Optic Nerve Sheath Lesion
Bernadette L. Koch, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
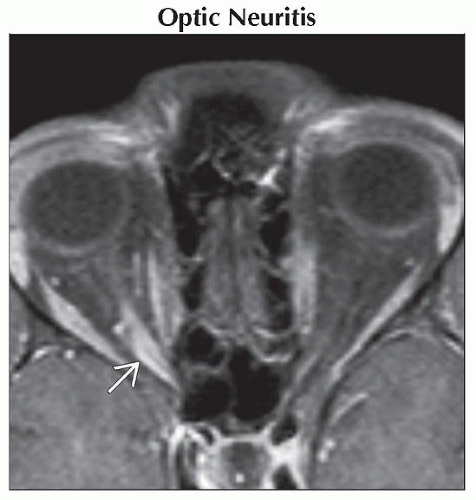
Optic Neuritis
Optic Pathway Glioma
Less Common
Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Disease (Pseudotumor)
Lymphoproliferative Lesions, Orbit
Sarcoidosis, Orbit
Rare but Important
Meningioma, Optic Nerve Sheath
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Optic Neuritis
Key facts: Inflammatory, autoimmune, infectious, post-radiation
Acute vision loss, unilateral (70%)
Imaging: Enhancement, minimal enlargement, focal or diffuse
Optic Pathway Glioma
Key facts: Pilocytic astrocytoma
30-40% have neurofibromatosis type 1
Imaging: Tubular enlargement and tortuosity of intraorbital optic nerve
Optic nerve, chiasm, tract &/or optic radiations, variable enhancement
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Idiopathic Orbital Inflammatory Disease (Pseudotumor)
Key facts: Painful, anterior subtype of IOID
Isolated or with other subtypes of IOID (myositic, lacrimal, diffuse, or apical)
Imaging: Irregular nerve sheath thickening and enhancement
Lymphoproliferative Lesions, Orbit
Key facts: Leukemia or lymphoma (low-grade small B-cell, large B-cell, Burkitt, or T-cell)
Imaging: Optic nerve sheath/complex enhancement ± solid mass anywhere in orbit
Sarcoidosis, Orbit
Key facts: Noncaseating granulomas
Lacrimal gland, EOMs, optic nerve/sheath complex, intraconal/extraconal space, or uvea/sclera
Imaging: Enhancing soft tissue mass or enlargement and enhancement of any involved orbital structure
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Meningioma, Optic Nerve Sheath
Key facts: Benign tumor from arachnoid “cap” cells within optic nerve sheath
Rare in children, minority have neurofibromatosis type 2
Imaging: “Tram track” = tumor enhancement or calcification on either side of optic nerve
Moderate to marked enhancement
“Perioptic cyst” = ↑ CSF surrounding optic nerve, between tumor and globe
Image Gallery