CHAPTER 16 a small solid structure located posterior to the epididymal head. benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) benign enlargement of the prostate gland; noninflammatory condition. cone-shaped area of the prostate gland located deep in the peripheral zone. separates the prostate and rectum; important landmark for radical prostatectomy long, tightly coiled ducts that carry sperm from the testis to the vas deferens. abnormal accumulation of serous fluid between the two layers of tunica vaginalis. thick portion of the tunica albuginea. the largest area of the prostate gland located just beneath the capsule. glandular tissue lining the proximal prostatic urethra. prostate specific antigen (PSA) a protein produced by the prostate; elevation is associated with carcinoma of the prostate gland. inflammation of the testis; commonly caused by Chlamydia. small paired structures that store sperm. retropubic space between the symphysis pubis and urinary bladder. supporting structure on the posterior border of the testes that courses through the inguinal canal. a cyst arising from the rete testis. hypoechoic connective tissue dividing the peripheral and central zones. two small areas of the prostate gland adjacent to the proximal urethral space. fibrous sheath enclosing each testis. Transurethral Resection Prostatectomy (TURP) dilatation of the spermatic veins; most common cause of male infertility. a small tube that transports the sperm from each testis to the prostatic urethra. • A two-compartment pouch that contains and supports each testis. • Divided by a medium raphe or septum. • Contains a number of tissue layers and vascular structures. • A cone-shaped retroperitoneal structure. • Inferior border (apex) provides an exit for the urethra. • Superior border (base) is in contact with the urinary bladder. • Consists of five lobes: anterior, middle, posterior, and two lateral lobes. • Divided into three zones: central, peripheral, and transitional zones. • Lies inferior to the seminal vesicles and urinary bladder. • Lies posterior to the symphysis pubis and anterior to the rectal ampulla (space of Retzius). • Lies anterior to Denonvilliers’ fascia. • Attached to the symphysis pubis by prostatic ligaments. • The urethra is the anatomical landmark dividing the prostate into anterior (fibromuscular) and posterior (glandular) sections. Congenital Anomalies—Scrotum and Prostate • Thin hyperechoic wall measuring 2 to 8 mm in thickness. • Small amount of anechoic fluid surrounds each testis.
Scrotum and prostate
Anatomy
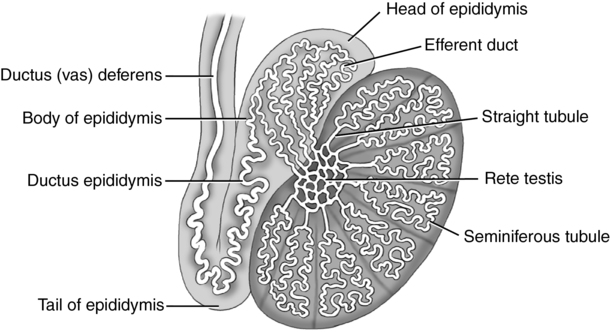
Scrotum (fig. 16-1)
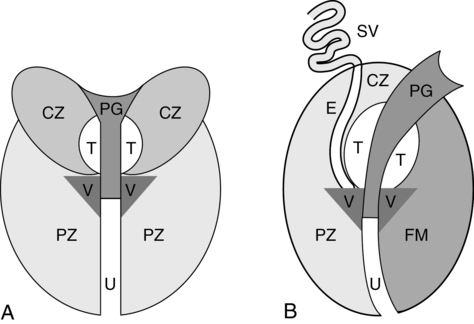
Prostate gland (fig. 16-2)
Vascular anatomy
Scrotum
Prostate
Urethral artery
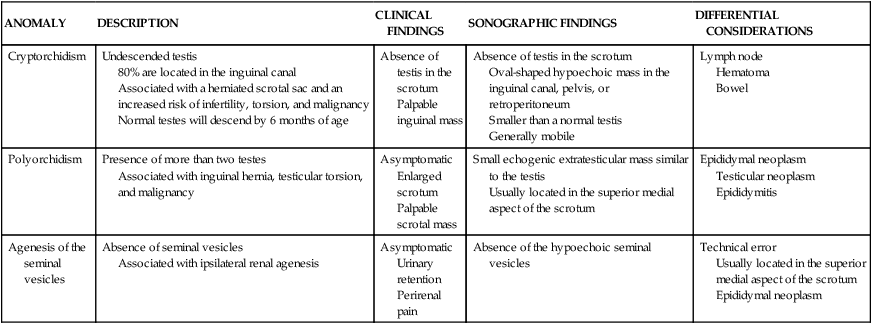
ANOMALY
DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL FINDINGS
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Cryptorchidism
Undescended testis
80% are located in the inguinal canal
Associated with a herniated scrotal sac and an increased risk of infertility, torsion, and malignancy
Normal testes will descend by 6 months of age
Absence of testis in the scrotum
Palpable inguinal mass
Absence of testis in the scrotum
Oval-shaped hypoechoic mass in the inguinal canal, pelvis, or retroperitoneum
Smaller than a normal testis
Generally mobile
Lymph node
Hematoma
Bowel
Polyorchidism
Presence of more than two testes
Associated with inguinal hernia, testicular torsion, and malignancy
Asymptomatic
Enlarged scrotum
Palpable scrotal mass
Small echogenic extratesticular mass similar to the testis
Usually located in the superior medial aspect of the scrotum
Epididymal neoplasm
Testicular neoplasm
Epididymitis
Agenesis of the seminal vesicles
Absence of seminal vesicles
Associated with ipsilateral renal agenesis
Asymptomatic
Urinary retention
Perirenal pain
Absence of the hypoechoic seminal vesicles
Technical error
Usually located in the superior medial aspect of the scrotum
Epididymal neoplasm
Sonographic appearance
Scrotum