10.5 Inborn errors of metabolism
• acute decompensations – at any age, usually triggered by an intercurrent illness or dietary changes
IEM, particularly in those presenting acutely, remain underdiagnosed. Diagnostic clues such as:
are often overlooked or are misinterpreted as being due to a precipitating infection or dehydration. Investigations often have the highest yield during an acute decompensation. Rapid diagnosis and institution of appropriate therapy are essential to avoid death or permanent neurological damage.
• Inborn errors of metabolism, particularly those presenting acutely, remain significantly underdiagnosed.
• Presence of hypoglycaemia, presence or inappropriate absence of ketoacidosis, metabolic or lactic acidosis, or respiratory alkalosis should raise suspicion of a disorder of metabolism.
• In a child presenting acutely with a metabolic acidosis or hypoglycaemia, it is essential that the first urine passed is analysed for organic acids, as the diagnostic metabolites can clear quickly once intravenous glucose is given.
• Plasma ammonium values increase markedly if the specimen is allowed to sit around – collect the sample on ice and analyse it quickly.
• Abnormal liver function tests are not always indicative of hepatic pathology; for example, increased levels of aspartate and alanine aminotransferase (AST and ALT) occur in muscle disease also warranting the need to check creatine kinase levels.
• Pan-hypopituitarism can present in the neonatal period with hypoglycaemia plus conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia.
Acute metabolic decompensation
Neonatal presentations
The following can act as clues to prompt consideration of an IEM in an acutely unwell neonate:
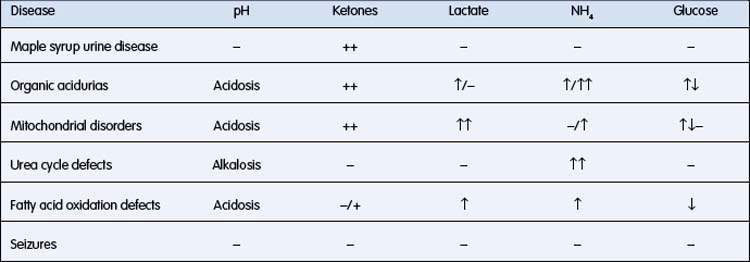
• Specific pattern of biochemical derangements (Table 10.5.1). (Note that ketosis in a neonate is always abnormal and must prompt consideration of an IEM)
• Multisystem organ involvement
• Specific end-organ involvement
• Family history of neonatal deaths or sudden infant death syndrome
Hypoglycaemia
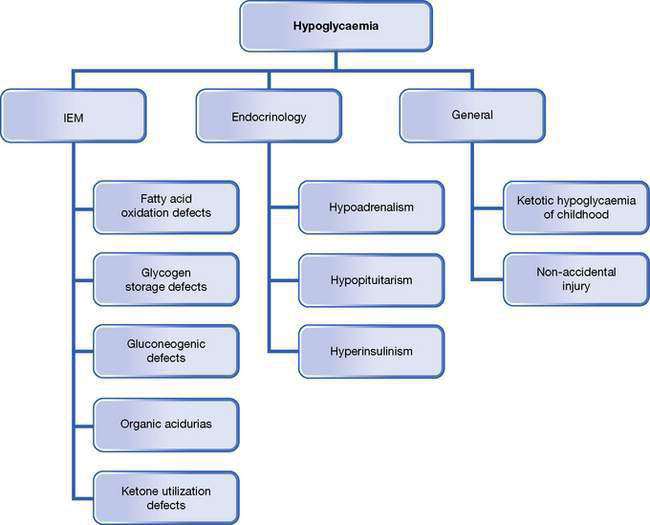
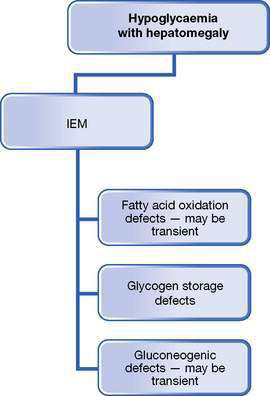
Hypoglycaemia is a common issue in general paediatrics; it is always abnormal in children, and must be investigated and managed promptly. See Figures 10.5.1–10.5.3 for an overview of the practical approaches to refining a differential diagnosis of hypoglycaemia and an investigation pathway and the Practical points box on hypoglycaemia, below.
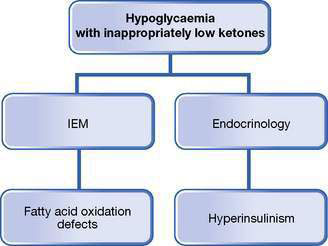
Fig. 10.5.3 Differential diagnoses of hypoglycaemia associated with inappropriately low ketone levels.
Tests to be collected at the time of hypoglycaemia are: