Postpartum Pain/Fever
Anne Kennedy, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Endometritis
Bladder Flap Hematoma
Less Common
Adnexal Torsion
Ovarian Vein Thrombosis
Uterine Rupture
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Puerperal fever is defined as fever ≥ 38° C within 14 days of giving birth
Aim to differentiate pregnancy-related from other sources of fever
Check for vaginal bleeding, discharge
History of vaginal vs. cesarean delivery
History of prior C-section
Post-operative population at risk for pneumonia, venous thromboembolic disease, urinary tract infection
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Endometritis
Mixed echogenicity debris in endometrial cavity
Punctate bright echoes with distal shadowing suggest gas in cavity
Increased risk with retained products of conception, C-section
Bladder Flap Hematoma
Occurs after C-section
Typical location between lower uterine segment and bladder wall
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Adnexal Torsion
Increased risk in puerperium as ovaries descend back into pelvis
Ovary enlarged, edematous with peripheral follicles
Use Doppler to evaluate flow; venous flow obliterated before arterial
Ovarian Vein Thrombosis
Difficult diagnosis on ultrasound but contrast-enhanced CT shows typical findings
Distended ovarian vein with surrounding inflammation
Typical course extending from pelvis to inferior vena cava (IVC) on right, pelvis to renal vein on left
Inflammation can extend to surrounding bowel; do not confuse with appendicitis or other bowel pathology
Uterine Rupture
More common in labor but may occur as delayed event
History of prior C-section or uterine surgery
Anterior uterine segment hematoma at site of dehiscence ± intraperitoneal fluid
Other Essential Information
Mother should pump and discard breast milk for 24 hours after contrast-enhanced CT due to iodine excretion in breast milk
Image Gallery
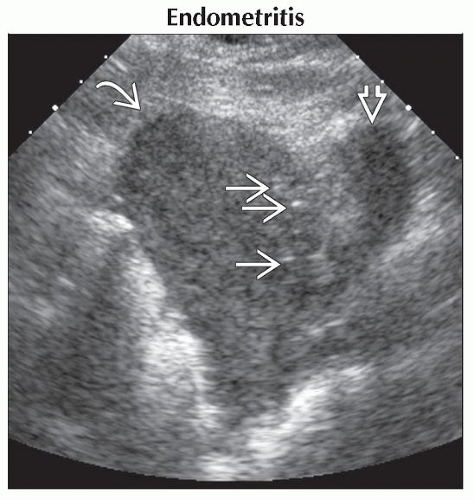 Sagittal ultrasound shows punctate echoes
 in the anterior myometrium and an area of inhomogeneous echoes between the uterus in the anterior myometrium and an area of inhomogeneous echoes between the uterus  and the bladder and the bladder  in a patient with fever and pain following C-section. in a patient with fever and pain following C-section.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|