Multiple Liver Lesions
Alexander J. Towbin, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Hemangioendothelioma/Hemangioma
Hepatic Pyogenic Abscess
Metastases
Neuroblastoma
Wilms Tumor
Lymphoma/Leukemia
Hepatoblastoma
Less Common
Mesenchymal Hamartoma
Nodular Regenerative Hyperplasia
Rare but Important
Caroli Disease
Peliosis Hepatis
Angiomyolipoma
Echinococcosis
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Various causes of multiple liver lesions
Benign and malignant
Primary hepatic neoplasms are uncommon
0.5-2% of all pediatric neoplasms
2/3 are malignant
Overlap in imaging appearance
Biopsy often required
Differential diagnosis can be focused by age
Lab tests may be helpful in forming differential diagnosis
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
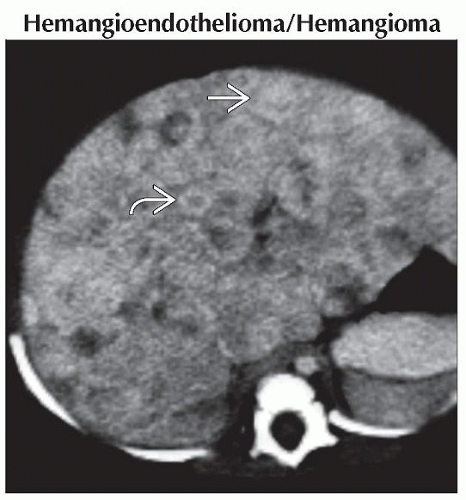
Hemangioendothelioma/Hemangioma
a.k.a. infantile hepatic hemangioma
Most common benign hepatic tumor
85% diagnosed in 1st 6 months
Skin hemangiomas present in ˜ 50%
Single, multiple, or diffuse lesions
Diffuse lesions often have severe clinical course
Can cause massive hepatomegaly leading to compression of inferior vena cava and thoracic cavity
Mass effect can lead to abdominal compartment syndrome and multiorgan failure
Can be associated with severe hypothyroidism
Hepatic Pyogenic Abscess
Associated with immunodeficiency, systemic infection, abdominal inflammatory processes, and chronic granulomatous disease
S. aureus most common organism
Fungal infections and B. henselae associated with microabscesses
Can be solitary or multiple
Multiple in 20-25% of children and up to 70% in neonates
Risks in neonate include necrotizing enterocolitis and umbilical vein catheterization
US useful for diagnosis and follow-up
Metastases
Neuroblastoma and Wilms tumor most common
Neuroblastoma metastasizes to liver (15%)
Wilms tumor metastasizes to liver (12%)
Hepatic metastases more common overall than primary hepatic tumors
Can appear as discrete nodules or diffuse hepatic involvement
Hepatoblastoma
Most common pediatric hepatic malignancy
Majority of patients diagnosed are < 18 months of age
More common in boys
Associated with low birth weight, hemihypertrophy, Beckwith-Wiedemann, familial adenomatous polyposis, trisomy 18, and fetal alcohol syndrome
90% have increased serum α-fetoprotein
Most common in right lobe of liver
Bilateral disease in 35%
Calcifications in 40-55%
Usually solitary solid mass
Can be multifocal although there is usually 1 dominant mass
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Mesenchymal Hamartoma
2nd most common benign hepatic mass
Typically diagnosed in 1st 2 years of life
Often presents as large RUQ mass
75% in right lobe
α-fetoprotein may be moderately elevated
Multiloculated cystic mass
Mixed cystic and solid
May be small or large
Multiple tiny cysts may appear solid
On US, septae of cysts may be mobile
Rare malignant transformation to undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma
Treatment via excision
Nodular Regenerative Hyperplasia
Multiacinar regenerative lesion of liver in noncirrhotic liver
Associated with systemic diseases, such as vasculitis, collagen disorders, cardiovascular disorders, and neoplasms
Can cause portal hypertension
Can occur after spontaneous portal vein thrombosis
Radiologic findings not specific
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Caroli Disease
a.k.a. type 5 choledochal cyst
May be associated with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
Congenital cystic dilation of intrahepatic bile ducts
Patients present with recurrent cholangitis or portal hypertension
Peliosis Hepatis
Multiple blood-filled cavities
Rare in children
Associated with underlying chronic conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, malnutrition, Fanconi anemia, Marfan syndrome, and adrenal tumors
Angiomyolipoma
Associated with tuberous sclerosis
Less common than renal angiomyolipoma
Often multiple when present
Lesions have imaging characteristics of fat
Echinococcosis
a.k.a. hydatid disease
Most common in Mediterranean, Middle East, eastern Europe, Africa, South America, China, and Australia
Generally asymptomatic
Appears as single or multiple cysts
Daughter cysts present in 75%
Cysts slowly expand over years
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
2nd most common hepatic malignancy in children
Rare before age 5
More common in males
Most pediatric cases not associated with prior liver disease (> 60%)
Can be associated with preexisting cirrhosis due to biliary atresia, Fanconi syndrome, viral hepatitis, hereditary tyrosinemia, or glycogen storage disease
Other risk factors: Prior androgen steroid treatment, oral contraceptives, methotrexate
Metastases common at diagnosis
Regional lymph nodes, lungs, bone
Disease is multifocal in > 50%
Multifocal tumors influence overall survival and possibility of surgical resection
Image Gallery
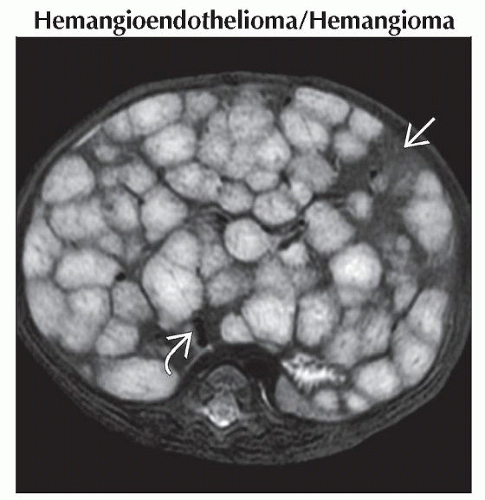 Axial T2WI MR shows innumerable hyperintense lesions throughout the liver. Only a small area of normal liver remains
 . The inferior vena cava . The inferior vena cava  is compressed by multiple masses. is compressed by multiple masses.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|