CHAPTER 26 shortening of the bones of the hands or feet. crescent shape to the cerebellum displayed with a coexisting neural tube defect. protrusion or bulging of the forehead associated with hydrocephalus. overt enlargement of the lateral ventricles secondary to an increase in intracranial pressure. abnormally widespread position of the orbits. abnormally close position of the orbits. appearance of the dilated bladder superior to the obstructed male urethra. concavity to the front bones of the fetal cranium; associated with spina bifida. shortening of the middle portion of a limb. shortening of all portions of a limb. distance between the calvaria and posterior skin line. protrusion of nasal tissue above the orbits shortening of the proximal portion of a limb. ventricular enlargement characterized by excessive cerebrospinal fluid within the ventricles. structure located between the hemispheres of the cerebellum.
Fetal abnormalities
ABNORMALITY
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Acrania
Abnormal migration of mesenchymal tissues
Skull is absent
Brain is present
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein levels
Coexisting spinal defects, clubfoot, cleft lip and palate
Lack of hyperechoic bony calvaria
Brain tissue development
Prominent sulcal markings
Anencephaly
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Failure of callosal fibers to form a normal connection
May be partial or complete
Associated with multiple anomalies
Dilation of the third ventricle
Outward angling of the frontal and lateral horns (steer sign)
Dilation of the occipital horn
Absent cavum septum pellucidi
Holoprosencephaly
Arachnoid cyst
Congenital abnormality of the pia-arachnoid layer
A result of trauma, infarction, or infection
Splaying of cerebellum hemispheres
Normal vermis
Dandy-Walker cyst
Prominent cisterna magna
Vein of Galen aneurysm
Improper technique
Arnold Chiari Type II malformation
Displacement of the cerebellar vermis, fourth ventricle, medulla oblongata through foramen of magna into the upper cervical canal
Compressed shape to the cerebellum (banana sign)
Obliteration of the cisterna magna
Ventriculomegaly
Lemon-shaped cranium
Spina bifida
Dandy-Walker syndrome
Congenital malformation of the cerebellum with associated maldevelopment of the fourth ventricle
Result of alcohol abuse, autosomal recessive disorder, or viral infection
Enlarged posterior fossa
Splaying of the cerebellar hemispheres
Complete or partial agenesis of the vermis
Cisterna magna >1.0 cm in diameter
Ventriculomegaly
Prominent posterior fossa
