associated with Crohn disease (‘like knife cuts in skin’)
associated with Crohn disease (‘like knife cuts in skin’)
![]() a feature of Behçet syndrome (a chronic painful condition with aphthous genital and ocular ulceration)
a feature of Behçet syndrome (a chronic painful condition with aphthous genital and ocular ulceration)
![]() malignant (see below)
malignant (see below)
![]() associated with lichen planus (see below) or Stevens–Johnson syndrome
associated with lichen planus (see below) or Stevens–Johnson syndrome
![]() tropical (lymphogranuloma venereum, chancroid, granuloma inguinale).
tropical (lymphogranuloma venereum, chancroid, granuloma inguinale).
Infection
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


