CHAPTER 4 Aetiology
The main aetiological factors are:
When the period arrives, new blood has not been produced and old blood is being discharged; at this time women become irritable and they should avoid overstrain, stress and emotional problems. It is also most important that they avoid cold food and sitting or lying in cold and damp places. During the period the pores are open, old blood enters the Penetrating Vessel in order to be discharged. Exposure to cold at this time stops old blood from moving downwards; it will instead accumulate in the body giving rise to stagnant Blood, palpable masses, dysmenorrhoea or short periods. New blood is produced 1–2 days after the end of the period; exposure to cold at this time prevents the production of new blood leading to exhaustion of Blood manifesting with a sallow complexion, lassitude, long cycle and leucorrhoea. This is why women suffer from more diseases that are difficult to cure. Women from rich families are arrogant and often hide their feelings. They cannot stop eating cold fruits if these are delicious; this causes Cold to invade the Stomach. These women cool themselves too much in summertime as they do not know that it is harmful to health. After some time, diseases will occur and they may suffer from infertility. It must be pointed out that women should avoid exposure to wind and cold and eating cold foods during the period. To eliminate Blood stasis, this is the best time to give treatment [during the period]. Tonics should be taken after the end of the period. By following these rules a weak woman can get stronger, she will not suffer from diseases and will be able to give birth to many children.1
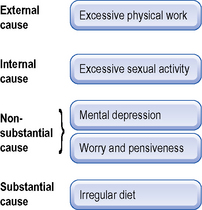
He included excessive sexual activity with ‘overwork’ and considered physical overwork as an external cause and excessive sexual activity as an internal cause of disease (within the category of ‘overwork’). He said that ‘mental depression’ is different from the ‘Six Stagnations’ (stagnation of Qi, Blood, Heat, Food, Dampness and Phlegm) and that ‘worry and pensiveness’ are a non-substantial cause of disease while dietary irregularity is a substantial one. Dr Chen’s reference to ‘mental depression’ is interesting and very modern. He specifically says that is not equivalent to the depression caused by the Six Stagnations (defined by Zhu Dan Xi and for which Yue Ju Wan Gardenia-Chuanxiong Pill is used). By ‘mental depression’ he means a general state of unhappiness which may be due to many different patterns rather than purely stagnation; as we shall see below, by ‘depression’ he also means a state of mental frustration due to unfulfilled sexual desire (Fig. 4.1). Dr Chen said that overwork should be treated with the tonification method; emotional depression be treated by moving and opening Qi; pungent herbs be used for worry and pensiveness; dietary irregularities should be treated by digestive herbs that dissolve retained food. Passages from his work will be discussed below.
Exterior pathogenic factors
When the climate is moderate and harmonized, the periods are calm. Cold congeals, Heat boils, Wind makes [the periods] surge; external pathogenic factors enter the Uterus and deplete the Directing and Penetrating Vessels causing menstrual problems.2
Shen Yao Feng, author of the Summary of Gynecology (1850), says: “Warm, harmonious weather makes the periods quiet; cold congeals them; heat makes them overflow; wind makes them surge.”3
The three most common Exterior pathogenic factors in gynecology are Cold, Dampness and Heat.
Heat
Exterior pathogenic factors
Cold
Dampness
Emotional stress
Emotional stress has a profound influence on menstruation, pregnancy, labour and menopause. The Golden Mirror of Medicine (1742), when discussing emotional causes of disease in gynecology, says: “Worry, anger, depression injure the emotional life, Blood flows up rebelling upwards bringing Qi with it.”4
The Uterus Vessel connects the Uterus to the Heart: since the Heart is always affected by emotional problems, this connection explains the profound influence of emotional stress on the menstrual function. For example, Chapter 33 of the Simple Questions says:
When menstruation does not come, this is due to the Uterus Vessel being blocked. The Uterus Vessel pertains to the Heart and connects with the Uterus; when Qi rebels upwards towards the Lungs, Heart-Qi cannot flow downwards and the periods do not come.5
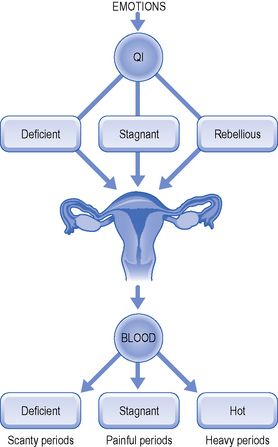
Emotional stress influences menstruation by affecting first the movement of Blood by Qi. In fact, the first effect of emotional stress is to impair or alter the circulation of Qi by depleting Qi, making Qi stagnant or making Qi rebellious. Each of these pathologies will affect Blood which follows Qi and becomes deficient, stagnant or rebellious and/or Hot (Fig. 4.2).
The Golden Mirror of Medicine says:
Women cannot control themselves and are frequently affected by worry, pensiveness, anger or depression: these make the Blood move, stop, rebel or conform, which is all due to Qi movement.6
Sadness and grief
In women, sadness may sometimes affect the Liver directly, causing Liver-Blood deficiency. Chapter 8 of the Spiritual Axis says: “When sadness affects the Liver it injures the Ethereal Soul; this causes mental confusion … the Yin is damaged, the tendons contract and there is hypochondrial discomfort.”7 When sadness affects the Liver (which is fairly common in women), it easily causes gynecological problems such as amenorrhoea, scanty periods or delayed cycle, all associated with depression and a feeling of aimlessness due to the Ethereal Soul not being rooted in Liver-Blood.
Worry
The Qing dynasty gynecologist Chen Jia Yuan wrote with regard to worry:
Worry injures the Lungs and pensiveness injures the Spleen, when these two organs are injured Qi and Blood stagnate, there is a feeling of indignation, palpitations, a feeling of oppression of the chest and amenorrhoea.8
Anger
The Great Treatise of Beneficial Formulae for Women (1237) says of anger:
Anger causes Qi to rebel upwards: Blood follows Qi and also rebels upwards. If the lower back and legs are affected, there will be pain and a sensation of heaviness there during the period, which will disappear at the end of the period … If anger damages the Liver, there will be dizziness, hypochondrial pain, spitting of blood, acute skin infections and prolonged uterine bleeding.10
Fear
The Great Treatise of Beneficial Formulae for Women (1237) says about fear:
Fear during the period causes disturbances of Blood, the blood vessels and channels become obstructed, Qi rebels upwards in the Blood portion, and this may lead to a severe deficiency.11
Guilt
Emotional stress
Sadness and grief
Fear
Guilt
Irregular diet
Diet is an important aetiological factor in gynecology. The Golden Mirror of Medicine says: “Blood is the essence refined from food and water, if the Stomach and Spleen are injured, fluids are not regulated, Blood dries up, and the periods become unregulated.”12 The Qing dynasty gynecologist Chen Jia Yuan said:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree