Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Roya Sohaey, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Placental Insufficiency
Less Common
Chromosome Abnormality
Trisomy 18 (T18)
Trisomy 13 (T13)
Triploidy
Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome
Isolated Anomalies with IUGR
Gastroschisis
Single Umbilical Artery
Rare but Important
Infection
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) defined as estimated fetal weight (EFW) < 10th percentile for gestational age (GA)
Accurate GA essential for diagnosis
IUGR vs. small for gestational age (SGA)
IUGR: Fetus not reached growth potential
SGA: Fetus is small but normally grown
Difficult to differentiate prenatally
Look at parents and siblings
Symmetric vs. asymmetric IUGR
Symmetric: All biometry equally affected
Often early and severe IUGR
Suggests fetal problem
Possible early placental dysfunction
Asymmetric: “Head sparing” with abdomen, extremities more severely affected
Often presents later in pregnancy
Suggests placental cause
Better prognosis if not severe
Early IUGR vs. late IUGR
Early IUGR more likely fetal cause
Look for anomalies
Consider amniocentesis
Late IUGR more likely placental cause
IUGR differential diagnosis approach
Rule out fetal anomaly as cause for IUGR
Amniocentesis if fetal anomaly suspected
Consider maternal medical history
Assess amniotic fluid
Assess fetal/placental circulation
Doppler
Biophysical profile (BPP)
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Placental Insufficiency
Maternal causes
Hypertension (acute or chronic)
Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus
Thrombophilia
Collagen vascular disease
Drugs/alcohol/smoking
Malnutrition
Uterine-placental causes
Chronic abruption
Infarction
Confined placental mosaicism
Marginal or velamentous cord insertion
Doppler findings
↑ Uterine artery (UtA) resistance with post-systolic notch
↑ Umbilical artery (UA) resistance
↑ Ductus venosus (DV) resistance
↓ Middle cerebral artery (MCA) resistance
Findings in addition to IUGR
Oligohydramnios
Placental sonolucencies
Poor BPP score
Management/treatment
Manage maternal condition
Increased surveillance
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Trisomy 18 (T18)
IUGR in 51% (rarely isolated)
Early onset, symmetric IUGR
Anomalies associated with T18
Cardiac defects
Dandy-Walker continuum
Spina bifida
Omphalocele
Clenched hands + overlapping index finger, rockerbottom feet
Markers associated with T18
Choroid plexus cyst
Single umbilical artery
Umbilical cord cyst
Nuchal thickening
Trisomy 13 (T13)
IUGR in 50% (rarely isolated)
Early onset, with microcephaly
Anomalies associated with T13
Holoprosencephaly, microcephaly
Hypotelorism, cyclopia, proboscis
Dandy-Walker continuum
Polydactyly
Cardiac defects
Gastrointestinal anomalies
Markers associated with T13
Echogenic cardiac focus
Single umbilical artery
Nuchal thickening
Triploidy
69 chromosomes (extra haploid set)
Maternal or paternal extra set
Early severe IUGR is hallmark finding
Asymmetric if maternal extra set
Variable placenta findings according to source of extra set
Thick and cystic (paternal)
Small or normal (maternal)
Ovarian theca lutein cysts
Fetal anomalies often severe but difficult to completely characterize prenatally
Small fetus
Oligohydramnios
Thick cystic placenta displaces fetus
Twin-Twin Transfusion Syndrome
Monochorionic twinning with artery-to-vein anastomoses in placenta
Donor twin partly perfuses recipient twin
Donor twin with IUGR
Oligohydramnios
Abnormal Doppler
Gastroschisis
Bowel herniation through right paramedial abdominal wall defect
50% develop IUGR
Often leads to early delivery
Bowel complications may develop during pregnancy
Dilatation, ischemia, rupture
Single Umbilical Artery
15% of fetuses with an isolated single umbilical artery (SUA) have IUGR
Follow-up for growth into 3rd trimester
Non-isolated SUA
50% aneuploidy rate
T18 most common
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Infection
IUGR and hydrops are early findings
Common infections: Parvovirus, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, varicella
Other findings
Echogenic bowel
Brain, liver, spleen calcifications
Other Essential Information
Late presentation case: Is fetus small or are dates wrong?
Look for lower extremity ossification centers to verify dating
Distal femoral epiphyseal ossification ≥ 32 weeks
Proximal tibial epiphyseal ossification ≥ 35 weeks
Look at fluid and Doppler values
Associated with aneuploidy, syndromes
Amniocentesis warranted
Image Gallery
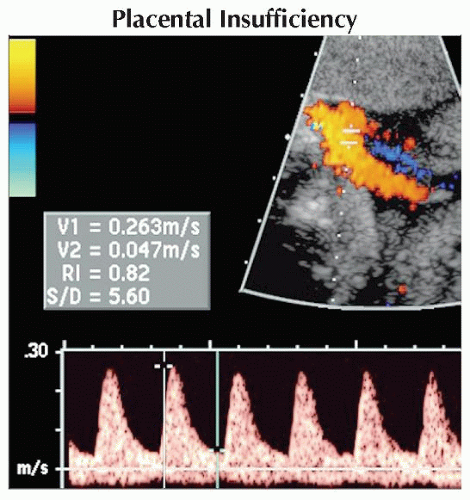 Pulsed Doppler ultrasound of the umbilical artery shows elevated UA resistance in a fetus with third trimester IUGR and oligohydramnios. The systolic/diastolic ratio (S/D) is 5.6 and should be < 3.0.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|