Arachnoid cyst
Vein of Galen aneurysm
Artifact
Hydranencephaly
Destruction of the cerebral cortex resulting from vascular compromise or congenital infection (usually carotid area)
Brain tissue is replaced by cerebrospinal fluid
Anechoic brain tissue
Not associated with other abnormalities
Presence of the falx cerebri
Brain stem usually spared
Choroid plexus may be displayed
Variable presence of the third ventricle
Severe hydrocephalus
Holoprosencephaly
Hydrocephalus (ventriculomegaly)
Increase in ventricular volume caused by outflow obstruction, decrease in cerebrospinal fluid (CSP) production, or overproduction of CSP
Occipital horn dilates first
Ventriculomegaly is generally symmetrical
Mild Enlargement
Lateral ventricle measuring 10-15 mm
Severe Enlargement
Lateral ventricle measuring >15 mm
Dangling of the choroid plexus
Echogenic rim of solid brain tissue
Hydranencephaly
Holoprosencephaly
Improper technique
Holoprosencephaly
Group of disorders arising from abnormal development of the forebrain
Strongly associated with Trisomy 13
Alobar
Monoventricular cavity
Most severe form
Semilobar
Monoventricular cavity
Milder form
Lobar
Two large lateral ventricles
Mildest form
Alobar
Large central single ventricle
Fused thalami
Absence of cavum septum pellucidi, falx cerebri, corpus callosum, and third ventricle
Normal cerebellum
Hypotelorism
Cyclopia
Proboscis
Semilobar
Large central single ventricle
Occipital and temporal horns may be present
Variable development of the falx
Associated with cleft lip and palate
Lobar
Two large lateral ventricles
Absent cavum septum pellucid, and cavum callosum
Severe hydrocephalus
Hydranencephaly
Lemon shape
May be a normal finding
Associated with spina bifida
Bilateral indentation of the frontal bones
Dolichocephaly
Microcephaly
Overall reduction in brain size
Chromosomal aberration
Intrauterine infection
Difficult to detect before 24 wks
Small biparietal diameter (BPD) and head circumference (HC)
Decreased HC/abdominal circumference (AC) ratio
Sloping forehead
Anencephaly
Encephalocele
Prosencephaly
A result of infarction or hemorrhage of the brain
Anechoic mass within an area of brain tissue
Midline brain shift
Cystic leukomalacia
Strawberry shape
Associated with Trisomy 18
Flattened occiput diameter and narrowing of the frontal portion of the skull
Brachycephaly
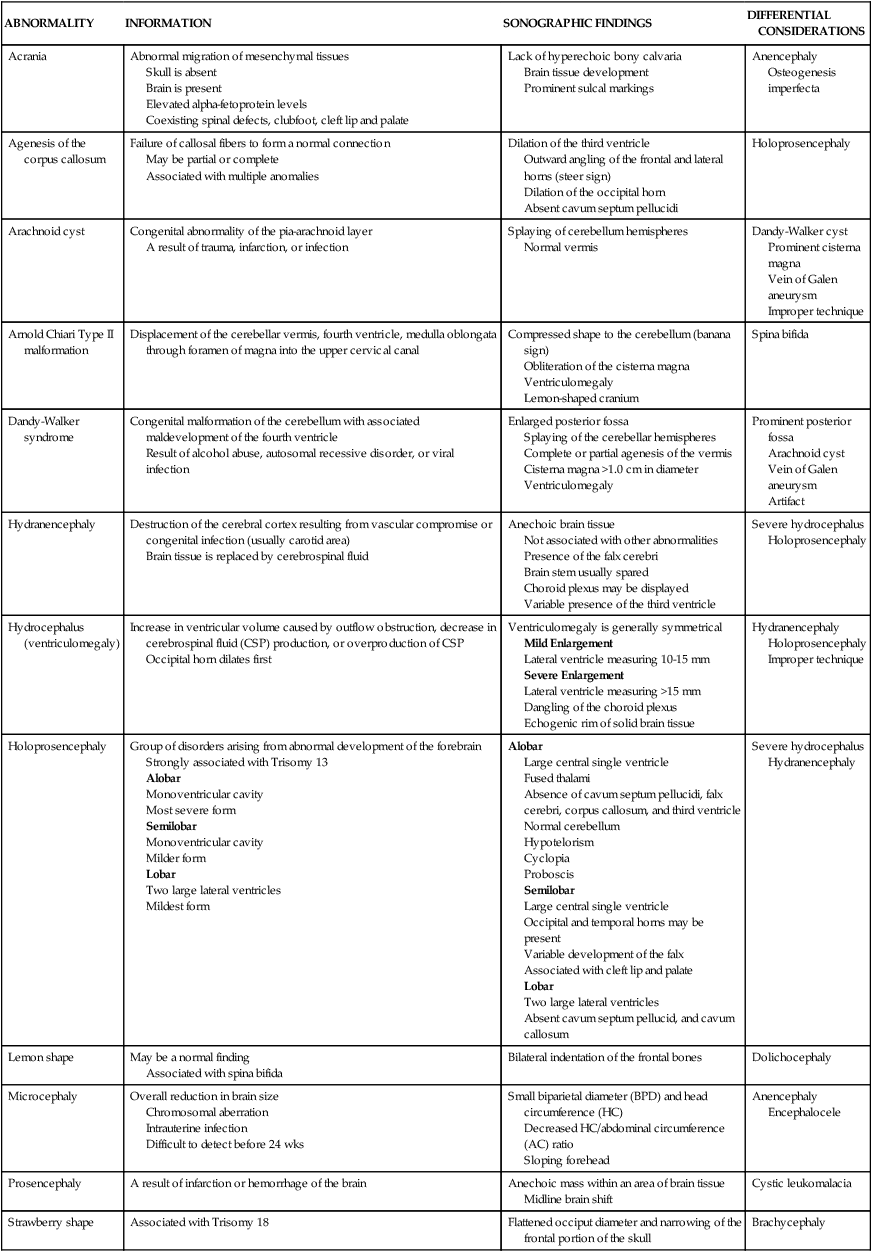
DEFECT
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Anencephaly
Failure of the cephalic end of the neural tube to close completely
Portions of the midbrain and brain stem may be present.
Most common neural tube defect
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels
Associated with malformations of the spine, face, feet, and abdominal wall
Absence of the cranial vault
Bulging eyes (froglike face)
Rudimentary brain tissue herniating from the defect
Macroglossia
Polyhydramnios
Increase in fetal activity
Severe microcephaly
Acrania
Encephalocele
Amniotic band syndrome
Caudal regression
Structural abnormality of the caudal end of the neural tube
More common in patients with diabetes
Associated with genitourinary, gastrointestinal, and cardiovascular abnormalities
Absent sacrum
Fused pelvis
Short femurs
Skeletal dysplasia
Encephalocele
Normal AFP level
Presence of brain in a cranial protrusion
More commonly arises in the occipital region
Spherical fluid-filled or brain-filled sac extending from the calvaria
Bony calvarial defect
Cystic hygroma
Cloverleaf skull deformity
Amniotic band syndrome
Microcephaly
Spina bifida
Failure of the neural tube to close completely
Occulta
Defect is covered by normal soft tissue
Normal AFP level
Rarely diagnosed with ultrasound
Aperta
Defect is uncovered
Elevated AFP level
Associated with cleft lip and palate, cardiac defects, encephalocele, gastrointestinal anomalies, and clubfoot
Coronal
Disappearance of the middle hyperechoic line
Widening of the external hyperechoic lines
Sagittal
Posterior hyperechoic line and overlying soft tissues are absent
Transverse
Outward splaying of the lateral posterior ossification centers into a “U” or “V” shape
Cystic or complex mass protruding from spinal defect
Cerebellum takes on a crescent shape (banana sign)
Frontal bones are concave (lemon shaped)
Sacrococcygeal teratoma
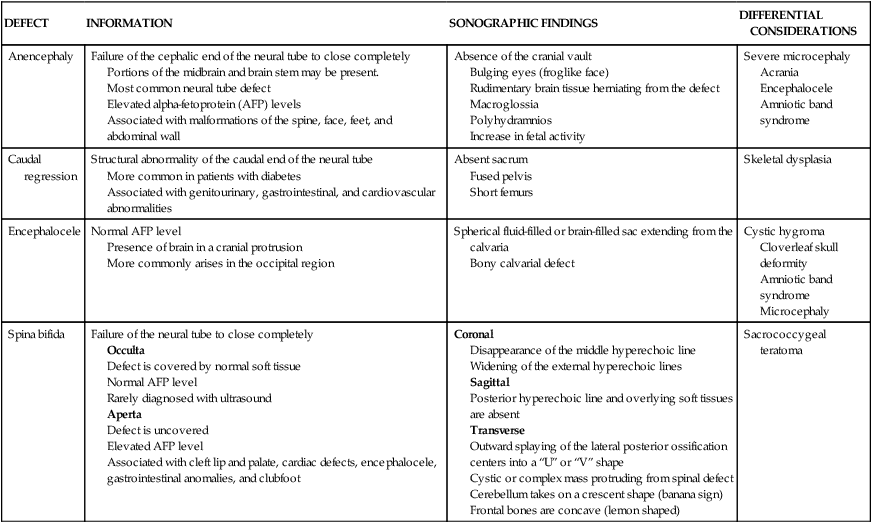
ABNORMALITY
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Anophthalmia
Lack of fusion of the maxillary prominences with the nasal prominence on one or both sides
Failure of the optic vesicle to form
Absence of the globe or often the orbit
Poor fetal position
Technical error
Cyclopia
Midline fusion of the orbits
Associated with holoprosencephaly, Trisomy 13, microcephaly, Williams syndrome
Single midline orbit
Poor fetal position
Technical error
Facial cleft
Defect of the upper lip
Most common facial abnormality
Anechoic defect between the upper lip and nostrils
Polyhydramnios
Small stomach
Technical error
Hypotelorism
Orbits placed closer together than expected
Abnormally small interocular distance for gestational age
Poor fetal position
Technical error
Hypertelorism
Orbits placed wider apart than expected
Associated with Trisomy 18, Noonan syndrome, Median cleft syndrome, craniosynostosis, and anterior cephalocele
Abnormally wide interocular distance for gestational age
Poor fetal position
Technical error
Macroglossia
Associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann and Down syndromes
Persistent protrusion of the tongue
Persistent protrusion of the fetal tongue
Polyhydramnios
Normal tongue
Umbilical cord
Micrognathia
Hypoplastic mandible
Associated with Trisomy 18
Small receding chin and lower lip
Polyhydramnios
Protrusion of the upper lip
Technical error
Normal chin
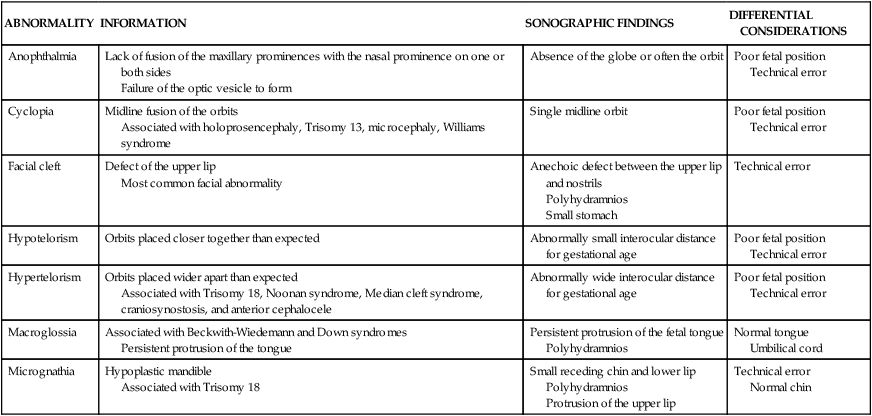
ABNORMALITY
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Cystic hygroma
Developmental defect of the lymphatic system
Associated with chromosomal abnormalities, fetal hydrops, and fetal heart failure
Multilocular anechoic cervical mass
Thin surrounding membrane
No cranial defect
Continuous with abnormal skin and subcutaneous tissues
Encephalocele
Cystic teratoma
Normal umbilical cord
Thyroglossal cyst
Nuchal edema
Nuchal edema
Thickening of the nuchal fold
Associated with chromosomal abnormalities
Anechoic posterior cervical mass
Midline septum
Cystic hygroma
ABNORMALITY
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Cystic adenomatoid malformation
Abnormal formation of the bronchial tree
Replacement of normal pulmonary tissues with cysts
May be associated with renal or gastrointestinal abnormalities
Simple or multiloculated cystic chest mass
Mediastinal shift
Diaphragm is visible and intact
Fetal hydrops
Polyhydramnios
Usually unilateral
Diaphragmatic hernia
Pleural effusion
Pericardial fluid
Ectopia cordis
Partial or complete displacement of the heart outside of the thorax
Small thorax
Heart located outside of the thorax
Extrathoracic pulsating mass
Acardiac twin
Diaphragmatic hernia
Ebstein anomaly
Displacement of the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valves into the right ventricle
Variable in degree
Four-chamber heart
Enlargement of the heart (especially right atrium)
Regurgitation across the tricuspid valve with Color and Spectral Doppler
Tetralogy of Fallot
Ventricular septal defect
Diaphragmatic hernia
Diaphragm fails to close allowing herniation of the abdominal cavity
Associated with cardiac, renal, chromosomal, and central nervous system anomalies
Stomach or liver located in the thorax
Inability to visualize normal diaphragm
Mediastinal shift
Small abdominal circumference
Polyhydramnios
Usually unilateral
Left-sided defect more common
Cystic adenomatoid malformation
Pleural effusion
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
