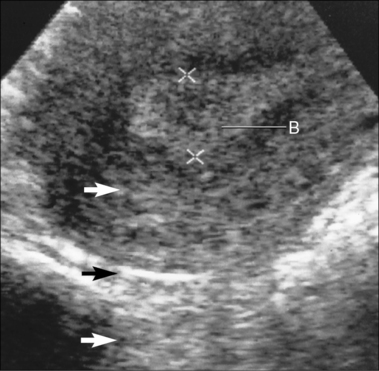
CHAPTER 19 • Pelvis begins at the iliac crests and ends at the symphysis pubis. • Divided into the true and false pelvis by the iliopectineal line. • Also known as pelvic cavity. • Located inferior to the pelvic brim. • Muscles and ligaments form a pelvic floor. • Anterior boundary—symphysis pubis. • Posterior boundary—sacrum and coccyx. • Posterolateral wall—piriformis and coccygeus muscles. • Anterolateral wall—hip bone and obturator internus muscles. • Lateral boundaries—fused ilium and ischium. • Pelvic floor—levator ani and coccygeus muscles. • Contains—female reproductive system, urinary bladder, distal ureters, and bowel. • Located superior to the pelvic brim. • Anterior boundary—abdominal wall. • Posterior boundary—flanged portions of the iliac bones and base of the sacrum. • Lateral boundaries—abdominal wall. • Not routinely visualized by ultrasound. • With intraperitoneal fluid collections, ligaments will appear moderately thin and hyperechoic. • Not uncommon to visualize a small amount of free fluid in the retrouterine pouch. • Masses within the space of Retzius will displace the urinary bladder posteriorly. • Masses within the vesicouterine pouch will displace the urinary bladder anteriorly. • Ectopic pregnancy or hemorrhagic ovarian cyst (hemoperitoneum) accumulates in these spaces. • Collapsed muscular tube located posterior to the urinary bladder and urethra and anterior to the rectum and anus. • Extends from the vulva to the cervix. • Sides of the vagina are enclosed between the levator ani muscles. • Half of the vagina lies above and the other half below the pelvic brim. • Supplied by the vaginal and uterine arteries and empties into the internal iliac veins. • Hollow, pear-shaped retroperitoneal organ. • Derived from the fused caudal portion of the paired, hollow müllerian ducts. • Muscular organ covered by peritoneum, except below the anterior cervical os. • Supported by the levator ani muscles, cardinal ligaments, and uterosacral ligaments. • Uterine growth begins at approximately 7 to 8 years of age, accelerates during puberty, and continues to grow until approximately 20 years of age. • Anterior–posterior thickness is measured in the sagittal plane. • Measured from echogenic interface to echogenic interface (functional layer). • Thin hypoechoic area (basal layer) is not included in the measurement. • Fluid within the endometrial cavity is not included in the measurement.
Pelvic anatomy
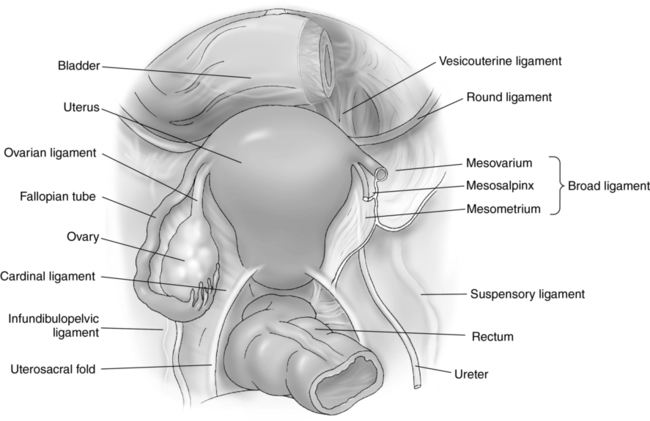
Pelvic anatomy (fig. 19-1)
True pelvis
False pelvis
PELVIC MUSCLE
DESCRIPTION
LOCATION
SONOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
Levator ani
Most caudal structures within the pelvic cavity
Medial to the obturator internus muscles
Posterior to the vagina and cervix
Low-level, mildly curved linear echoes posterior to the vagina
Hypoechoic compared to the normal uterus
Iliopsoas muscles
Formed by the psoas major and iliacus muscles
Lateral landmark of the true pelvis
Course anterior and lateral through the false pelvis
Descend until attaching to the lesser trochanter of the femur
Low-level gray echoes with a distinct central hyperechoic focus
Piriformis muscles
Arise from the sacrum
Form part of the pelvic floor
Course through the greater sciatic notch
Posterior to the uterus, ovaries, vagina, and rectum
Anterior to the sacrum
Course diagonally to the obturator internus muscle
Low-level linear echoes
Hypoechoic compared to the normal uterus
Psoas major
Arises from the lumbar spine
Descends into the false pelvis
Course laterally and anteriorly into the false pelvis
Exits posterior to the inguinal ligament
Low-level echogenicity
Round in shape in the transverse plane
Obturator internus muscles
Lateral margins of the true pelvis
Surround the obturator foramen
Posterior and medial to the iliopsoas muscles
Level of the vagina
Lateral to the ovaries
Low-level linear echoes abutting the lateral walls of the urinary bladder
Pelvic ligaments
PELVIC LIGAMENT
DESCRIPTION
Broad
Winglike double fold of peritoneum
Drapes over the fallopian tubes, uterus, ovaries, and blood vessels
Extends from the lateral walls of the uterus to the sidewalls of the pelvis
Provides a small amount of support for the uterus
Creates the retrouterine and vesicouterine pouches
Divided into the mesometrium, mesosalpinx, and mesovarium segments
Cardinal
Continuation of the broad ligament
Extends across the pelvic floor
Attaches at the isthmus portion of the uterus
Firmly supports the cervix
Ovarian
Extends from the cornua of the uterus to the medial aspect of the ovary
Round
Arises in the uterine cornua, anterior to the fallopian tubes
Extends from the uterine fundus to the pelvic sidewalls
Helps to maintain anteflexion of the uterine body and fundus
Excessive stretching can permit retroflexion of the uterine body and fundus
Contracts during labor
Suspensory
Also known as infundibulopelvic ligament
Extends from the lateral portion of the ovary to the pelvic sidewall
Uterosacral
Extends from the upper cervix to the lateral margins of the sacrum
Firmly supports the cervix
VESSEL
LOCATION
INFORMATION
Arcuate vessels
Prominent vascular structures in the outer one third of the myometrium
Branch of the uterine artery
Radial arteries arise from the arcuate arteries
Spiral arteries of the endometrium arise from the radial arteries
Radial arteries branch into straight arteries to support the inner myometrium and endometrium
Larger-caliber vessels are typically arcuate veins
Internal iliac arteries
Posterior to the uterus and ovaries
Follows a posterior course and enters the true pelvis near the sacral prominence
Aka: hypogastric arteries
Supply the bladder, uterus, vagina, and rectum
Give rise to the uterine arteries
Ovarian arteries
Arise from the lateral margins of the abdominal aorta, slightly inferior to the renal arteries
Course medial within the suspensory ligaments
Primary blood supply to the ovaries
Connect with the uterine arteries
Ovarian veins
Course within the suspensory ligaments
Right ovarian vein empties directly into the inferior vena cava
Left ovarian vein empties into the left renal vein
Uterine arteries
Medial in the levator ani muscles
Ascend in a tortuous course lateral to the uterus within the broad ligament
Supply the cervix, vagina, uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes
Course lateral and terminate at the confluence with the ovarian artery
Pelvic spaces
PELVIC SPACE
LOCATION
Retrouterine Pouch
Posterior cul de sac
Pouch of Douglas
Anterior to the rectum
Posterior to the uterus
Most inferior point in the pelvic cavity
Most common site for fluid to accumulate
Space of Retzius
Retropubic space
Prevesical space
Anterior to the urinary bladder
Posterior to the symphysis pubis
Vesicouterine Pouch
Anterior cul de sac
Anterior to the uterus
Posterior to the urinary bladder
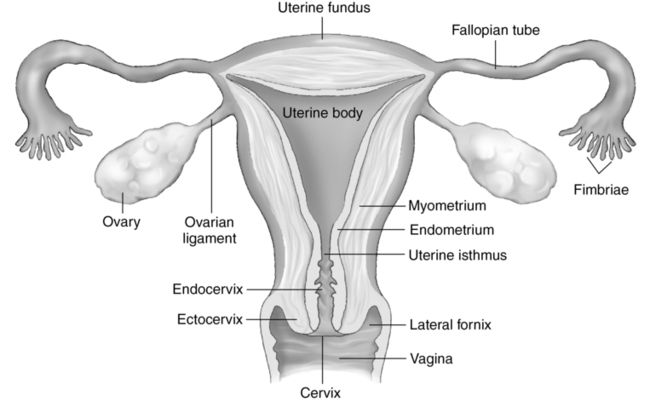
Female reproductive system (fig. 19-2)
Vagina
Uterus
Tissue layers of the uterus
Endometrium
REGION
DESCRIPTION
Body
Aka: corpus
Largest portion of the uterus
Thick muscular segment of the uterus
Located posterior to the vesicouterine pouch
Located anterior to the retrouterine pouch
Located medial to the broad ligaments and uterine vessels
Cervix
Inferior portion of the uterus
Projects into the vaginal canal
More fibrous and less flexible
Anchored at the angle of the bladder by the parametrium
Located between the vagina and the uterine isthmus
Peritoneal reflection is not demonstrated anterior to the cervix
Approximately 2.5 cm in length
Cornua
Lateral funnel-shaped horns of the uterus
Located between the uterine fundus and the interstitial portion of the fallopian tube
Endometrial cavity
Consists of a superficial functional layer and a deep basal layer
Functional layer sheds with menses
Basal layer regenerates new endometrium
Thickness is dependent on hormone levels
Fundus
Dome-shaped widest, most superior portion of the uterus
Located superior to the insertion of the fallopian tubes
Position may vary with bladder filling
Isthmus
“Narrow waist” of the uterus
Located between the cervix and body of the uterus
Termed lower uterine segment during pregnancy
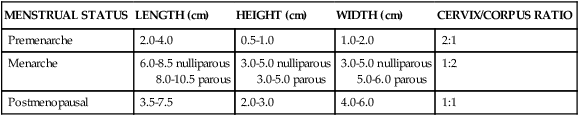
Measuring the endometrium (fig. 19-4)
MENSTRUAL STATUS
LENGTH (cm)
HEIGHT (cm)
WIDTH (cm)
CERVIX/CORPUS RATIO
Premenarche
2.0-4.0
0.5-1.0
1.0-2.0
2:1
Menarche
6.0-8.5 nulliparous
8.0-10.5 parous
3.0-5.0 nulliparous
3.0-5.0 parous
3.0-5.0 nulliparous
5.0-6.0 parous
1:2
Postmenopausal
3.5-7.5
2.0-3.0
4.0-6.0
1:1
POSITION
DESCRIPTION
Anteflexion
Uterine fundus bends on the cervix
Anteversion
Uterus bends slightly forward
Cervix forms an angle ≤90° with the vaginal canal
Most common uterine position
Dextroflexion
Uterine body is displaced or flexed to the right of the cervix
Transverse imaging plane is best to evaluate whether uterus is dextroflexed
Levoflexion
Uterine body is displaced or flexed to the left of the cervix
Transverse imaging plane is best to evaluate whether uterus is levoflexed
Retroflexion
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access