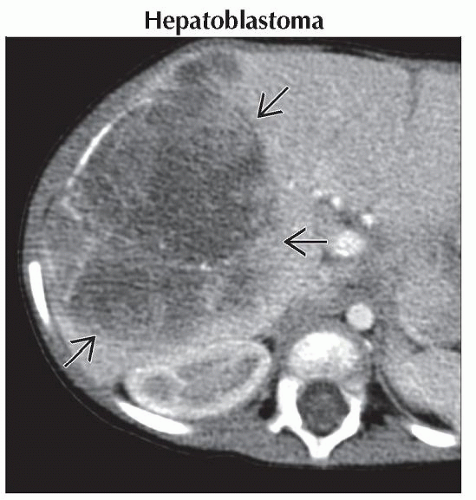
Hepatic Mass in a Child
Alexander J. Towbin, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Hepatoblastoma
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hemangioendothelioma
Less Common
Abscess
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
Metastases
Rare but Important
Choledochal Cyst
Mesenchymal Hamartoma
Embryonal Sarcoma
Hepatic Adenoma
Angiomyolipoma (AML)
Nodular Regenerative Hyperplasia
Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Biliary Rhabdomyosarcoma
Angiosarcoma
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Primary hepatic neoplasms uncommon in children
0.5-2% of all pediatric neoplasms
2/3 malignant
Differential diagnosis can be focused by age
Biopsy often needed for diagnosis
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Hepatoblastoma
Most common pediatric liver malignancy
1% of all pediatric malignancies
79% of all liver malignancies < 15 years of age
Majority diagnosed under 18 months
More common in boys
Associated with low birth weight, hemihypertrophy, Beckwith-Wiedemann, familial adenomatous polyposis, trisomy 18, and fetal alcohol syndrome
Often presents as asymptomatic mass
90% have increased serum AFP
Most common in right lobe of liver, bilateral in 35%
Calcifications occur in 40-55%
Distant metastases in 20% at diagnosis
Lung most common, followed by brain and bone
Staged via PRETEXT staging system
Treatment via resection
Contraindications: Extensive bilateral disease, vascular invasion, or distant metastases
75% 5-year survival rate
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
2nd most common liver malignancy in children
Rare before age 5
More common in males
˜ 75% not associated with liver disease
Risk factors: Preexisting cirrhosis due to biliary atresia, Fanconi syndrome, viral hepatitis, or glycogen storage disease
Other risks: Androgen steroids, oral contraceptives, methotrexate
Metastases common at diagnosis
Regional lymph nodes, lungs, bone
Elevated AFP in 60-80%
Staged via PRETEXT system
Poor long-term survival
Hemangioendothelioma
a.k.a. infantile hemangioendothelioma
Most common benign hepatic tumor
85% diagnosed in 1st 6 months
Often asymptomatic in childhood
Skin hemangiomas present in ˜ 50%
Hint: High-output heart failure + liver tumor
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Abscess
Associated with bacteremia, parasites, and chronic granulomatous disease
Can be seen with inflammatory process involving bowel
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
Occurs in all age groups
Well-circumscribed lobulated lesion with central stellate scar
More common in females and in patients who have received chemotherapy
Metastases
Neuroblastoma and Wilms most common
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Choledochal Cyst
Cystic or fusiform dilation of biliary tree
Todani classification with 5 types
Type 1 most common
Associated with ductal and vascular anomalies
Anomalous hepatic arteries, accessory ducts, and primary duct strictures
Ultrasound is best screening test
Treated with excision due to risk of malignant degeneration
Mesenchymal Hamartoma
2nd most common benign hepatic tumor of childhood
6-8% of pediatric hepatic neoplasms
85% present before age 3
Often present as large RUQ mass
75% in right lobe
AFP can be elevated
Multiloculated cystic mass
Tiny cysts can give solid appearance
On US, septae of cysts may be mobile
Large portal vein branch may feed mass
Calcification uncommon
Associated with congenital heart disease, malrotation, esophageal atresia, annular pancreas, biliary atresia, and exomphalos
Also associated with myelomeningocele and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Rare malignant degeneration to undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma
Treatment via excision
Embryonal Sarcoma
a.k.a. undifferentiated sarcoma
Accounts for 9-15% of all hepatic tumors
3rd most common malignant hepatic tumor in children
Usually occurs between 6-10 years of age
On US, appears as solid mass with cystic areas
On CT, appears hypodense with septations and fibrous pseudocapsule
Case reports of spontaneous rupture
4-year survival: 70-83%
Hepatic Adenoma
Most common in young women
↑ risk with oral contraceptive or anabolic steroid use
Angiomyolipoma (AML)
Associated with tuberous sclerosis
Less common than renal AML
Nodular Regenerative Hyperplasia
Multi-acinar regenerative lesion of liver
Associated with systemic diseases
1/2 of patients have portal hypertension
Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Occurs in adolescents, young adults
Calcifications seen in 35-68%
Central scar present in 20-71%
Low signal on all MR pulse sequences
Dismal prognosis if not resectable
Biliary Rhabdomyosarcoma
Accounts for 0.5% of rhabdomyosarcomas
Intraductal mass on CT or MR
Angiosarcoma
a.k.a. hemangioendothelioma, type 2
M:F = 1:2
Mean age: 3-4 years
Resembles hemangioendothelioma
Tumor usually involves both lobes
Metastases to lungs, nodes, pleura, bones, and adrenals
Image Gallery
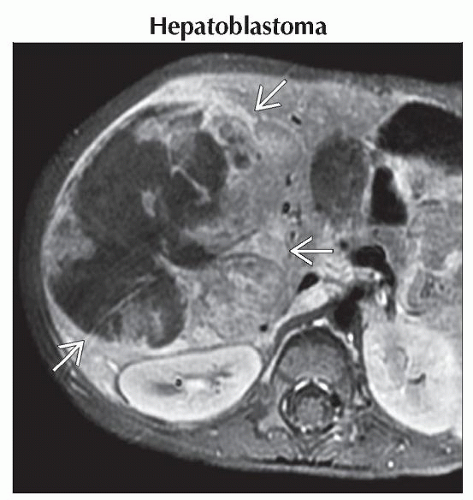 Axial T1WI C+ FS MR in the same patient shows a large mass
 in the right lobe of the liver. The mass is heterogeneous with a large central area that is hypointense to the rest of the liver. in the right lobe of the liver. The mass is heterogeneous with a large central area that is hypointense to the rest of the liver.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|