CHAPTER 27 severe generalized massive edema often seen with hydrops fetalis. inward curving of the fifth finger associated with Down syndrome. abnormal outward bending or twisting of the elbow. a condition where the skull is defective, causing exposure or extrusion of the brain demise of a twin that is too large to reabsorb. underdevelopment of the jaw, especially the mandible. abnormal smallness of one or both eyes. congenital anomaly characterized by the presence of more than the normal number of digits. premature rupture of membranes (PROM) early rupture of the gestational sac with leakage of part or all of the amniotic fluid. onset of labor before 37 weeks’ gestation. Increased distance between the first and second toes associated with Down syndrome. overlapping of the cranial bones associated with fetal demise. congenital anomaly characterized by the fusion of the fingers or toes. twin–twin transfusion syndrome (TTS) the arterial blood of the donor twin pumps into the venous system of the receiving twin. • Demonstrate normal karyotype. • Malformation refers to a defect of an organ that results from an intrinsically abnormal development process. • Deformation refers to an abnormal form, shape, or position of a part caused by mechanical forces antenatally. • Disruption is a defect of an organ resulting from the breakdown of previously normal tissue. • Sequence refers to a pattern of multiple anomalies that result from a single anomaly or mechanical factor. • An abnormal interstitial accumulation of fluid in the body cavities and soft tissues. • Fluid accumulation may result in anasarca, ascites, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, placentomegaly, and polyhydramnios. • Hydrops may result from antibodies in the maternal circulation that destroy the fetal red blood cells (immune) or without evidence of blood group incompatibility (nonimmune). • Sonography cannot differentiate immune from nonimmune hydrops. • Seventy percent of pregnancies beginning with twins will deliver a singleton pregnancy. • Monozygotic twins result from a single fertilized ovum. • Dizygotic twins result from two separate ova. • Majority of pregnancies are dizygotic. • Dizygotic pregnancies are always dichorionic/diamniotic. • Label each fetus with Twin A closest to the internal os. • IUGR is the most common cause of discordant growth in a dichorionic multifetal gestation. • Twin–twin transfusion syndrome is the most common cause of discordant growth in a monochorionic multifetal gestation.
