Heterotaxia Syndromes
Eva Ilse Rubio, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Total Situs Inversus
Less Common
Left-Sided Isomerism
Right-Sided Isomerism
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Total Situs Inversus
All nonsymmetric organs (cardiac structures, lungs, liver, spleen, stomach) are exactly reversed from normal
Estimated occurrence = .01% of general population
Risk of congenital heart disease slightly more common than general population
May be seen in Kartagener syndrome
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Left-Sided Isomerism
Slightly more common in females
Significantly better prognosis
Cardiac findings
Less severe cardiac disease with normal to increased pulmonary vascularity; usually noncyanotic
Common: Interrupted inferior vena cava, bilateral functional left atria, septal defects
May have bilateral superior vena cavae
Pulmonary findings
Bilateral bi-lobed lungs
Both main bronchi lie under pulmonary arteries
Intraabdominal findings
Midline or left-sided liver; may have absent gallbladder
Indeterminate/variable stomach position, may be in right upper quadrant
Multiple spleens (which may be located right, left, or centrally within abdomen)
Malrotation may be present
Right-Sided Isomerism
Slightly more common in males
More dire prognosis
Cardiac findings
More severe cardiac disease with normal to decreased pulmonary vascularity; often cyanotic
Common: Anomalous pulmonary venous return, bilateral functional right atria, atrioventricular canal defects, pulmonary outflow tract obstruction, single ventricle
May have bilateral superior vena cavae
Pulmonary findings
Bilateral tri-lobed lungs
Both main bronchi course over pulmonary arteries
Intraabdominal findings
Midline liver
Indeterminate/variable stomach position
Absent spleen
Malrotation common
Image Gallery
 AP radiograph shows dextrocardia
 , the stomach in the right upper quadrant , the stomach in the right upper quadrant  , the liver in the left upper quadrant , the liver in the left upper quadrant  , and a right aortic arch displacing the trachea leftward , and a right aortic arch displacing the trachea leftward 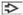 . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|