Chapter 591 Encephalopathies
Encephalopathy is a generalized disorder of cerebral function that may be acute or chronic, progressive or static. The etiologies of the encephalopathies in children include infectious, toxic (carbon monoxide, drugs, lead), metabolic, genetic and ischemic causes. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is discussed in Chapter 93.5.
591.1 Cerebral Palsy
See Chapters 33 and 91.2.
Clinical Manifestations
CP is generally divided into several major motor syndromes that differ according to the pattern of neurologic involvement, neuropathology, and etiology (Table 591-1). The physiologic classification identifies the major motor abnormality, whereas the topographic taxonomy indicates the involved extremities. CP is also commonly associated with a spectrum of developmental disabilities, including mental retardation, epilepsy, and visual, hearing, speech, cognitive, and behavioral abnormalities. The motor handicap may be the least of the child’s problems.
Table 591-1 CLASSIFICATION OF CEREBRAL PALSY AND MAJOR CAUSES
| MOTOR SYNDROME (APPROX % OF CP) | NEUROPATHOLOGY/MRI | MAJOR CAUSES |
|---|---|---|
| Spastic diplegia (35%) | Periventricular leukomalacia Periventricular cysts or scars in White matter, enlargement of ventricles, squared of posterior ventricles | Prematurity |
| Ischemia | ||
| Infection | ||
| Endocrine/metabolic (e.g., thyroid) | ||
| Spastic quadriplegia (20%) | Periventricular leukomalacia | Ischemia, infection |
| Multicystic encephalomalacia Cortical malformations | Endocrine/metabolic, genetic/developmental | |
| Hemiplegia (25%) | Stroke: in utero or neonatal Focal infarct or cortical, subcortical damage Cortical malformations | Thrombophilic disorders |
| Infection | ||
| Genetic/developmental | ||
| Periventricular hemorrhagic infarction | ||
| Extrapyramidal (athetoid, dyskinetic) (15%) | Asphyxia: symmetric scars in putamen and thalamus Kernicterus: scars in globus pallidus, hippocampus Mitochondrial: scaring globus pallidus, caudate, putamen, brainstem No lesions: ? dopa-responsive dystonia | Asphyxia |
| Kernicterus | ||
| Mitochondrial | ||
| Genetic/metabolic |
Infants with spastic hemiplegia have decreased spontaneous movements on the affected side and show hand preference at a very early age. The arm is often more involved than the leg and difficulty in hand manipulation is obvious by 1 yr of age. Walking is usually delayed until 18-24 mo, and a circumductive gait is apparent. Examination of the extremities may show growth arrest, particularly in the hand and thumbnail, especially if the contralateral parietal lobe is abnormal, because extremity growth is influenced by this area of the brain. Spasticity refers to the quality of increased muscle tone which increases with the speed of passive muscle stretching and is greatest in antigravity muscles. It is apparent in the affected extremities, particularly at the ankle, causing an equinovarus deformity of the foot. An affected child often walks on tiptoe because of the increased tone in the antigravity gastrocnemius muscles, and the affected upper extremity assumes a flexed posture when the child runs. Ankle clonus and a Babinski sign may be present, the deep tendon reflexes are increased, and weakness of the hand and foot dorsiflexors is evident. About one third of patients with spastic hemiplegia have a seizure disorder that usually develops in the 1st yr or 2; approximately 25% have cognitive abnormalities including mental retardation. MRI is far more sensitive than CT for most lesions seen with CP, although a CT scan may be useful for detecting calcifications associated with congenital infections. In the European CP study, 34% of children with hemiplegia had injury to the white matter that probably dated to the in utero period and 27% had a focal lesion that may have resulted from a stroke. Other children with hemiplegic CP had had malformations from multiple causes including infections (e.g., cytomegalovirus), lissencephaly, polymicrogyria, schizencephaly, or cortical dysplasia. Focal cerebral infarction (stroke) secondary to intrauterine or perinatal thromboembolism related to thrombophilic disorders, like the presence of anticardiolipin antibodies, is an important cause of hemiplegic CP (Chapter 594). Family histories suggestive of thrombosis and inherited clotting disorders, such as factor V Leiden mutation, may be present and evaluation of the mother may provide information valuable for future pregnancies and other family members.
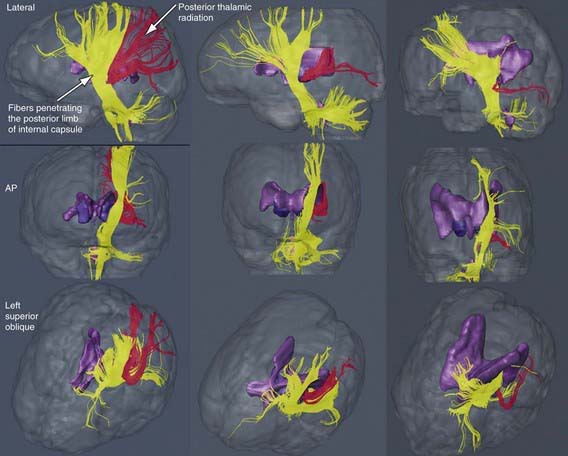
The most common neuropathologic finding in children with spastic diplegia is PVL, which is visualized on MRI in more than 70% of cases. MRI typically shows scarring and shrinkage in the periventricular white matter with compensatory enlargement of the cerebral ventricles. However, neuropathology has also demonstrated a reduction in oligodendroglia in more widespread subcortical regions beyond the periventricular zones, and these subcortical lesions may contribute to the learning problems these patients can have. MRI with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is being used to map white matter tracks more precisely in patients with spastic diplegia, and this technique has shown that thalamocortical sensory pathways are often injured as severely as motor corticospinal pathways (Fig 591-1). These observations have led to greater interest in the importance of sensory deficits in these patients, which may be important for designing rehabilitative techniques.