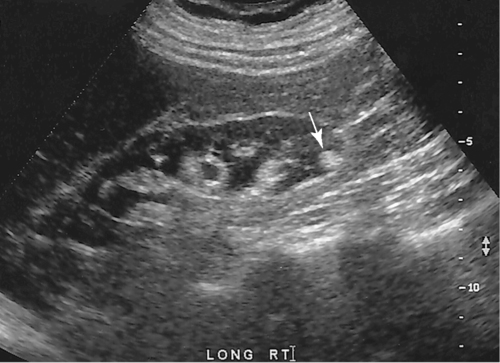
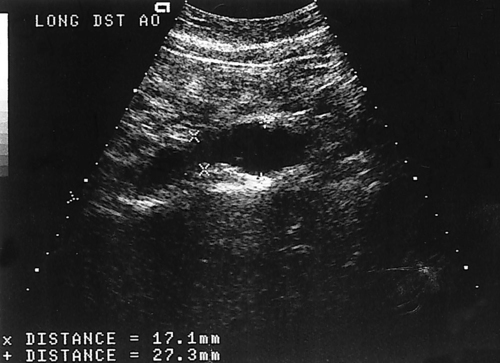
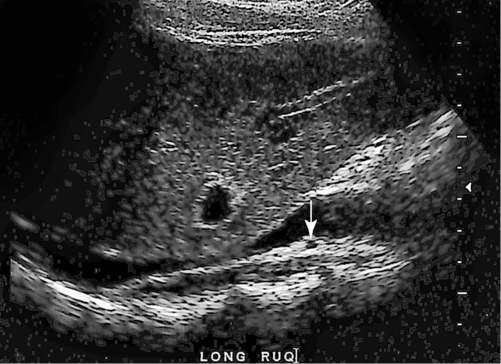
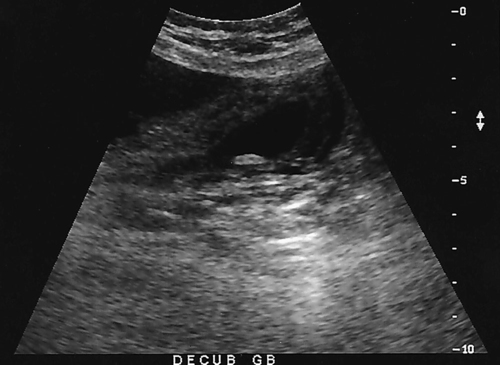
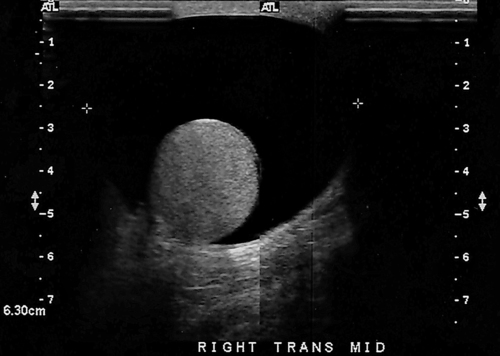
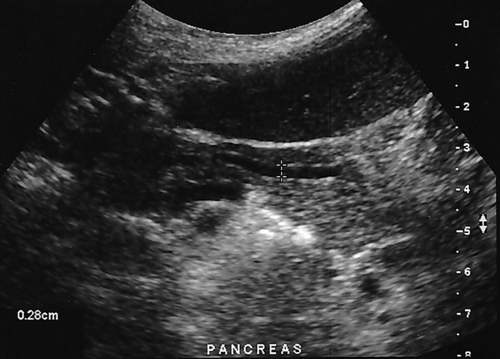
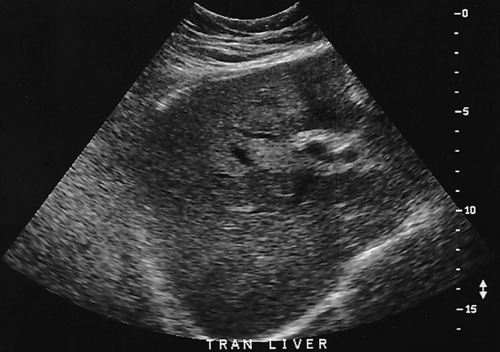
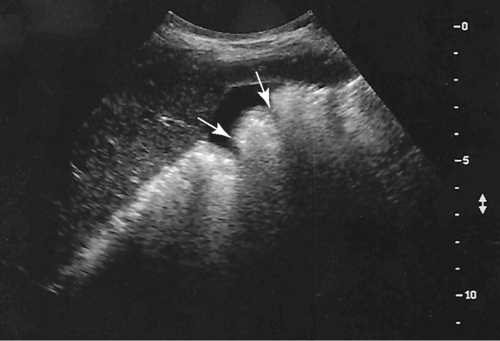
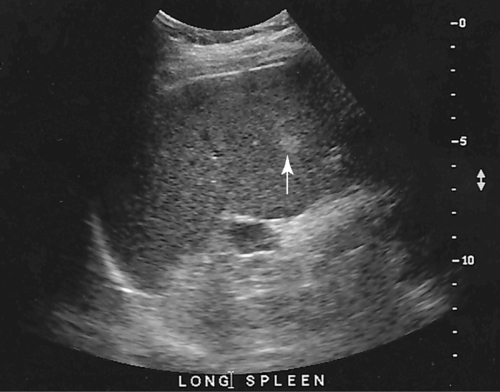
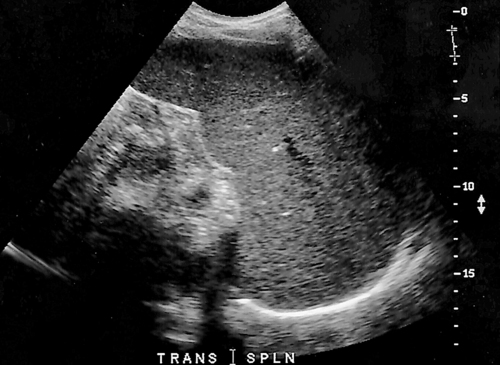
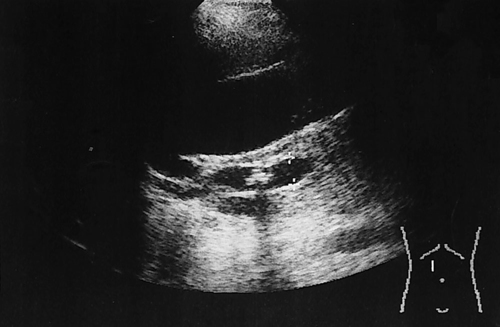
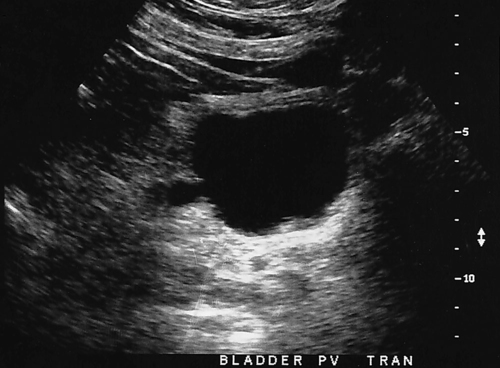
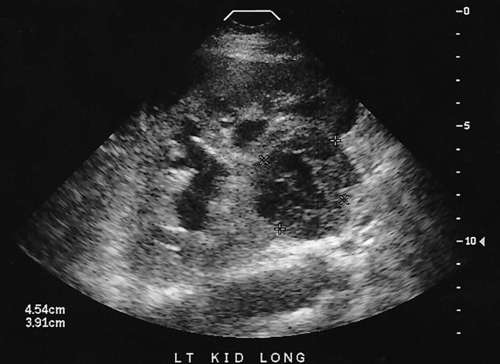
1. Which of the following structures is used as a sonographic landmark in locating the gallbladder fossa? 2. Which of the following conditions is the most common cause of acute pancreatitis? 3. Gerota fascia provides a protective covering around which of the following organs? 4. Increased pressure within the portosplenic venous system will most likely lead to which of the following conditions? 5. Normal diameter of the main portal vein should not exceed: 6. The integrity of which of the following structures is evaluated with the Thompson test? 7. A small hyperechoic pancreas is identified on ultrasound. This is most suspicious for which of the following abnormalities? 8. Which of the following structures is a part of the endocrine system? 9. Which of the following is a sonographic finding of an echinococcal cyst? 10. A predisposing risk factor associated with the development of cholangiocarcinoma may include a history of: 11. A synovial cyst located in the medial popliteal fossa describes a: 12. Normal caliber of the superior mesenteric vein should not exceed: 13. A patient presents with a history of abdominal pain and lower-extremity edema. An ultrasound is requested to rule out Budd-Chiari syndrome. The sonographer should thoroughly evaluate which of the following organs? 14. Which of the following structures divide the left lobe into two segments? a. left portal vein and ligamentum of Teres b. left hepatic vein and ligamentum venosum c. left hepatic vein and ligamentum of Teres 15. Cholecystokinin is stimulated after food reaches the: 16. The gallbladder is located on the posterior surface of the liver and: a. medial to the inferior vena cava b. anterior to the main lobar fissure c. anterior to the right kidney 17. The pyloric canal is considered abnormal when the length exceeds: 18. A patient presents with a history of severe back pain, weight loss, and painless jaundice. An abnormality in which of the following organs is most likely to correlate with these symptoms? 19. The popliteal artery is considered dilated after the diameter exceeds: 20. Which of the following structures surrounds the liver? 21. Which of the following conditions is associated with Mirizzi syndrome? 22. A spaghetti-like echogenic tubular structure within a bile duct is a sonographic finding associated with: 23. Gallbladder wall thickening is not a sonographic finding in: 24. The Whipple procedure is a surgical resection of which of the following organs? 25. A fluid collection caused by extravasated bile is termed a: 26. Renal artery stenosis is suggested after the renal artery to aortic ratio exceeds: 27. Which of the following peritoneal spaces most commonly demonstrates ascites? 28. Which of the following structures lies within the anterior pararenal space? 29. The crura of the diaphragm are located: a. anterior to the inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta b. posterior to the inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta c. anterior to the inferior vena cava and posterior to the abdominal aorta d. posterior to the inferior vena cava and anterior to the abdominal aorta 30. Splenomegaly is a consistent finding in which of the following liver pathologies? 31. Carcinoma in which of the following structures can directly extend into the gallbladder? 32. Enlargement of the gallbladder caused by obstruction of the common bile duct by a distal external neoplasm is termed: 33. Which of the following structures define the superior and inferior borders of the retroperitoneum? b. pancreas and urinary bladder c. crura of the diaphragm and symphysis pubis d. posterior peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall muscles 34. Elevation in prostatic specific antigen (PSA) is suspicious for: 35. Thrombosis involving the hepatic veins describes which of the following conditions? 36. A patient presents with a history of right upper quadrant pain, nausea, and vomiting. A sonogram of the right upper quadrant demonstrates a calculus lodged in the cystic duct. This finding is a predisposing factor for developing: 37. Which of the following structures may be mistaken for an extrarenal pelvis? 38. A patient presents with a history of intermittent fever, nausea, and elevated alkaline phosphatase. He admits to traveling to the Middle East recently. A complex, solitary mass is identified in the right lobe of the liver. This mass is most suspicious for a(n): 39. Which of the following terms is more commonly used to describe an enlarged or dilated vein? 40. Which of the following conditions most commonly causes the formation of a hepatic abscess? 41. Which of the following structures is located in the anterolateral portion of the pancreatic head? 42. A patient presents with a palpable neck mass. A sonogram demonstrates an echogenic mass in the superior lobe of the right thyroid gland. A prominent hypoechoic ring surrounds this nodule. This mass is most suspicious for which of the following neoplasms? 43. Which of the following organs is responsible for manufacturing heparin? 44. The length of a normal adult spleen should not exceed: 45. Which type of aneurysm is most commonly associated with a bacterial infection? 46. The stomach produces which of the following enzymes? 47. Which of the following conditions is associated with rebound pain at McBurney point? 48. A round anechoic mass is identified next to the renal pelvis. This is most suspicious for which of the following? 49. Which of the following is the most common clinical symptom associated with portal vein thrombosis? 50. The diameter of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) should measure a minimum of: Using Fig. 1, answer questions 51 and 52. 51. A retroperitoneal ultrasound is ordered to follow up on previously documented hydronephrosis of the right kidney. The patient is presently asymptomatic. An image of the right kidney demonstrates a small hyperechoic focus in the inferior pole of the kidney (arrow). This focus is most suspicious for a renal: 52. Regarding the patient’s previous history of hydronephrosis, the sonographer’s technical impression on this current image should include: Using Fig. 2, answer question 53. 53. A patient presents with a history of a pulsatile abdominal mass found on a physical examination. The sonogram of the distal abdominal aorta is most consistent with a(n): Using Fig. 3, answer question 54. Using Fig. 4, answer question 55. 55. A patient presents to the emergency department with severe right upper quadrant pain. Laboratory tests demonstrate leukocytosis and elevation in total bilirubin levels. On the basis of this clinical history, the pathology identified is most suspicious for: Using Fig. 5, answer question 56. 56. A 70-year-old man presents with a history of scrotal enlargement. He denies trauma to the scrotum or groin areas. On the basis of this clinical history, the sonographic finding is most suspicious for a(n): Using Fig. 6, answer question 57. 57. A patient presents with a history of elevated liver function tests. An anechoic tubular structure is identified in the body of the pancreas. This structure most likely represents the: Using Fig. 7, answer question 58. 58. An obese patient presents with a history of elevated liver function tests discovered during a life insurance medical examination. The patient has no complaints. The sonographic findings in this image are most suspicious for: Using Fig. 8, answer question 59. Using Fig. 9, answer question 60. 60. A 30-year-old patient presents with a history of right upper quadrant pain. Laboratory tests are within normal limits. An image of the spleen demonstrates an incidental hyperechoic mass. This mass is most suspicious for a(n): Using Fig. 10, answer questions 61 and 62. 61. A patient presents with a history of alcohol abuse. Which of the following splenic pathologies is most likely identified in this sonogram? 62. With this pathological finding, the sonographer should evaluate for: Using Fig. 11, answer question 63. 63. A patient presents to the emergency department with a history of severe epigastric pain. Laboratory results are pending. An abdominal ultrasound is ordered to rule out biliary disease. Which of the following pathologies is identified in this sonogram of the porta hepatis? Using Fig. 12, answer question 64. 64. An older patient presents with a history of elevated creatinine and microscopic hematuria. An abnormal finding identified in this sonogram is most consistent with a: Using Fig. 13, answer questions 65 and 66. 65. A patient presents with a history of uncontrolled hypertension and painless hematuria. A hypervascular complex mass is identified near the renal hilum. On the basis of the clinical history, the mass is most suspicious for a:
Abdomen mock exam
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


mock exam