CHAPTER 2 process whereby sound energy is dissipated in a medium, primarily in the form of heat. resistance of sound as it propagates through a medium. relating to the strength of the compression wave; maximum variation of an acoustic variable. amount of space within a specific boundary. weakening of sound as it propagates through a medium. attenuation occurring with each centimeter that sound travels. range of frequencies found in pulse ultrasound. distance around the perimeter of an object. region of high pressure or density in a compression wave. a nonpulsed wave in which cycles repeat indefinitely. one complete variation in pressure or other acoustic variable. concentration of mass, weight, or matter per unit volume. dependence of velocity or other physical parameters on frequency. amount of space from one object to another. fraction of time that pulse ultrasound is on. comparison of range of frequencies (bandwidth) with operating frequency. number of cycles in a wave occurring in 1 second. one cycle per second; unit of frequency. direction of incident beam with respect to the media boundary. rate at which energy transmits over a specific area. one thousand cycles per second. wave traveling in a straight line. incident ultrasound traveling at an oblique angle to the media boundary. incident ultrasound traveling at an angle perpendicular to the media boundary. speed at which a wave moves through a medium. a collection of a number of cycles that travel together. time between the beginning of one cycle and the beginning of the next cycle. regions of low pressure or density in a compression wave. occurs when the reflector is much smaller than the wavelength of the sound beam. the beam redirected back to the transducer after striking a media boundary. redirection (return) of a portion of the sound beam back to the transducer. angle between the reflected sound and a line perpendicular to the media boundary. change in direction of the sound wave after passing from one medium to another. a traveling variation of acoustic variables. distance over which a pulse occurs. resistance of a material to compression. the sound beam continuing on to the next media boundary. amount of occupied space of an object in three dimensions. • A traveling variation of acoustic variables (pressure, density, and particle motion). • Longitudinal, mechanical, pressure waves. • Matter must be present for sound to travel; it cannot travel through a vacuum. • Sound waves carry energy—not matter—from one place to another. • Vibrations from one molecule carry to the next molecule along the same axis. These oscillations continue until friction causes the vibrations to cease. • Contain regions of compression (high pressure) and rarefaction (low pressure). Wave Variables Wavelength (λ) = Propagation Speed (c)/Frequency (ƒ) • Electrical energy applied to the transducer produces short bursts of acoustic energy. • A pulse must have a beginning and an end. • There are two components to a pulse: transmitting (on) and receiving (off). Properties of Pulse Ultrasound
Physics principles
Sound waves
METRIC PREFIX
VALUE
SYMBOL
Tetra
1012 (trillion)
T
Pico
10−12 (trillionth)
p
Giga
109 (billion)
G
Nano
10−9 (billionth)
n
Mega
106 (million)
M
Micro
10−6 (millionth)
μ
Kilo
103 (thousand)
k
Milli
10−3 (thousandth)
m
Hecto
102 (hundred)
h
Centi
10−2 (hundredth)
c
Deca
101 (ten)
Da
Deci
10−1 (tenth)
d
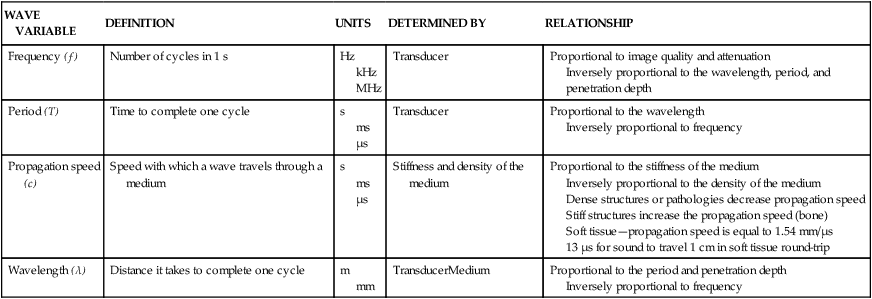
WAVE VARIABLE
DEFINITION
UNITS
DETERMINED BY
RELATIONSHIP
Frequency (ƒ)
Number of cycles in 1 s
Hz
kHz
MHz
Transducer
Proportional to image quality and attenuation
Inversely proportional to the wavelength, period, and penetration depth
Period (T)
Time to complete one cycle
s
ms
μs
Transducer
Proportional to the wavelength
Inversely proportional to frequency
Propagation speed (c)
Speed with which a wave travels through a medium
s
ms
μs
Stiffness and density of the medium
Proportional to the stiffness of the medium
Inversely proportional to the density of the medium
Dense structures or pathologies decrease propagation speed
Stiff structures increase the propagation speed (bone)
Soft tissue—propagation speed is equal to 1.54 mm/μs
13 μs for sound to travel 1 cm in soft tissue round-trip
Wavelength (λ)
Distance it takes to complete one cycle
m
mm
TransducerMedium
Proportional to the period and penetration depth
Inversely proportional to frequency
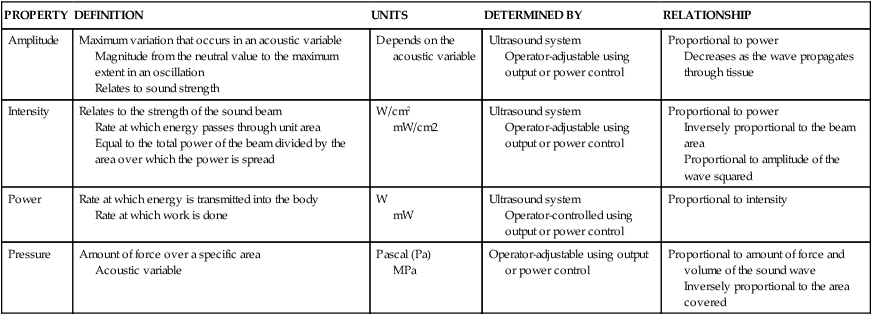
PROPERTY
DEFINITION
UNITS
DETERMINED BY
RELATIONSHIP
Amplitude
Maximum variation that occurs in an acoustic variable
Magnitude from the neutral value to the maximum extent in an oscillation
Relates to sound strength
Depends on the acoustic variable
Ultrasound system
Operator-adjustable using output or power control
Proportional to power
Decreases as the wave propagates through tissue
Intensity
Relates to the strength of the sound beam
Rate at which energy passes through unit area
Equal to the total power of the beam divided by the area over which the power is spread
W/cm2
mW/cm2
Ultrasound system
Operator-adjustable using output or power control
Proportional to power
Inversely proportional to the beam area
Proportional to amplitude of the wave squared
Power
Rate at which energy is transmitted into the body
Rate at which work is done
W
mW
Ultrasound system
Operator-controlled using output or power control
Proportional to intensity
Pressure
Amount of force over a specific area
Acoustic variable
Pascal (Pa)
MPa
Operator-adjustable using output or power control
Proportional to amount of force and volume of the sound wave
Inversely proportional to the area covered
Pulse ultrasound
PROPERTY
DEFINITION
UNITS
DETERMINED BY
RELATIONSHIP
Bandwidth
Range of frequencies contained in a pulse
MHz
Transducer
Ultrasound system
Cannot be adjusted by the operator
Inversely proportional to the length of the pulse (SPL) and Q factor
Portion of the bandwidth used is adjusted with the multi-Hertz or harmonic control
Duty factor (DF)
Percentage of time that pulsed ultrasound is transmitting (on-time)
None
Transducer
Operator-adjustable with depth control
Proportional to PRF and PD
Inversely proportional to PRP
Pulse duration (PD)
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
