Chapter 138 Childhood Asthma
Etiology
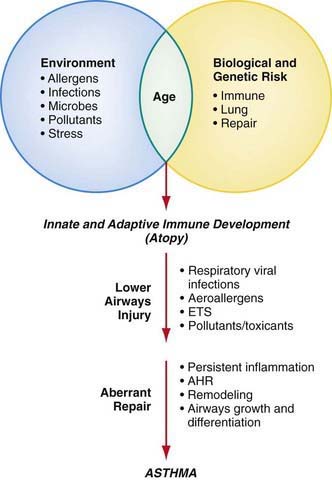
Although the cause of childhood asthma has not been determined, contemporary research implicates a combination of environmental exposures and inherent biologic and genetic vulnerabilities (Fig. 138-1). Respiratory exposures in this causal environment include inhaled allergens, respiratory viral infections, and chemical and biologic air pollutants such as environmental tobacco smoke. In the predisposed host, immune responses to these common exposures can be a stimulus for prolonged, pathogenic inflammation and aberrant repair of injured airways tissues. Lung dysfunction (i.e., AHR and reduced airflow) develops. These pathogenic processes in the growing lung during early life adversely affect airways growth and differentiation, leading to altered airways at mature ages. Once asthma has developed, ongoing exposures appear to worsen it, driving disease persistence and increasing the risk of severe exacerbations.
Epidemiology
Approximately 80% of all asthmatic patients report disease onset prior to 6 yr of age. However, of all young children who experience recurrent wheezing, only a minority go on to have persistent asthma in later childhood. Early childhood risk factors for persistent asthma have been identified (Table 138-1). Prediction of asthma includes major (parent asthma, eczema, inhalant allergen sensitization) and minor (allergic rhinitis, wheezing apart from colds, ≥4% eosinophils, food allergen sensitization) risk factors. Allergy in young children has emerged as a major risk factor for the persistence of childhood asthma.
Types of Childhood Asthma
Asthma is considered to be a common clinical presentation of intermittent, recurrent wheezing and/or coughing, resulting from different airways pathologic processes underlying different types of asthma. There are 2 main types of childhood asthma: (1) recurrent wheezing in early childhood, primarily triggered by common viral infections of the respiratory tract, and (2) chronic asthma associated with allergy that persists into later childhood and often adulthood. A 3rd type of childhood asthma typically emerges in females who experience obesity and early-onset puberty (by 11 yr of age). Some children may be hypersensitive to common air pollutants (environmental tobacco smoke, ozone, endotoxin) such that exposures to these pollutants might not only make existing asthma worse but may also have a causal role in the susceptible. The most common persistent form of childhood asthma is associated with allergy and susceptibility to common respiratory virus–induced exacerbations (Table 138-2).
Table 138-2 RECURRENT COUGHING/WHEEZING PATTERNS IN CHILDHOOD, BASED ON NATURAL HISTORY
TRANSIENT EARLY WHEEZING
PERSISTENT ATOPY-ASSOCIATED ASTHMA
NONATOPIC WHEEZING
ASTHMA WITH DECLINING LUNG FUNCTION
LATE-ONSET ASTHMA IN FEMALES, ASSOCIATED WITH OBESITY AND EARLY-ONSET PUBERTY
OCCUPATIONAL-TYPE ASTHMA IN CHILDREN
Children with asthma associated with occupational-type exposures known to trigger asthma in adults in occupational settings (e.g., endotoxin exposure in children raised on farms)
From Taussig LM, Landau LI, et al, editors: Pediatric respiratory medicine, ed 2, Philadelphia, 2008, Mosby/Elsevier, p 822.
Pathogenesis
Airflow obstruction in asthma is the result of numerous pathologic processes. In the small airways, airflow is regulated by smooth muscle encircling the airways lumens; bronchoconstriction of these bronchiolar muscular bands restricts or blocks airflow. A cellular inflammatory infiltrate and exudates distinguished by eosinophils, but also including other inflammatory cell types (neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, mast cells, basophils), can fill and obstruct the airways and induce epithelial damage and desquamation into the airways lumen. Helper T lymphocytes and other immune cells that produce proallergic, proinflammatory cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-13), and chemokines (eotaxin) mediate this inflammatory process. Pathogenic immune responses and inflammation may also result from a breach in normal immune regulatory processes (such as regulatory T lymphocytes that produce IL-10 and transforming growth factor [TGF]-β) that dampen effector immunity and inflammation when they are no longer needed. Hypersensitivity or susceptibility to a variety of provocative exposures or triggers (Table 138-3) can lead to airways inflammation, AHR, edema, basement membrane thickening, subepithelial collagen deposition, smooth muscle and mucous gland hypertrophy, and mucus hypersecretion—all processes that contribute to airflow obstruction (Chapter 134).
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
Asthma symptoms can be triggered by numerous common events or exposures: physical exertion and hyperventilation (laughing), cold or dry air, and airways irritants (see Table 138-3). Exposures that induce airways inflammation, such as infections (rhinovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, metapneumovirus, torque teno virus, parainfluenza virus, influenza virus, adenovirus, Mycoplasma pneumonia, Chlamydia pneumoniae), and inhaled allergens, also increase AHR to irritant exposures. An environmental history is essential for optimal asthma management (Chapter 135).
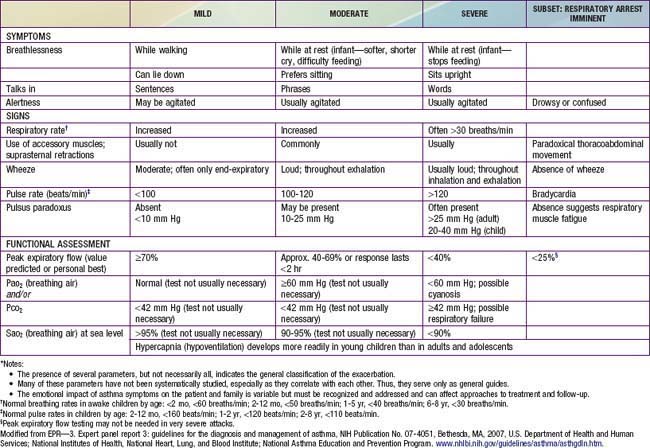
During asthma exacerbations, expiratory wheezing and a prolonged expiratory phase can usually be appreciated by auscultation. Decreased breath sounds in some of the lung fields, commonly the right lower posterior lobe, are consistent with regional hypoventilation owing to airways obstruction. Crackles (or rales) and rhonchi can sometimes be heard, resulting from excess mucus production and inflammatory exudate in the airways. The combination of segmental crackles and poor breath sounds can indicate lung segmental atelectasis that is difficult to distinguish from bronchial pneumonia and can complicate acute asthma management. In severe exacerbations, the greater extent of airways obstruction causes labored breathing and respiratory distress, which manifests as inspiratory and expiratory wheezing, increased prolongation of exhalation, poor air entry, suprasternal and intercostal retractions, nasal flaring, and accessory respiratory muscle use. In extremis, airflow may be so limited that wheezing cannot be heard (Table 138-4).
Differential Diagnosis
Many childhood respiratory conditions can present with symptoms and signs similar to those of asthma (Table 138-5). Besides asthma, other common causes of chronic, intermittent coughing include gastroesophageal reflux (GER) and rhinosinusitis. Both GER and chronic sinusitis can be challenging to diagnose in children. Often, GER is clinically silent in children, and children with chronic sinusitis do not report sinusitis-specific symptoms, such as localized sinus pressure and tenderness. In addition, both GER and rhinosinusitis are often co-morbid with childhood asthma and, if not specifically treated, may make asthma difficult to manage.
Table 138-5 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF CHILDHOOD ASTHMA
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT CONDITIONS
MIDDLE RESPIRATORY TRACT CONDITIONS
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT CONDITIONS
Laboratory Findings
Lung function tests can help to confirm the diagnosis of asthma and to determine disease severity.
Pulmonary Function Testing
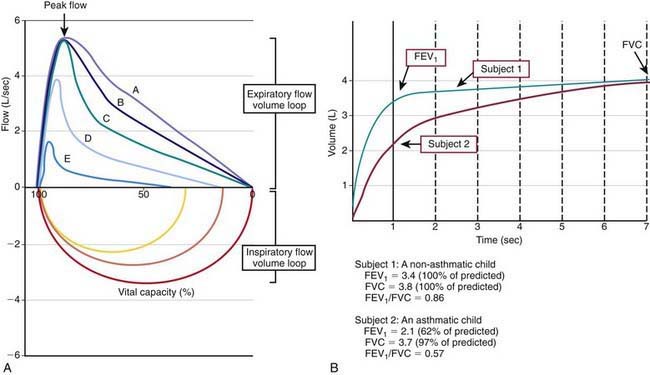
Many asthma guidelines promote spirometric measures of airflow and lung volumes during forced expiratory maneuvers as standard for asthma assessment. Spirometry is helpful as an objective measure of airflow limitation (Fig. 138-2). Knowledgeable personnel are needed to perform and interpret findings of spirometry tests. Valid spirometric measures depend on a patient’s ability to properly perform a full, forceful, and prolonged expiratory maneuver, usually feasible in children > 6 yr of age (with some younger exceptions). Reproducible spirometric efforts are an indicator of test validity; if the FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in 1 sec) is within 5% on 3 attempts, then the highest FEV1 effort of the 3 is used. This standard utilization of the highest of 3 reproducible efforts is indicative of the effort dependence of reliable spirometric testing.
In asthma, airways blockage results in reduced airflow with forced exhalation and smaller partial-expiratory lung volumes (see Fig. 138-2). Because asthmatic patients typically have hyperinflated lungs, FEV1 can be simply adjusted for full expiratory lung volume—the forced vital capacity (FVC)—with an FEV1/FVC ratio. Generally, an FEV1/FVC ratio <0.80 indicates significant airflow obstruction (Table 138-6). Normative values for FEV1 have been determined for children on the basis of height, gender, and ethnicity. Abnormally low FEV1 as a percentage of predicted norms is 1 of 6 criteria used to determine asthma severity in the National Institutes of Health (NIH)–sponsored asthma guidelines.
Table 138-6 LUNG FUNCTION ABNORMALITIES IN ASTHMA
FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 sec; FVC, forced vital capacity.
Such measures of airflow alone are not diagnostic of asthma, because numerous other conditions can cause airflow reduction. Bronchodilator response to an inhaled β-agonist (e.g., albuterol) is greater in asthmatic patients than nonasthmatic persons; an improvement in FEV1 ≥12% or >200 mL is consistent with asthma. Bronchoprovocation challenges can be helpful in diagnosing asthma and optimizing asthma management. Asthmatic airways are hyperresponsive and therefore more sensitive to inhaled methacholine, histamine, and cold or dry air. The degree of AHR to these exposures correlates to some extent with asthma severity and airways inflammation. Although bronchoprovocation challenges are carefully dosed and monitored in an investigational setting, their use is rarely practical in a general practice setting. Exercise challenges (aerobic exertion or “running” for 6-8 min) can help to identify children with exercise-induced bronchospasm. Although the airflow response of non-asthmatic persons to exercise is to increase functional lung volumes and improve FEV1 slightly (5-10%), exercise often provokes airflow obstruction in persons with inadequately treated asthma. Accordingly, in asthmatic patients, FEV1 typically decreases during or after exercise by >15% (see Table 138-6). The onset of exercise-induced bronchospasm is usually within 15 min after a vigorous exercise challenge and can spontaneously resolve within 30-60 min. Studies of exercise challenges in school-aged children typically identify an additional 5-10% with exercise-induced bronchospasm and previously unrecognized asthma. There are two caveats regarding exercise challenges: first, treadmill challenges in the clinic are not completely reliable and can miss exertional asthma that can be demonstrated on the playing field; and second, treadmill challenges can induce severe exacerbations in at-risk patients. Careful patient selection for exercise challenges and preparedness for severe asthma exacerbations are required.