Complications in pregnancy
Chromosomal abnormalities
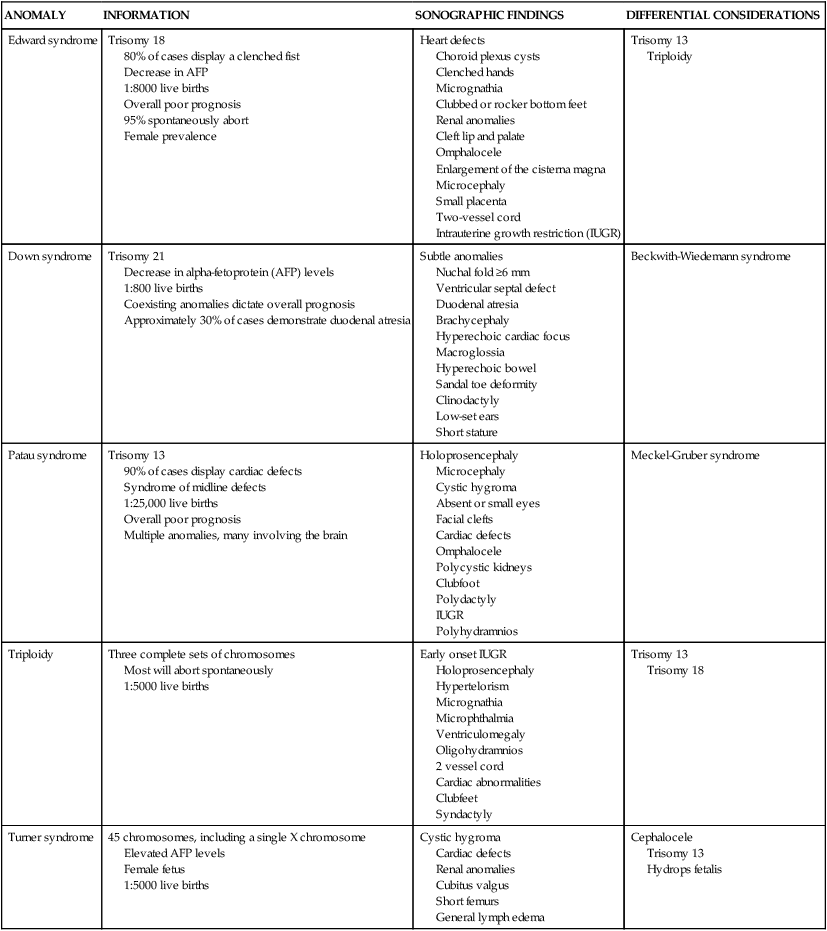
ANOMALY
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Edward syndrome
Trisomy 18
80% of cases display a clenched fist
Decrease in AFP
1:8000 live births
Overall poor prognosis
95% spontaneously abort
Female prevalence
Heart defects
Choroid plexus cysts
Clenched hands
Micrognathia
Clubbed or rocker bottom feet
Renal anomalies
Cleft lip and palate
Omphalocele
Enlargement of the cisterna magna
Microcephaly
Small placenta
Two-vessel cord
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
Trisomy 13
Triploidy
Down syndrome
Trisomy 21
Decrease in alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels
1:800 live births
Coexisting anomalies dictate overall prognosis
Approximately 30% of cases demonstrate duodenal atresia
Subtle anomalies
Nuchal fold ≥6 mm
Ventricular septal defect
Duodenal atresia
Brachycephaly
Hyperechoic cardiac focus
Macroglossia
Hyperechoic bowel
Sandal toe deformity
Clinodactyly
Low-set ears
Short stature
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Patau syndrome
Trisomy 13
90% of cases display cardiac defects
Syndrome of midline defects
1:25,000 live births
Overall poor prognosis
Multiple anomalies, many involving the brain
Holoprosencephaly
Microcephaly
Cystic hygroma
Absent or small eyes
Facial clefts
Cardiac defects
Omphalocele
Polycystic kidneys
Clubfoot
Polydactyly
IUGR
Polyhydramnios
Meckel-Gruber syndrome
Triploidy
Three complete sets of chromosomes
Most will abort spontaneously
1:5000 live births
Early onset IUGR
Holoprosencephaly
Hypertelorism
Micrognathia
Microphthalmia
Ventriculomegaly
Oligohydramnios
2 vessel cord
Cardiac abnormalities
Clubfeet
Syndactyly
Trisomy 13
Trisomy 18
Turner syndrome
45 chromosomes, including a single X chromosome
Elevated AFP levels
Female fetus
1:5000 live births
Cystic hygroma
Cardiac defects
Renal anomalies
Cubitus valgus
Short femurs
General lymph edema
Cephalocele
Trisomy 13
Hydrops fetalis
Fetal syndromes
