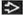Intracranial Cysts: Midline
Anne Kennedy, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
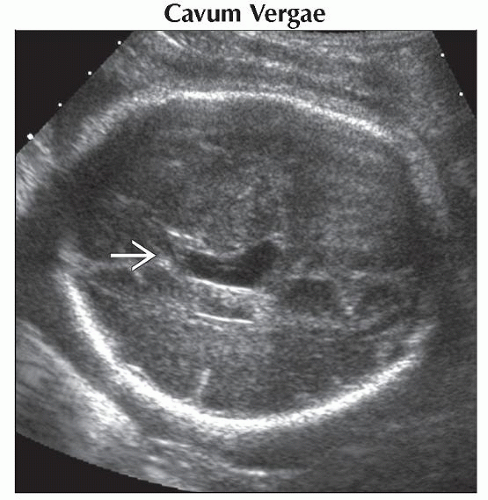
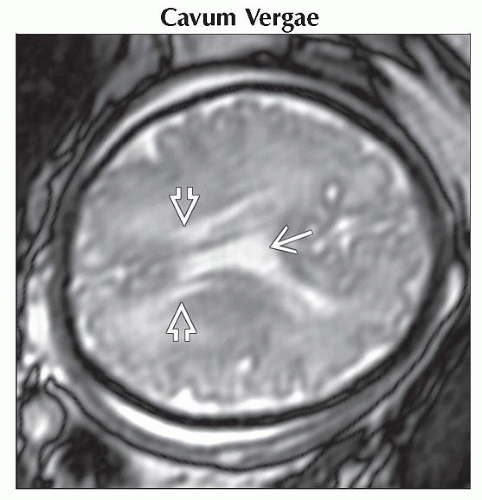
Cavum Vergae
Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum
Dandy-Walker Continuum: Classic
Dandy-Walker Continuum: Variant
Alobar Holoprosencephaly
Semilobar/Lobar Holoprosencephaly
Arachnoid Cyst
Less Common
Glioependymal Cyst
Cystic Teratoma
Syntelencephaly
Rare but Important
Vein of Galen Malformation
Arteriovenous Fistula
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Is it a vascular structure?
Could it be a thrombosed arteriovenous fistula (AVF)?
Where is it?
Supratentorial
Are there 2 separate cerebral hemispheres?
Is the corpus callosum (CC) intact?
Are there any solid components?
Is it simple or multiloculated?
Infratentorial
Is the cerebellar vermis normal?
Is the cyst in continuity with the 4th ventricle?
Is the torcular (confluence of sinuses) elevated?
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Cavum Vergae
Anatomic variant
Cavum vergae is the posterior extension of the cavum septi pellucidi (CSP)
Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum
Absence of CC and high-riding 3rd ventricle create prominent midline cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) space
Associated with midline cysts (usually glioependymal)
Absent CSP
Parallel lateral ventricles
Colpocephaly (tear-drop shaped ventricles)
“Steer horn” or “trident” configuration of frontal horns on coronal view
Abnormal branch pattern of anterior cerebral artery
Stenogyria: Gyri in radial “sunray” distribution in sagittal plane
Dandy-Walker Continuum: Classic
Vermis severely hypoplastic or absent
Cystic dilatation of 4th ventricle
Large posterior fossa with big CSF cyst
4th ventricle appears “open” and contiguous with cyst
Elevation of torcular
Ventriculomegaly may be present
Dandy-Walker Continuum: Variant
Inferior vermis absent/dysplastic
Torcular position normal
Posterior fossa not enlarged
“Keyhole” appearance of 4th ventricle
Alobar Holoprosencephaly
Monoventricle
Absent CSP
Absent falx
Often abnormal facies
Hypotelorism, cyclopia, facial cleft
Proboscis, absent nose, ethmocephaly, cebocephaly
Associated with aneuploidy, particularly trisomy 13
Semilobar/Lobar Holoprosencephaly
Monoventricle anteriorly
Absent CSP
Separation into two lobes posteriorly
May be associated with abnormal facies
Arachnoid Cyst
Extra-axial, avascular, simple
Majority over convexities but may be midline
1/3 in posterior fossa in the fetus
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Glioependymal Cyst
Avascular, may be multiloculated
More commonly midline and associated with agenesis of corpus callosum
Cystic Teratoma
Part cystic, part solid mass
Gross distortion of cerebral architecture
Hydrocephalus
Polyhydramnios
Syntelencephaly
Separate ventricle anteriorly and posteriorly
Parietal gyral continuity
Fusion of ventricles in prefrontal area
Associated with 13q-deletion
Syndactyly
Hypoplastic thumbs
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Vein of Galen Malformation
Elongated tubular midline vascular structure
Aneurysmal dilatation of median prosencephalic vein of Markowski
Located in cistern of velum interpositum and quadrigeminal plate cistern
Look for enlarged neck vessels
Look for cardiomegaly/hydrops from high output state
May cause hydrocephalus
May cause ischemic encephalomalacia
Arteriovenous Fistula
Tubular structures in midline
Look for flow on Doppler
Thrombosed AVF looks hypoechoic, low level internal echoes, occasional echogenic clot within hypoechoic area
Associated with intracranial hemorrhage
Echogenic clot in ventricle
Echogenic ependyma
Associated with ischemic encephalomalacia
Loss of grey white matter differentiation
Ventriculomegaly
Porencephalic cyst
Microcephaly
Other Essential Information
Prognosis varies with etiology
Cavum vergae: No clinical significance
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Prognosis depends on any associated syndromes/brain malformations
Dandy-Walker continuum
Outcome worse for classic malformation
Cognitive outcome depends upon associated syndromes/other brain malformations
Holoprosencephaly spectrum
Alobar: Many die in utero, rare survival beyond neonatal period reported
Semilobar/lobar outcome varies with type and severity of malformation
Developmental delay, seizure disorder, hypothalamic pituitary malfunction and visual impairment all reported
Arachnoid or glioependymal cyst
Prognosis depends on underlying brain malformation
Shunt placement required for obstructive hydrocephalus
Cystic teratoma
Dismal prognosis; 97% mortality if diagnosed before 30 weeks
Vascular malformations
Poor outcome if associated intracranial hemorrhage or ischemic encephalomalacia
Image Gallery
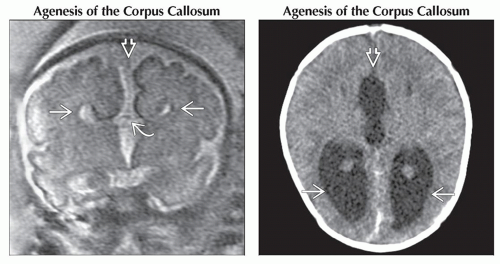 (Left) Coronal T2WI MR shows a “steer horn” configuration of the anterior horns
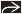 , absence of the corpus callosum , absence of the corpus callosum 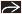 , and increased CSF space between the hemispheres , and increased CSF space between the hemispheres 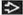 that can be mistaken for a midline cyst. (Right) Axial NECT in a newborn shows colpocephaly that can be mistaken for a midline cyst. (Right) Axial NECT in a newborn shows colpocephaly  , a typical finding in agenesis of the corpus callosum. Note the interhemispheric collection of cerebrospinal fluid , a typical finding in agenesis of the corpus callosum. Note the interhemispheric collection of cerebrospinal fluid 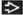 , which can mimic a a midline cyst. , which can mimic a a midline cyst.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|