Chapter 510 Rapidly Progressive (Crescentic) Glomerulonephritis
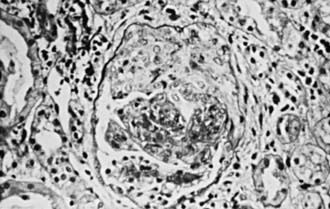
“Rapidly progressive” describes the clinical course of several forms of glomerulonephritis (RPGN) whose unifying feature is the histopathologic finding of crescents in the majority of glomeruli (Fig. 510-1). Therefore the terms rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) and crescentic glomerulonephritis (CGN) are synonymous. The natural history of most forms of CGN is rapid and relentless progression to end-stage renal failure.
Classification
CGN can be a severe manifestation of essentially every defined primary and secondary GN, but particular forms of GN are more likely to manifest as RPGN or evolve into CGN (Table 510-1). If no underlying cause is identified by systemic features, serologic testing, or histologic examination, the disease is classified as idiopathic CGN. The incidence of specific etiologies of CGN in children varies widely in reports from different centers; certain common themes are shared in all such reports. Patients with systemic vasculitis appear to be particularly prone to develop CGN. Patients with Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–mediated GN (microscopic polyangiitis and Wegener granulomatosis), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) account for the majority of patients with CGN. Poststreptococcal GN rarely progresses to CGN, but because it is the most common form of GN in childhood it accounts for a significant percentage of patients with CGN in most reports. Membranoproliferative GN and idiopathic cases make up most of the remaining cases of CGN. Immunoglobulin (Ig)A nephropathy, a common GN, only rarely is rapidly progressive. Goodpasture disease often has rapidly progressive GN as a component of the syndrome, but its rarity in childhood results in its making up only a small percentage of children with CGN.
Table 510-1 CLASSIFICATION OF RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE (CRESCENTIC) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
ANTI-GBM ANTIBODY-MEDIATED RPGN
RPGN ASSOCIATED WITH GRANULAR IMMUNE DEPOSITS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree