Intracranial Calcifications
Paula J. Woodward, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Maternal Infection
Cytomegalovirus
Toxoplasmosis
Varicella
Rare but Important
Teratoma
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Significant overlap in imaging findings of in utero infections
Intrahepatic and intracranial calcifications most common findings
Intracranial calcifications may be non-shadowing and subtle
Requires maternal/fetal serologies to make definitive diagnosis
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Cytomegalovirus
Most common congenital infection
Main reservoir is children under < 2 years
Brain most commonly affected area
Calcifications (predominately periventricular), ventriculomegaly, microcephaly
Other findings include intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), hepatosplenomegaly, cardiomyopathy, echogenic bowel and hydrops
Toxoplasmosis
Cats are definitive hosts: Oocyst shed in feces
Human infection from contaminated soil, water, undercooked meats
Non-shadowing intracranial and intrahepatic calcifications
Intracranial calcifications may be periventricular or random in distribution
Other findings include ventriculomegaly, IUGR and echogenic bowel
Varicella
Transplacental infection of fetus following maternal chickenpox infection
Intrahepatic and intracranial calcifications
May also see liver, heart, renal calcifications
Polyhydramnios due to neurologic impairment of swallowing
Limb hypoplasia and contractures
Paradoxical diaphragmatic motion on real time sonography due to unilateral paralysis
Cutaneous lesions in dermatomal distribution seen in neonate
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Teratoma
Most common brain tumor in fetus
Obvious, large, destructive mass with cystic and solid components
Calcification most specific feature but not always present
Image Gallery
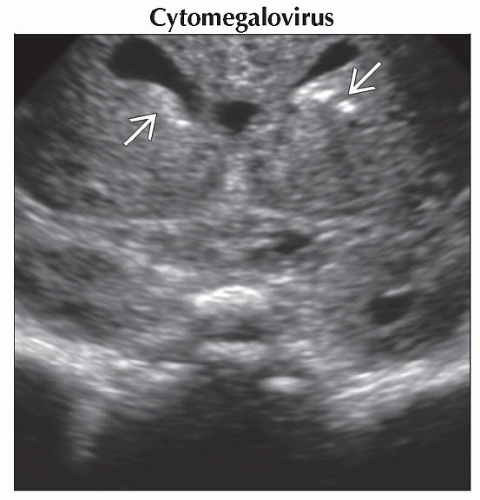 Coronal ultrasound focused on the frontal horns shows periventricular calcifications
 . Only minimal shadowing is seen, which is typical. . Only minimal shadowing is seen, which is typical.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|