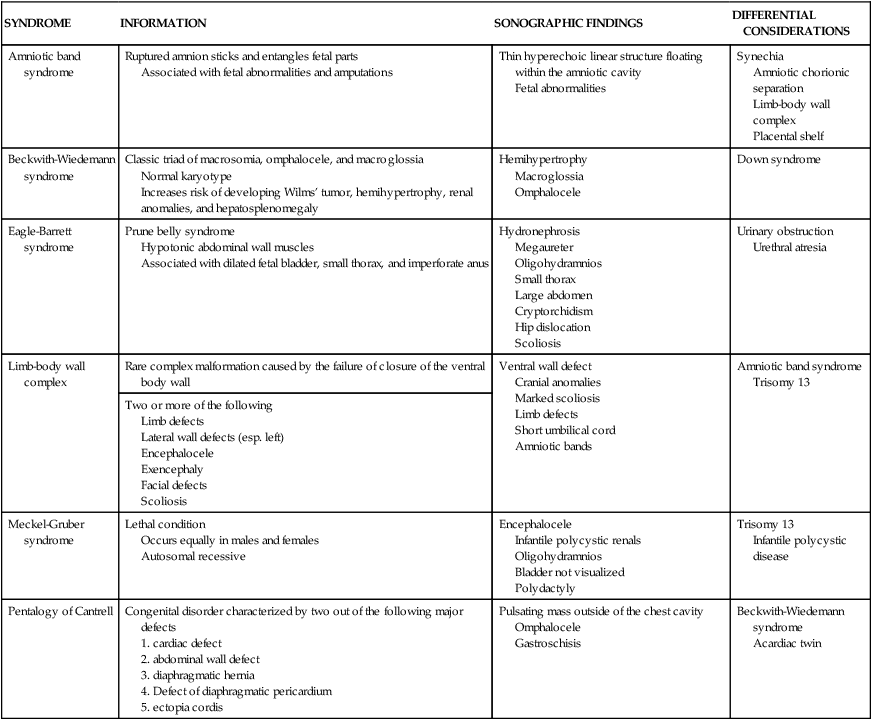
SYNDROME
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Amniotic band syndrome
Ruptured amnion sticks and entangles fetal parts
Associated with fetal abnormalities and amputations
Thin hyperechoic linear structure floating within the amniotic cavity
Fetal abnormalities
Synechia
Amniotic chorionic separation
Limb-body wall complex
Placental shelf
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Classic triad of macrosomia, omphalocele, and macroglossia
Normal karyotype
Increases risk of developing Wilms’ tumor, hemihypertrophy, renal anomalies, and hepatosplenomegaly
Hemihypertrophy
Macroglossia
Omphalocele
Down syndrome
Eagle-Barrett syndrome
Prune belly syndrome
Hypotonic abdominal wall muscles
Associated with dilated fetal bladder, small thorax, and imperforate anus
Hydronephrosis
Megaureter
Oligohydramnios
Small thorax
Large abdomen
Cryptorchidism
Hip dislocation
Scoliosis
Urinary obstruction
Urethral atresia
Limb-body wall complex
Rare complex malformation caused by the failure of closure of the ventral body wall
Ventral wall defect
Cranial anomalies
Marked scoliosis
Limb defects
Short umbilical cord
Amniotic bands
Amniotic band syndrome
Trisomy 13
Two or more of the following
Meckel-Gruber syndrome
Lethal condition
Occurs equally in males and females
Autosomal recessive
Encephalocele
Infantile polycystic renals
Oligohydramnios
Bladder not visualized
Polydactyly
Trisomy 13
Infantile polycystic disease
Pentalogy of Cantrell
Congenital disorder characterized by two out of the following major defects
Pulsating mass outside of the chest cavity
Omphalocele
Gastroschisis
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Acardiac twin
Hydrops fetalis
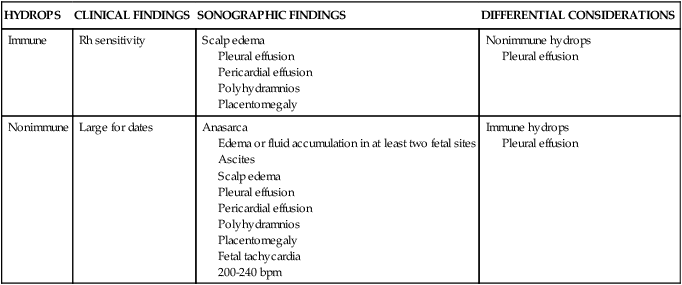
HYDROPS
CLINICAL FINDINGS
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Immune
Rh sensitivity
Scalp edema
Pleural effusion
Pericardial effusion
Polyhydramnios
Placentomegaly
Nonimmune hydrops
Pleural effusion
Nonimmune
Large for dates
Anasarca
Edema or fluid accumulation in at least two fetal sites
Ascites
Scalp edema
Pleural effusion
Pericardial effusion
Polyhydramnios
Placentomegaly
Fetal tachycardia
200-240 bpm
Immune hydrops
Pleural effusion
Multifetal gestations
Complications in pregnancy



