Fig. 44.1
A clinical photograph showing a large congenital pancreatic cyst
They may however be symptomatic as a result of pressure on adjacent structures leading to:
Abdominal distention
Vomiting
Jaundice
Pancreatitis
The majority of patients present before the age of 2 years, and associated anomalies were found in 30% of cases. These include:
Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune syndrome)
Short-limb dwarfism
Polydactyly
von Hippel–Lindau disease
Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome
Hemihypertrophy
Renal tubular ectasia
Anorectal malformation
Polycystic kidneys
Diagnosis
Modern imaging techniques usually show a well-defined unilocular cyst; however, even with the combined use of laboratory data, clinical features, and diagnostic imaging, it may be difficult to accurately differentiate congenital pancreatic cyst from other nearby cystic lesions of the abdomen. This is specially so if they are large in size (Figs. 44.2, 44.3, 44.4, and 44.5).
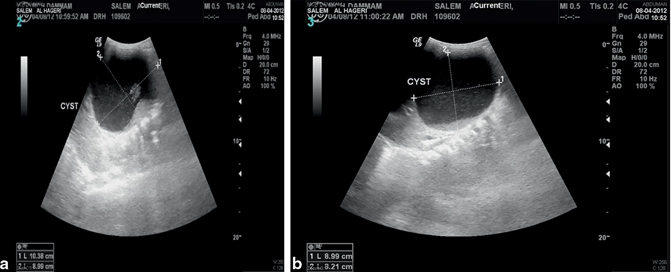
Fig. 44.2
a and b Abdominal ultrasound showing a large pancreatic congenital cyst
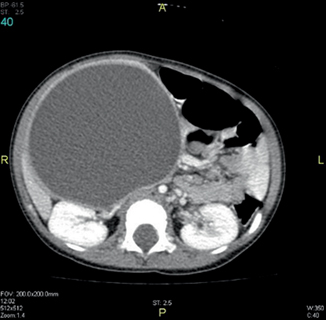
Fig. 44.3
Abdominal CT scan showing a very large congenital pancreatic cyst. Note the thick wall of the cyst
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


