Small Chest
Paula J. Woodward, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Severe Oligohydramnios
Renal Agenesis
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease, Severe
Bilateral Multicystic Dysplastic Kidneys
Posterior Urethral Valves, Complete
Severe Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
Less Common
Skeletal Dysplasias
Thanatophoric Dysplasia (TD)
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)
Achondroplasia
Achondrogenesis
Asphyxiating Thoracic Dysplasia (Jeune Syndrome)
Short Rib-Polydactyly
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Is the chest truly small?
Large heart or distended abdomen may create appearance of a small chest
Anything that causes severe oligohydramnios can result in a small chest and pulmonary hypoplasia
Fetal compression causes decreased space for lung growth and restriction of breathing movements
Efflux of lung fluid into amniotic space
Fetal lung fluid functions as a stent keeping developing air spaces distended
Vital for normal lung development
Many skeletal dysplasias have a small thoracic cavity
Must look at multiple factors in order to make appropriate diagnosis
Which long bones are effected and how severely?
Is ossification normal or decreased?
Are there rib/long bone fractures or bowing?
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Renal Agenesis
Absent kidneys and bladder
Anhydramnios
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease, Severe
Large, echogenic kidneys
Abdominal circumference often enlarged
Amount of amniotic fluid varies according to severity of renal disease
Bilateral Multicystic Dysplastic Kidneys
Non-functioning kidneys filled with multiple cysts of varying size
Absent bladder
Posterior Urethral Valves, Complete
Grossly distended bladder in male fetus
Look for “keyhole” appearance of dilated posterior urethra
May have associated hydronephrosis
Severe Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
Asymmetric IUGR: Abdomen and chest are small, with “sparing” of head growth
Often associated with oligohydramnios
Early onset asymmetric IUGR very concerning for triploidy
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Thanatophoric Dysplasia (TD)
Divided into 2 subtypes based on morphologic findings
Chest findings are similar in both types
Thorax is small and narrow with short horizontal ribs
Ossification is normal
No rib fractures
Pulmonary hypoplasia
TD type I
“Telephone receiver” femur
All long bones severely affected (micromelia) with bowing
Platyspondyly
Prominent lumbar kyphosis
Trident-shaped hands (short fingers, appear same length; gap between 3rd and 4th fingers)
TD type II
Kleeblattschädel (“cloverleaf”) skull
Femurs longer, less curved
Platyspondyly less marked
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI)
Presence of fractures distinguishes OI from other skeletal dysplasias (except achondrogenesis type 1A)
Multiple different types based on phenotype
Type II is most severe form and most likely to be diagnosed in utero
Type II is perinatal lethal
Chest is small with “beaded” ribs (result of multiple rib fractures)
Long bone shortening/angulation secondary to fractures
Callus formation gives bones a “crumpled” appearance
Decreased mineralization
Brain “too well seen”
Skull deformation from transducer pressure (“soft” bones)
Achondroplasia
Most common heritable, non-lethal skeletal dysplasia
Chest usually has mild “bell-shaped” appearance
Much less severe than other dysplasias
Early scans usually normal
Rhizomelia (proximal limb shortening) noted after 22 weeks
Normal ossification without fractures
No bowing or angulation seen prenatally
Progressive macrocephaly with frontal bossing
Prominent thoracolumbar kyphosis
Trident hands
Achondrogenesis
Group of lethal disorders with severe micromelia, unossified spine, short trunk and disproportionately large head
Chest findings vary with type
Type 1A
Multiple rib fractures
Poorly ossified skull
Type 1B
No rib fractures
Poorly ossified skull
Type II
No rib fractures
Normal skull ossification
Asphyxiating Thoracic Dysplasia (Jeune Syndrome)
Characterized by a severely constricted, long, narrow thorax
Cystic kidneys
Normal ossification
Polydactyly in 15%
Limbs shortened but may not be as profound as in other conditions
Short Rib-Polydactyly
Characterized by severe micromelia, short horizontal ribs, polydactyly, visceral anomalies
Visceral anomalies include cardiac, urogenital and central nervous system
Alternative Differential Approaches
Decreased ossification with beaded ribs
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Achondroplasia type Ia
Absent spine ossification
Achondrogenesis (all types)
Small chest and polydactyly
Short rib-polydactyly
Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia
Image Gallery
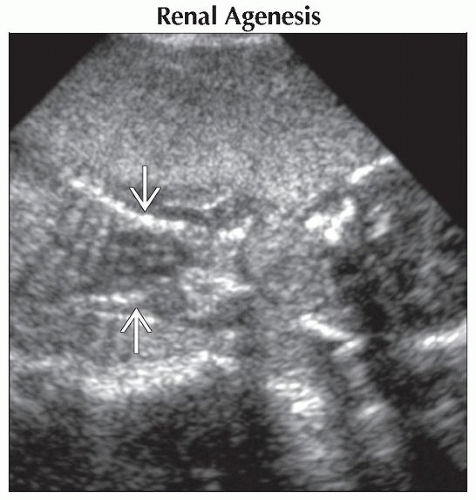 Coronal ultrasound of a fetus with renal agenesis shows a very small bell-shaped chest
 . There is complete anhydramnios. . There is complete anhydramnios.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|