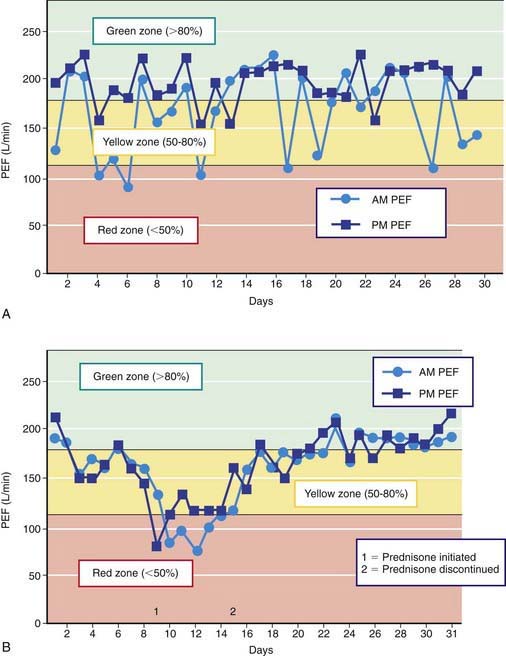
Peak expiratory flow (PEF) monitoring devices provide simple and inexpensive home-use tools to measure airflow and can be helpful in a number of circumstances (Fig. 138-3). “Poor perceivers” of airflow obstruction due to asthma can benefit by monitoring PEFs daily to assess objectively airflow as an indicator of asthma control or problems that would be more sensitive than their symptom perception. PEF devices vary in the ability to detect airflow obstruction: they are generally less sensitive than spirometry to airflow obstruction such that, in some patients, PEF values decline only when airflow obstruction is severe. Therefore, PEF monitoring should be started by measuring morning and evening PEFs (best of 3 attempts) for several weeks for patients to practice the technique, to determine a “personal best,” and to correlate PEF values with symptoms (and ideally spirometry). PEF variation >20% is consistent with asthma (see Fig. 138-3 and Table 138-6).
Radiology
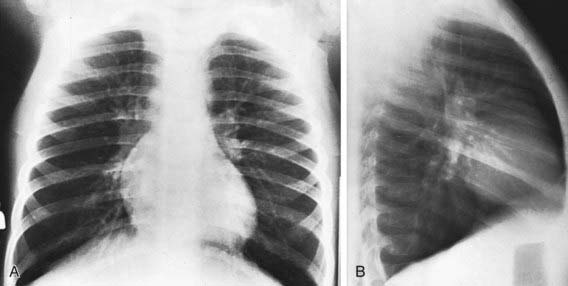
The findings of chest radiographs (posteroanterior and lateral views) in children with asthma often appear to be normal, aside from subtle and nonspecific findings of hyperinflation (flattening of the diaphragms) and peribronchial thickening (Fig. 138-4). Chest radiographs can be helpful in identifying abnormalities that are hallmarks of asthma masqueraders (aspiration pneumonitis, hyperlucent lung fields in bronchiolitis obliterans), and complications during asthma exacerbations (atelectasis, pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax). Some lung abnormalities can be better appreciated with high-resolution, thin-section chest CT scans. Bronchiectasis, which is sometimes difficult to appreciate on chest radiograph but is clearly seen on CT scan, implicates an asthma masquerader, such as cystic fibrosis, allergic bronchopulmonary mycoses (aspergillosis), ciliary dyskinesias, or immune deficiencies.
