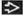Bleeding With IUP
Anne Kennedy, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Failed Pregnancy
Perigestational Hemorrhage
Early Normal Pregnancy
Anembryonic Pregnancy
Less Common
Partial Mole
Twin Demise
Rare but Important
Interstitial Ectopic
Cervical Ectopic
C-section Scar Ectopic
Heterotopic Pregnancy
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Is there a gestational sac?
Imperative to differentiate a normal early gestational sac from a pseudosac seen in ectopic pregnancy
If no intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) look for adnexal mass, echogenic fluid in cul-de-sac
Where is the sac located?
Compare to prior studies if available
Has there been appropriate interval development?
Must know normal developmental milestones
Normal sac development
Intradecidual sac sign (IDSS) earliest sign of IUP
IDSS seen by 4-4.5 weeks after last menstrual period (LMP)
Gestational sac “burrows” into endometrium
Echogenic ring is eccentric to linear interface of endometrial surfaces
Must follow to confirm appropriate growth/milestones
Double decidual sac sign (DDSS) seen by 5-5.5 weeks post LMP
Initially described as first reliable transabdominal sign of IUP
Decidua parietalis (endometrium) surrounds decidua capsularis (gestational sac) = two echogenic rings
Pseudosac associated with ectopic pregnancy
No DDSS
Flatter shape than normal gestational sac
Central in cavity rather than eccentric
Even if normal IUP seen beware heterotopic pregnancy if patient symptomatic/has risk factors
Placenta previa/abruption are NOT first trimester diagnoses
Placenta often covers internal os in first trimester
Placenta large relative to uterine size
Lower uterine segment (LUS) elongates after 28 weeks
Placental trophotropism results in migration of placenta away from cervix/LUS as pregnancy progresses
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
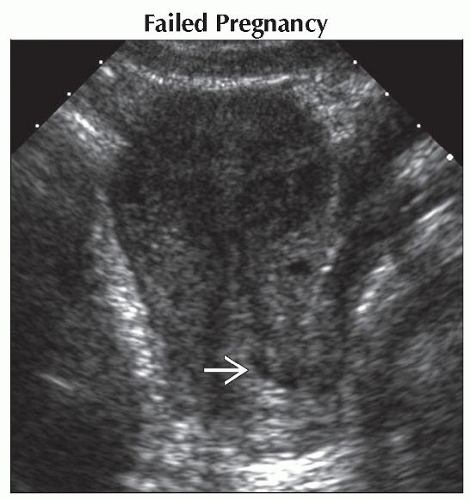
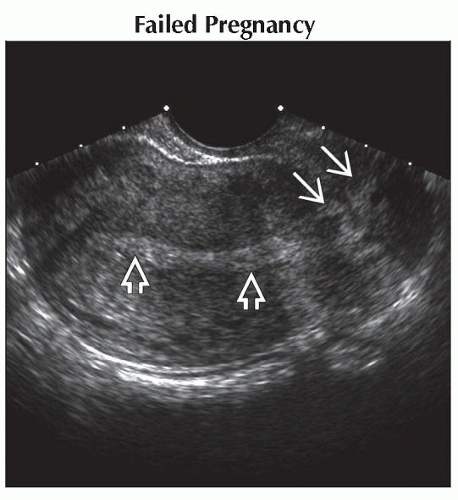
Failed Pregnancy
Cardiac activity will be absent
Sac being expelled from uterus, may contain yolk sac or embryo
Sac often flattened/irregular shape
Sac in endometrial/cervical canal not implanted into uterus
Color Doppler shows lack of normal trophoblastic flow
Perigestational Hemorrhage
May be asymptomatic or present with vaginal bleeding
Echogenic fluid deep to chorion
Becomes hypoechoic over time
Normal gestational sac contents
Early Normal Pregnancy
Bleeding in pregnancy before visualization of gestational sac (presumed to be implantation bleeding)
Follow all apparent IDSS to ensure normal developmental milestones
Beware tiny cystic structures in endometrium, may be dilated endometrial glands
Idiopathic bleeding: Normal sac/embryo seen but no obvious collection of blood
Anembryonic Pregnancy
No visible embryo in gestational sac with diameter ≥ 18 mm by transvaginal exam
Look for “empty amnion” sign
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Interstitial Ectopic
Look for interstitial line sign
Eccentric placement of sac in relation to uterine cavity
< 5 mm of surrounding myometrium very suggestive
Cervical Ectopic
Sac implanted in cervical stroma
Look for rim of tissue around sac rather than sac within endocervical canal
Sac positioned low in uterus but still perfused (compared to abortion in progress with flattened sac, lack of perfusion)
C-section Scar Ectopic
Gestational sac implants into scar from prior C-section, extends to serosa
Heterotopic Pregnancy
Intrauterine & ectopic pregnancy
Look for adnexal mass, echogenic fluid in addition to IUP
Differential: Normal IUP with hemorrhagic corpus luteum
Risk factors for heterotopic pregnancy
Assisted reproduction
Intrauterine contraceptive device
History of pelvic inflammatory disease
History of endometriosis
Other Essential Information
Important to recognize unusual (other than tubal) ectopics
Pregnancy is “in uterus” but not in correct place
C-section scar ectopic treated with systemic methotrexate or percutaneous injection
Risk of torrential bleeding/emergent hysterectomy if curettage attempted in cervical ectopic
Interstitial ectopic also best treated conservatively if patient stable
Alternative Differential Approaches
Bleeding with intrauterine sac but no fetal pole
Anembryonic pregnancy
Pseudosac from ectopic pregnancy
Perigestational hemorrhage
Bleeding with an embryo
Perigestational hemorrhage
Idiopathic (no obvious collection of blood)
Bleeding with no visible IUP
Very early normal pregnancy
Complete abortion
Tubal ectopic pregnancy
Image Gallery
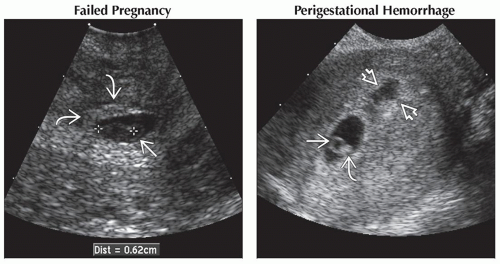 (Left) Sagittal transvaginal ultrasound in the same case “zoomed” on the cervical area shows the collapsed gestational sac
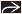 containing a 6 mm dead embryo (calipers) and a yolk sac containing a 6 mm dead embryo (calipers) and a yolk sac  . This spontaneously passed shortly after the exam. (Right) Sagittal ultrasound shows an IUP with a yolk sac . This spontaneously passed shortly after the exam. (Right) Sagittal ultrasound shows an IUP with a yolk sac  and embryo and embryo 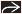 . There is an adjacent perigestational hemorrhage . There is an adjacent perigestational hemorrhage 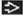 . This pregnancy failed. . This pregnancy failed.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|