Chapter 85 The Porphyrias
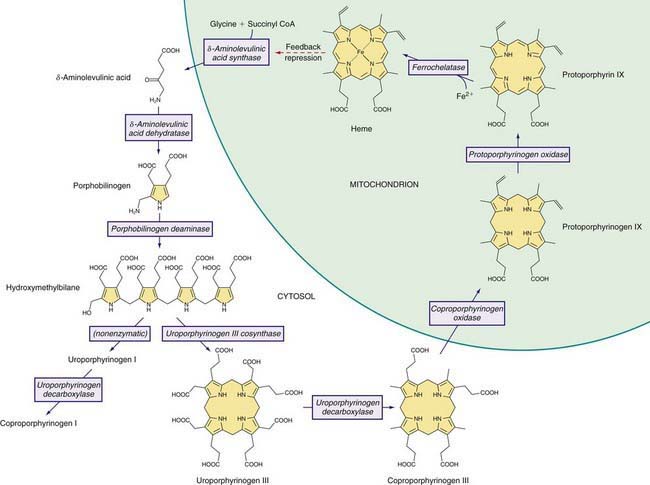
The Heme Biosynthetic Pathway
Heme is required for a variety of hemoproteins such as hemoglobin, myoglobin, respiratory cytochromes, and cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs). It is believed that the 8 enzymes in the pathway for heme biosynthesis are active in all tissues. Hemoglobin synthesis in erythroid precursor cells accounts for about 85% of daily heme synthesis in humans. Hepatocytes account for most of the rest, primarily for synthesis of CYPs, which are especially abundant in the liver endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and turn over more rapidly than many other hemoproteins, such as the mitochondrial respiratory cytochromes. As shown in Figure 85-1, pathway intermediates are the porphyrin precursors δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA, also known as 5-aminolevulinic acid) and porphobilinogen (PBG), and porphyrins (mostly in their reduced forms, known as porphyrinogens). At least in humans, these intermediates do not accumulate in significant amounts under normal conditions or have important physiologic functions.
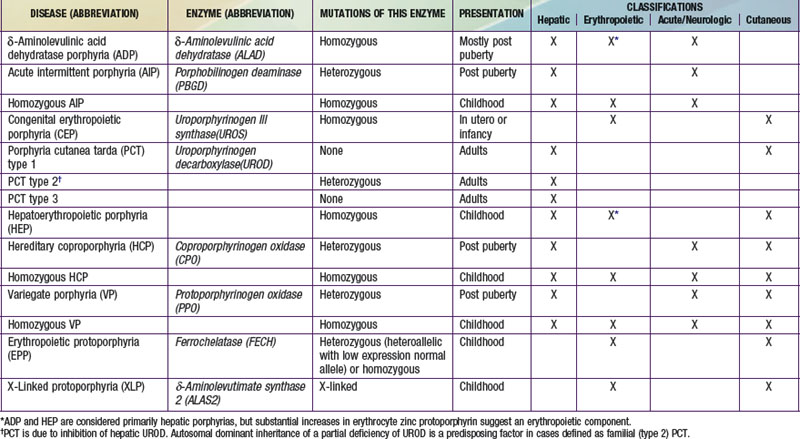
A deficiency of each enzyme in the pathway is associated with a specific porphyria (Table 85-1). The 1st enzyme, ALA synthase (ALAS), occurs in 2 forms. An erythroid specific form, termed ALAS2, is deficient in X-linked sideroblastic anemia, due to mutations of the ALAS2 gene on chromosome Xp11.2. Gain of function mutations of ALAS2 due to deletions in the last exon have been found in a variant form of erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP). The housekeeping or ubiquitous form of this enzyme, termed ALAS1, is found in all tissues including liver, and its gene is located on chromosome 3p21.1. Disease-related mutations of ALAS1 have not been described.
Table 85-1 THE HUMAN PORPHYRIAS: MUTATIONS, TIME OF PRESENTATION, AND TISSUE- AND SYMPTOM-BASED CLASSIFICATIONS
Regulation of heme synthesis differs in the 2 major heme-forming tissues. Liver heme biosynthesis is primary controlled by ALAS1. Synthesis of ALAS1 in liver is regulated by a “free” heme pool (see Fig. 85-1), which can be augmented by newly synthesized heme or by existing heme released from hemoproteins and destined for breakdown to biliverdin by heme oxygenase.
Intermediates of the heme biosynthetic pathway are efficiently converted to heme and, normally, only small amounts of the intermediates are excreted. Some may undergo chemical modifications before excretion. Whereas the porphyrin precursors ALA and PBG are colorless, nonfluorescent, and largely excreted unchanged in urine, PBG may degrade to colored products such as the brownish pigment called porphobilin or spontaneously polymerize to uroporphyrins. Porphyrins are red in color and display bright red fluorescence when exposed to long wavelength ultraviolet light. Porphyrinogens, which are colorless and nonfluorescent, are the reduced form of porphyrins, and when they accumulate are readily autoxidized to the corresponding porphyrins when outside the cell. Only the type III isomers of uroporphyrinogen and coproporphyrinogen are converted to heme (see Fig. 85-1).
Classification and Diagnosis of Porphyrias
Two classification schemes reflect either the underlying pathophysiology or clinical features, and both are useful for diagnosis and treatment (see Table 85-1). In hepatic and erythropoietic porphyrias, the source of excess production of porphyrin precursors and porphyrins is the liver and bone marrow, respectively. Acute porphyrias cause neurologic symptoms that are associated with increases of 1 or both of the porphyrin precursors ALA and PBG. In the cutaneous porphyrias, photosensitivity results from transport of porphyrins in blood from the liver or bone marrow to the skin. Dual porphyria refers to the very rare cases of porphyria with deficiencies of 2 different heme pathway enzymes.
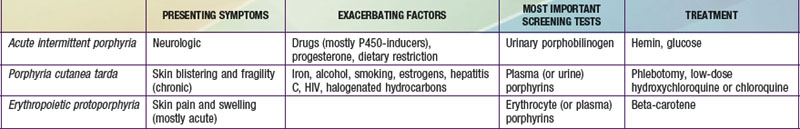
It is notable that acute intermittent porphyria (AIP), porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT), and erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP), the 3 most common porphyrias, are very different in clinical presentation, precipitating factors, methods of diagnosis, and effective therapy (Table 85-2). Two of the 4 acute porphyrias, hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) and variegate porphyria (VP), can also cause lesions indistinguishable from PCT (see Table 85-1). Congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP) causes more severe blistering lesions, often with secondary infection and mutilation. EPP is distinct from the other cutaneous porphyrias in causing nonblistering photosensitivity that occurs acutely after sun exposure. EPP is also the most common porphyria to become manifest before puberty.
First-Line Laboratory Diagnostic Testing
δ-Aminolevulinic Acid Dehydratase Porphyria (ADP)
Pathology and Pathogenesis
ALAD catalyzes the condensation of 2 molecules of ALA to form the pyrrole PBG (see Fig. 85-1). The enzyme is subject to inhibition by a number of exogenous and endogenous chemicals. ALAD is the principal lead-binding protein in erythrocytes, and lead can displace the zinc atoms of the enzyme. Inhibition of erythrocyte ALAD activity is a sensitive index of lead exposure.
Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP)
Etiology
AIP results from the deficient activity of the housekeeping form of PBG deaminase (PBGD). This enzyme is also known as hydroxymethylbilane (HMB) synthase; the prior term uroporphyrinogen I synthase is obsolete. PBGD catalyzes the deamination and head-to-tail condensation of 4 PBG molecules to form the linear tetrapyrrole, HMB (also known as preuroporphyrinogen; see Fig. 85-1). A unique dipyrromethane cofactor binds the pyrrole intermediates at the catalytic site until 6 pyrroles (including the dipyrrole cofactor) are assembled in a linear fashion, after which the tetrapyrrole HMB is released. The apo-deaminase generates the dipyrrole cofactor to form the holo-deaminase, and this occurs more readily from HMB than from PBG. Indeed, high concentrations of PBG may inhibit formation of the holo-deaminase. The product HMB can cyclize nonenzymatically to form nonphysiologic uroporphyrinogen I, but in the presence of the next enzyme in the pathway is more rapidly cyclized to form uroporphyrinogen III.
Pathology and Pathogenesis
Drugs that are unsafe in acute porphyrias (Table 85-3) include those having the capacity to induce hepatic ALAS1, which is closely associated with induction of CYPs. Some chemicals (e.g., griseofulvin) can increase heme turnover by promoting the destruction of specific CYPs to form an inhibitor (e.g., N-methyl protoporphyrin) of ferrochelatase (FECH, the final enzyme in the pathway). Sulfonamide antibiotics are harmful but apparently not inducers of hepatic heme synthesis. Ethanol and other alcohols are inducers of ALAS1 and some CYPs.
Table 85-3 DRUGS REGARDED AS UNSAFE AND SAFE IN ACUTE PORPHYRIAS
| UNSAFE | SAFE |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates | Narcotic analgesics |
| Sulfonamide antibiotics* | Aspirin |
| Meprobamate* (also mebutamate,* tybutamate*) | Acetaminophen |
| Carisoprodol* | Phenothiazines |
| Glutethimide* | Penicillin and derivatives |
| Methyprylon | Streptomycin |
| Ethchlorvynol* | Glucocorticoids |
| Mephenytoin | Bromides |
| Phenytoin* | Insulin |
| Succinimides | Atropine |
| Carbamazepine* | Cimetidine |
| Clonazepam | Ranitidine† |
| Primidone* | Acetaminophen (paracetamol) |
| Valproic acid* | Acetazolamide |
| Pyrazolones (aminopyrine, antipyrine) | Allopurinol |
| Griseofulvin* | Amiloride |
| Ergots | Bethanidine |
| Metoclopramide* | Bumetanide |
| Rifampin* | Cimetidine |
| Pyrazinamide* | Coumarins |
| Diclofenac* | Fluoxetine |
| Progesterone and synthetic progestins* | Gabapentin |
| Danazol* | Gentamicin |
| Alcohol | Guanethidine |
| ACE inhibitors (especially enalapril) | Ofloxacin |
| Calcium channel blockers (especially nifedipine) | Propranolol |
| Ketoconazole | Succinylcholine |
| Rifampin | Tetracycline |
This partial listing does not include all available information about drug safety in acute porphyrias. Other sources should be consulted for drugs not listed here.
* Porphyria is listed as a contraindication, warning, precaution, or adverse effect in U.S. labeling for these drugs. Estrogens are also listed as harmful in porphyria, but have been implicated as harmful in acute porphyrias mostly based only on experience with estrogen-progestin combinations. While estrogens can exacerbate PCT, there is little evidence they are harmful in the acute porphyrias.
† Porphyria is listed as a precaution in U.S. labeling for this drug. However, this drug is regarded as safe by other sources.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
An increased urinary PBG establishes that a patient has 1 of the 3 most common acute porphyrias (see Table 85-2). Measuring PBG in serum is preferred when there is coexistent severe renal disease but is less sensitive when renal function is normal. Measurement of urinary ALA is less sensitive than PBG and also less specific but will detect ADP, the fourth type of acute porphyria. Erythrocyte PBGD activity is decreased in most AIP patients and helps confirm the diagnosis in a patient with high PBG. A normal enzyme activity in erythrocytes does not exclude AIP.