Treatment
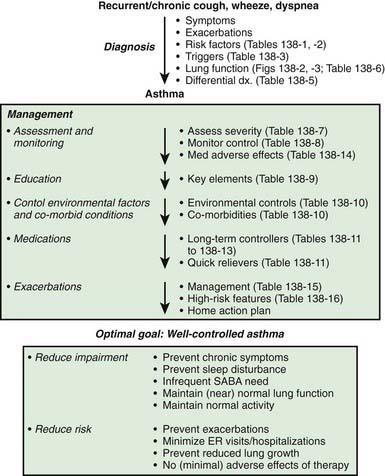
The National Asthma Education and Prevention Program’s Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma 2007 is available online (www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/asthma/asthgdln.htm), and the highlights of significant changes from the previous version of the guidelines have been published. The key components to optimal asthma management are specified (Fig. 138-5). Management of asthma should have the following components: (1) assessment and monitoring of disease activity; (2) provision of education to enhance the patient’s and family’s knowledge and skills for self-management; (3) identification and management of precipitating factors and co-morbid conditions that may worsen asthma; and (4) appropriate selection of medications to address the patient’s needs. The long-term goal of asthma management is attainment of optimal asthma control.
Component 1: Regular Assessment and Monitoring
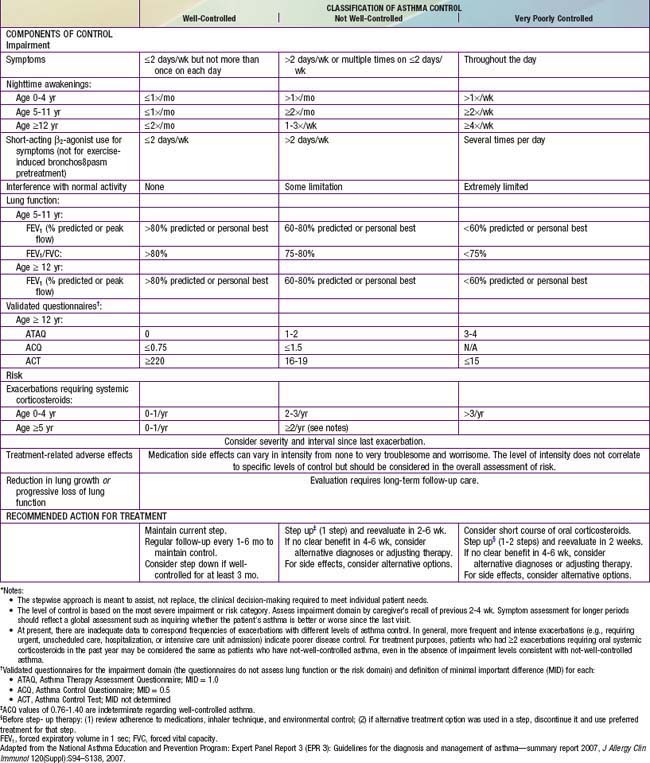
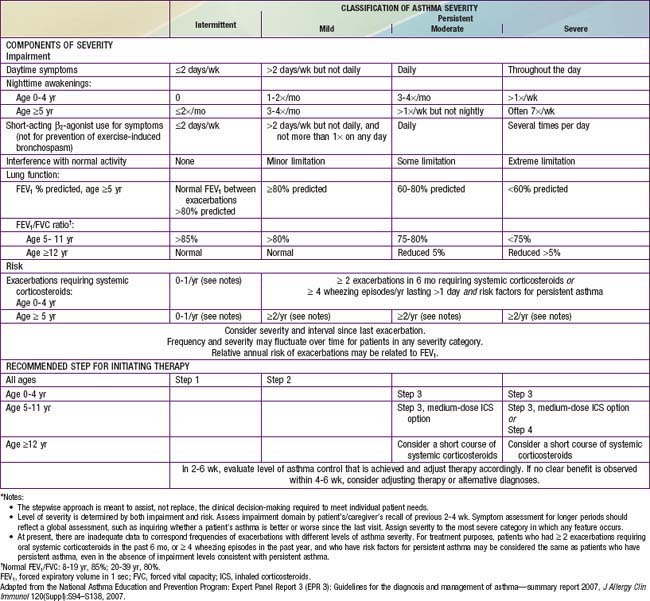
Classification of asthma severity and control is based on the domains of Impairment and Risk. These domains may not correlate with each other and may respond differently to treatment. The NIH guidelines have criteria for 3 age groups—0-4 yr, 5-11 yr, and ≥12 yr—for the evaluation of both severity (Table 138-7) and control (Table 138-8). The level of asthma severity or control is based on the most severe impairment or risk category. In assessing asthma severity, impairment consists of an assessment of the patient’s recent symptom frequency (daytime and nighttime with subtle differences in numeric cutoffs between the 3 age groups), need for short-acting β2-agonists for quick relief, ability to engage in normal or desired activities, and airflow compromise, which is evaluated with spirometry in children 5 yr and older. Risk refers to an evaluation of the likelihood of developing asthma exacerbations for the individual patient. Of note, in the absence of frequent symptoms, persistent asthma should be considered, and therefore long-term controller therapy should be initiated for infants or children who have risk factors for asthma (see earlier) and 4 or more episodes of wheezing over the past year that lasted longer than 1 day and affected sleep, or 2 or more exacerbations in 6 months requiring systemic corticosteroids.
Table 138-7 ASSESSING ASTHMA SEVERITY AND INITIATING TREATMENT FOR PATIENTS WHO ARE NOT CURRENTLY TAKING LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS*
