Chapter 34 Atrophic and dystrophic conditions
ATROPHIC CHANGES OF THE INTERNAL GENITAL ORGANS
Vulval atrophy in older women
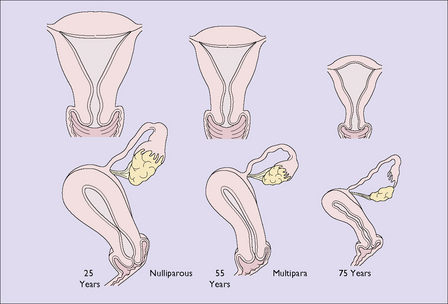
By the time a woman reaches the age of 75 the uterus, the Fallopian tubes and the ovaries have shrunk considerably (Fig. 34.1). In the uterus, the endometrium has become atrophic and the muscle fibres of the myometrium have been progressively replaced by fibrous tissue. The cervix has atrophied and the cervical canal may become obliterated. If the woman develops uterine infection the pus might not escape, leading to a pyometra. This may also occur if the woman develops an endometrial or cervical carcinoma. The woman may complain of lower abdominal pain, and an examination shows that the uterus is larger than expected for her age. The diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound scanning, which shows that the uterine cavity is enlarged and filled with fluid. If carcinoma is detected it is treated appropriately; if it is not present, the cervix is dilated and a drain inserted for a few days.
The pelvic floor
Deprived of oestrogen, the blood supply to the muscles of the pelvic floor diminishes. The pelvic floor muscles lose their tone and the connective tissue loses its elasticity, with the result that pelvic floor tissues damaged during childbirth are likely to relax, with varying degrees of prolapse (see Ch. 38).