18 Differential Diagnosis and Strategy Common diagnoses. Focal adenosis, adenoma/fibroadenoma, papilloma. Rare diagnoses. Lobulus, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), invasive carcinoma, intramammary lymph node, phyllodes tumor. Strategy. See Table 18.1. TABLE 18.1 Diagnostic work-up strategy for solitary focus
Solitary Focus
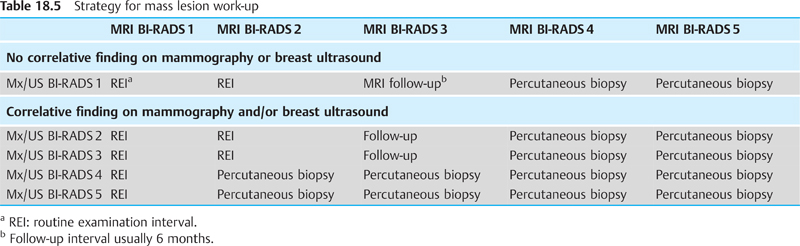
 A solitary focus on breast MRI should preferably be followed up after 6 months. The risk of this lesion being malignant is somewhat higher than that of multiple foci. Should this focus be a malignant lesion, the expected lesion size after 6 months is maximally 5–6 mm. The initial performance of an MRI-guided vacuum-assisted biopsy (VAB) can and should be avoided.
A solitary focus on breast MRI should preferably be followed up after 6 months. The risk of this lesion being malignant is somewhat higher than that of multiple foci. Should this focus be a malignant lesion, the expected lesion size after 6 months is maximally 5–6 mm. The initial performance of an MRI-guided vacuum-assisted biopsy (VAB) can and should be avoided.
Strategy: No correlative finding on mammography or breast ultrasound | |
Mx/US BI-RADS1 | MRI follow-upa (Figs. 18.1, 18.2, 18.3). |
Strategy: Correlative finding on mammography and/or breast ultrasoundb | |
Mx/US BI-RADS2 | Mx or US follow-upa |
Mx/US BI-RADS3 | Mx or US follow-upa |
Mx/US BI-RADS 4 | Percutaneous biopsy (US-CB or Mx-VAB) |
Mx/US BI-RADS 5 | Percutaneous biopsy (US-CB or Mx-VAB) |
a Follow-up interval usually 6 months.
b Small lesions often not found on second-look US.
Mx: x-ray mammography.
US: ultrasonography.
US-CB: US-guided core biopsy.
Mx-VAB: stereotactic vacuum-assisted biopsy.
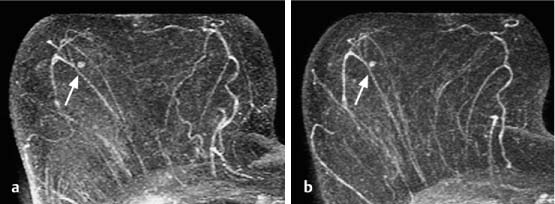
Fig. 18.1a, b Solitary focus. No change at follow-up breast MRI examination 6 months after detection.
a Subtraction slice image: initial detection of solitary focus in the right breast (arrow).
b Subtraction slice image (follow-up 6 months later): no progression (arrow).
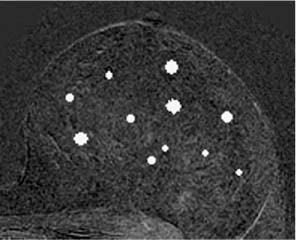
Fig. 18.2a, b Solitary focus. Size increase at follow-up breast MRI examination 6 months after detection.
a Subtraction slice image: initial detection of solitary focus in the left breast (arrow).
b Subtraction slice image (follow-up 6 months later): progression with focus size increase from 3 mm to 5 mm in diameter (arrow).
Histology: fibroadenoma (B2).
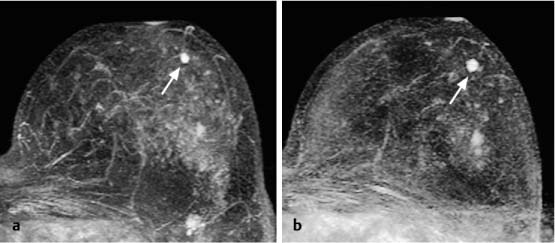
Fig. 18.3a, b Solitary focus. Size increase at follow-up breast MRI examination 6 months after detection.
a Subtraction slice image: initial detection of solitary focus in the left breast (arrow).
b Subtraction slice image (follow-up 6 months later): progression with focus size increase from 3 mm to 6 mm in diameter (arrow).
Histology: invasive ductal carcinoma (B5b).
Multiple Foci
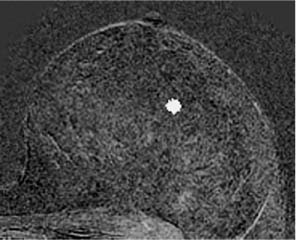
Common diagnoses. Lobuli (physiological enhancement), adenosis, adenomas/fibroadenomas.
Rare diagnoses. Papillomas, DCIS, invasive carcinoma (one of the multiple foci), multiple carcinomas, intramammary metastases.
Strategy. See Table 18.2.
 Multiple foci on breast MRI should preferably be followed up in the normal early breast cancer detection interval of 1 year. Should one of these foci be a malignant lesion, the expected lesion size after 12 months is maximally 8–10 mm. The initial performance of an MRI-guided VAB is not expedient because “one will always biopsy the wrong focus.”
Multiple foci on breast MRI should preferably be followed up in the normal early breast cancer detection interval of 1 year. Should one of these foci be a malignant lesion, the expected lesion size after 12 months is maximally 8–10 mm. The initial performance of an MRI-guided VAB is not expedient because “one will always biopsy the wrong focus.”
TABLE 18.2 Diagnostic work-up strategy for multiple foci
Strategy: No correlative finding on mammography or breast ultrasound | |
Mx/US BI-RADS1 | Examination at routine intervals (Figs. 18.4, 18.5, 18.6). |
Strategy: Correlative finding on mammography and/or breast ultrasound | |
Mx/US BI-RADS2 | Examination at routine intervals |
Mx/US BI-RADS3 | Mx or US follow-upa |
Mx/US BI-RADS 4 | Percutaneous biopsy (US-CB or Mx-VAB) |
Mx/US BI-RADS 5 | Percutaneous biopsy (US-CB or Mx-VAB) |
a Follow-up interval usually 6 months.
Mx: x-ray mammography. US: ultrasonography. US-CB: US-guided core biopsy. Mx-VAB: stereotactic vacuum-assisted biopsy.
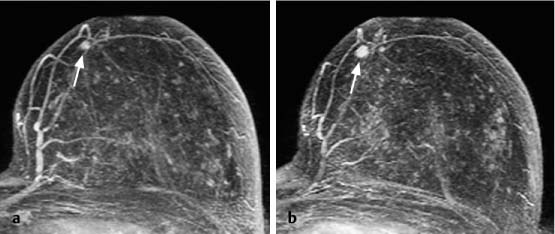
Fig. 18.4 Multiple foci. Subtraction MIP. The image is typical for physiological enhancement of lobuli.
Fig. 18.6 Multiple foci. Subtraction MIP. In follow-up breast MRI 16 months later the most prominent focus (arrow) showed progression.
Histology confirmed a DCIS (B5a).
Mass Lesion
Common diagnoses. Adenoma/fibroadenoma, adenosis, tumorforming adenosis, carcinoma, papilloma.
Rare diagnoses. Phyllodes tumor, hamartoma, granuloma, angiomatous hyperplasia, fibrosis, intramammary lymph node.
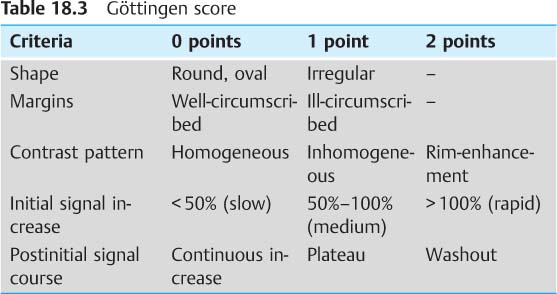
 The Göttingen score is useful for the evaluation of a hypervascularized breast MRI lesion and allows its assignment to one of the five MRI BI-RADS categories (Tables 18.3, 18.4).
The Göttingen score is useful for the evaluation of a hypervascularized breast MRI lesion and allows its assignment to one of the five MRI BI-RADS categories (Tables 18.3, 18.4).
Strategy. See Table 18.5.
Mass Lesion—Differential Diagnosis
Rim-Enhancement (Figs. 18.7, 18.8, 18.9, 18.10)