Asthma management can be optimized through regular clinic visits every 2-6 wk until good asthma control is achieved. For children already on controller medication therapy, management is tailored to the child’s level of control. The NIH guidelines provide tables for evaluating asthma control for the 3 age groups (see Table 138-8). In evaluation of asthma control, as in severity assessment, impairment includes an assessment of the patient’s symptom frequency (daytime and nighttime), need for short-acting β2-agonists for quick relief, ability to engage in normal or desired activities, and, for older children, airflow measurements. In addition, determination of quality of life measures for older children is included. Furthermore, with respect to risk assessment, besides considering severity and frequency of exacerbations requiring systemic corticosteroids, tracking of lung growth in older children and monitoring of untoward effects of medications are also warranted. As already mentioned, the degree of impairment and risk are used to determine the patient’s level of asthma control as well-controlled, not well-controlled, or very poorly controlled. Children with well-controlled asthma have: daytime symptoms ≤2 days/week and need a rescue bronchodilator ≤2 days/week; an FEV1 of >80% of predicted (and FEV1/FVC ratio >80% for children 5-11 yr of age); no interference with normal activity; and <2 exacerbations in the past year. The impairment criteria vary slightly depending on age group: there are different thresholds in the frequency of nighttime awakenings; addition of FEV1/FVC ratio criteria for children 5-11 yr old, and addition of validated questionnaires in evaluating quality of life for older children. Children whose status does not meet all of the criteria defining well-controlled asthma are determined to have either not well-controlled or very poorly controlled asthma, which is determined by the single criterion with the lowest rating.
Two to four asthma checkups per year are recommended for reassessing and maintaining good asthma control. During these visits, asthma control can be assessed by determining the: (1) frequency of asthma symptoms during the day, at night, and with physical exercise; (2) frequency of “rescue” SABA medication use and refills; (3) quality of life for youths with an assessment tool; (4) lung function measurements for older children and youths; (5) number and severity of asthma exacerbations; and (6) presence of medication adverse effects since the last visit (see Fig. 138-5). Lung function testing (spirometry) is recommended at least annually and more often if asthma is inadequately controlled or lung function is abnormally low. PEF monitoring at home can be helpful in the assessment of asthmatic children with poor symptom perception, other causes of chronic coughing in addition to asthma, moderate to severe asthma, or a history of severe asthma exacerbations. PEF monitoring is feasible in children as young as 4 yr who are able to master this skill. Use of a stoplight zone system tailored to each child’s “personal best” PEF values can optimize effectiveness and interest (see Fig 138-3
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree