Fig. 5.1
Unruptured ampullary ectopic pregnancy seen by laparoscopy
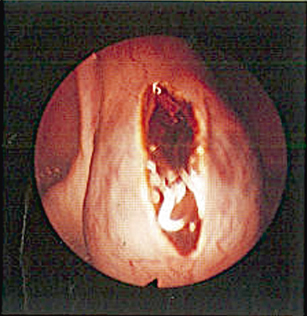
Fig. 5.2
Linear salpingostomy reveals the products of conception inside the fallopian tube, seen by laparoscopy
Clinical Pearls/Pitfalls
The discriminatory hCG level is not always reliable and may be altered by multiple gestations, uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, endometrial polyps, and obesity.
Laparoscopy, which is the preferred surgical treatment modality, is necessary if the patient is unstable, ongoing hemorrhage is suspected, or there is a contraindication to methotrexate therapy.
Laparoscopic salpingostomy increases the risk of recurrent ectopic pregnancy and persistent trophoblastic disease, but preserves the fallopian tube for possible improved future fertility.
If a salpingostomy is performed, the serum hCG needs to be serially examined until it is undetectable due to the risk of persistent trophoblastic disease.
Recent studies, however, demonstrate that the rates of subsequent intrauterine as well as ectopic pregnancies after salpingostomy or salpingectomy are comparable.
References
1.
2.
Murray H, Baakdah H, Bardell T, Tulandi T. Diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy. CMAJ. 2005;173(8):905.CrossRefPubMedCentralPubMed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


