Neonatal Distal Bowel Obstruction
Steven J. Kraus, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Hirschsprung Disease (HD)
Meconium Plug Syndrome (MPS)
Less Common
Meconium Ileus (MI)
Jejunoileal Atresia
Rare but Important
Anorectal Malformation (ARM)
Midgut Volvulus (MV)
Omphalomesenteric Duct Remnant Obstruction
Rectal Atresia
Colonic Atresia
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Findings of contrast enema (CE) limit differential diagnosis: Colonic vs. small bowel process
Antenatal or prenatal midgut volvulus late in natural history (ischemia); ileus can mimic distal bowel obstruction
Hirschsprung disease more common in patients with Down syndrome
Consider meconium ileus if family history of cystic fibrosis
Meconium plug syndrome associated with maternal Mg++ therapy, maternal diabetes
No rectal opening in male or single perineal opening in female patient with ARM
Abdominal radiographs: Many dilated bowel loops
± air-fluid levels
If dilated bowel loops but no air-fluid levels, suspect meconium ileus
If CE and upper GI (UGI) normal in face of obstruction, consider omphalomesenteric duct remnant anomaly
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Hirschsprung Disease (HD)
Often presents at birth with distal bowel obstruction
Contrast enema primary findings
Rectosigmoid ratio < 1
Transition most commonly sigmoid
Transition often missed if at anorectal verge; enema misinterpreted as normal
Other supporting CE findings
Distal colonic spasm
Colitis
Irregular contractions
Mucosal irregularity
Delayed evacuation
Total colonic Hirschsprung
Small colon without transition ± intraluminal terminal ileal calcification
Higher incidence in Down syndrome, especially total colonic disease
Radiologic transition not equivalent to histologic transition, especially in long-segment HD
Meconium Plug Syndrome (MPS)
Nonpathologic diagnosis
Association with Mg++ therapy for preeclampsia and diabetic mother
Presents clinically similar to Hirschsprung disease
Enema findings
Rectosigmoid ratio > 1
Small left colon, abrupt transition to dilated bowel at splenic flexure, colonic meconium pellets
Evacuation of meconium during and after enema
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Meconium Ileus (MI)
Possible radiographic findings
“Soap bubble” densities in right lower quadrant
Multiple dilated loops of air-filled bowel likely indicates simple MI
Air-fluid levels within bowel loops less likely due to thick meconium
Gasless abdomen indicates high risk of complicated MI
Peritoneal calcifications indicate meconium peritonitis (evidence of bowel perforation, complicated MI)
Contrast enema findings
Microcolon
Small terminal ileum (TI) filled with meconium pellets
Dilated ileum proximal to obstructing meconium
Possible ultrasound findings
Echogenic bowel loops
Meconium pseudocyst
Peritoneal calcifications
Almost always associated with cystic fibrosis
Jejunoileal Atresia
Possible radiographic findings
Multiple, dilated, air-filled bowel loops
Air-fluid levels within bowel loops
Gasless abdomen suggests bowel perforation
Peritoneal calcifications suggest meconium peritonitis due to bowel perforation
Contrast enema findings
Rectosigmoid ratio > 1
Microcolon
Normal caliber TI without meconium
Refluxed contrast in TI abruptly terminates in ileum or distal jejunum
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Anorectal Malformation (ARM)
Imperforate anus or anteriorly located stenotic rectal orifice on physical exam in male
Anterior stenotic rectal orifice or single perineal orifice on physical exam in female
Distal bowel obstruction
Colon generally more compliant; dilates more than small bowel
Midgut Volvulus (MV)
Late presentation: Dilated bowel due to ischemic ileus
Radiographs show multiple dilated bowel loops
Sometimes pneumatosis or bowel wall thickening
Normal caliber colon on CE
UGI shows duodenal obstruction
Partial: Corkscrew with dilation of proximal duodenum
Complete: No contrast distal to obstruction
Omphalomesenteric Duct Remnant Obstruction
Radiographs show dilated bowel loops of distal obstruction
Contrast enema: Usually normal caliber colon; reflux contrast into beak-shaped, obstructed terminal ileum
Normal duodenal rotation on UGI
Volvulus of omphalomesenteric duct remnant
Rectal Atresia
Radiographs show dilated bowel loops of distal obstruction
Colonic loops usually dilate more than small bowel loops
Contrast enema: Abrupt obstruction of colon just above anorectal verge
Considered by some to be a type of anorectal malformation
Colonic Atresia
Findings on radiographs similar to rectal atresia
Contrast enema: Obstruction of colon proximal to rectum
Etiology: Ischemic event in utero similar to small bowel atresias
Image Gallery
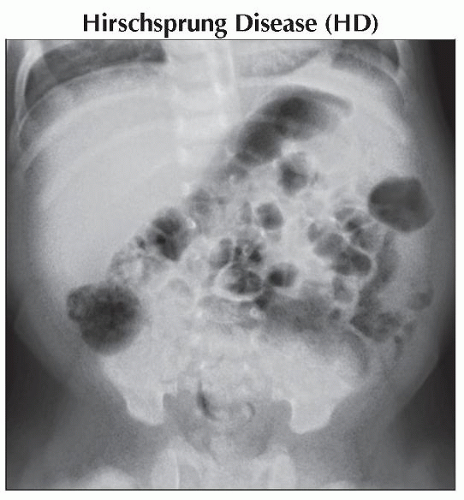 Anteroposterior fluoroscopic spot radiograph scout in an infant with infrequent stooling shows moderate to large stool load without other specific abnormality. The bones appear normal. |
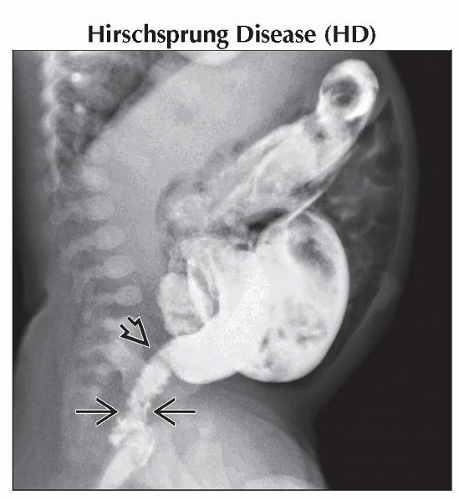 Lateral contrast enema in the same patient shows a narrow rectum with transition
 to the dilated colon at the rectosigmoid junction consistent with Hirschsprung disease. Note the spasm to the dilated colon at the rectosigmoid junction consistent with Hirschsprung disease. Note the spasm  in the distal segment. in the distal segment.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|