Chapter 409 Chylothorax
Etiology
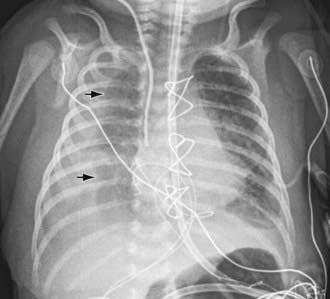
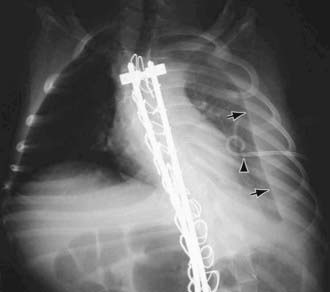
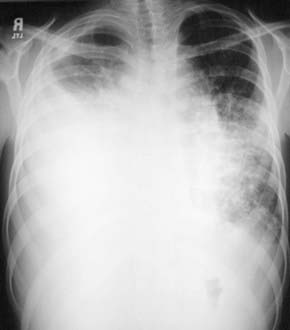
Chylothorax in children occurs most frequently because of thoracic duct injury as a complication of cardiothoracic surgery (Fig. 409-1). Other cases are associated with chest injury (Fig. 409-2) or with primary or metastatic intrathoracic malignancy (Fig. 409-3), particularly lymphoma. In newborns, rapidly increased venous pressure during delivery may lead to thoracic duct rupture. Less common causes include lymphangiomatosis; restrictive pulmonary diseases; thrombosis of the duct, superior vena cava, or subclavian vein; tuberculosis or histoplasmosis; and congenital anomalies of the lymphatic system (Fig. 409-4). Refractory chylothorax in the fetus has been associated with a missense mutation in integrin aα9. Chylothorax can occur in trauma and child abuse (Chapter 37). It is important to establish the etiology, because treatment varies with the cause. In some patients, no specific cause is identified.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree