Angulated Bones
Janice L. B. Byrne, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
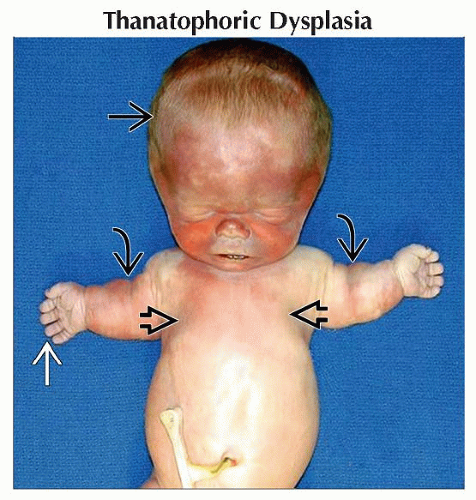
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Diabetic Embryopathy
Less Common
Campomelic Dysplasia
Kyphomelic Dysplasia
Abnormal Joint Angulation
Rare but Important
Hypophosphatasia
Fetal Trauma
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Are there fractures?
Is the ossification normal?
Is the angulation mid-shaft or at a joint?
Is the distal limb normal?
Is one limb affected or all?
Are both segments of the limb affected?
Are the abnormalities limited to the long bones or are other skeletal elements affected?
Are there other structural anomalies?
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
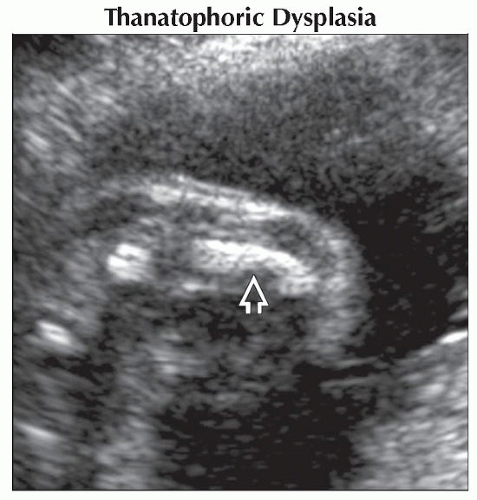
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
Micromelia
Normal ossification
No fractures
Short ribs with bell-shaped thorax
Platyspondyly
Lumbar kyphosis common
“Telephone receiver” femur in type I
Normal calvarium in type I
Femora less curved in type II
Cloverleaf-shaped skull (Kleeblattschädel) in type II
Polyhydramnios often severe and progressive in the second trimester
Other anomalies rare
Lethal within first few hours-to-days of life
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Fractures a prominent feature
Decreased ossification of all bones
Type II (perinatal lethal) with extensive in utero fractures, limb deformities
“Beaded” ribs due to healing fractures
Deformable skull with pressure from ultrasound transducer
Non-lethal types associated with less severe limb shortening, fewer in utero fractures
Progressive deformation, shortening may occur in type III/IV
Type III/IV may present with isolated bent femur in utero
Size of chest correlated with risk of lethal outcome
Diabetic Embryopathy
Uncontrolled diabetes most prevalent human teratogen
Abnormal femur common
Usually bilateral femur abnormality, but often discordant
Short, angulated or curved femur
Associated tibia-fibula abnormality
Preaxial polydactyly
Other structural defects common in uncontrolled diabetes
Cardiac
Central nervous system: Anencephaly, holoprosencephaly, spina bifida
Anorectal malformation
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Campomelic Dysplasia
Severe angulation of femora, tibiae, fibulae
Anterolateral bowing especially common
Scapula absent or hypoplastic
XY sex reversal (male to female) or ambiguity
Genotypic males appear phenotypically as females
Normal ossification
No fractures
Bell-shaped chest
Kyphoscoliosis
1st trimester cystic hygroma or increased nuchal translucency
Characteristic skin dimpling over area of angulation
Kyphomelic Dysplasia
Normal chest size
Less severe long bone shortening
Angulation or curvature of long bones
Normal ossification
No fractures
Abnormal Joint Angulation
Fixed vs. moveable joint
Normal distal extremity associated with dislocated joint
Knees, hips most commonly affected
Movement at the joint often observed in utero despite dislocation
May be unilateral or bilateral
May be associated with fetal malpresentation
Prolonged dislocation may result in dysplastic joint
Abnormal distal extremity often associated with abnormal joint or proximal bone
Joint usually without spontaneous movement
Wrist most commonly affected, but ankle also possible
Angle of deviation predicts which bone is hypo- or aplastic; angulation is toward the hypoplastic element
Radial deviation associated with hypoplasia or aplasia of radius and thumb
Ulnar deviation less common; associated with ulnar hypoplasia
Tibial or fibular hypoplasia or aplasia associated with fixed angulation of ankle
Associated oligodactyly common
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Hypophosphatasia
Multiple sub-types including perinatal lethal, infantile and late onset (adult)
In general the later the onset, the less severe the clinical course
Undermineralization of calvarium results in brain being seen “too well” on ultrasound
Perinatal lethal type with prominent midtrimester ultrasound findings of severe undermineralization and micromelia of all long bones and calvarium
In general long bones thin and bowed with absent posterior shadowing
Spurs often seen along mid-shaft of long bones
Fetal Trauma
Isolated fractures due to fetal trauma rare in absence of severe maternal trauma
Other Essential Information
Distinguish between angulated bones and angulated joints when evaluating the fetus
Curvature of multiple bones predicts generalized osteochondrodystrophy
Severity of associated limb length shortening and chest size will predict lethal vs. non-lethal skeletal dysplasia
Alternative Differential Approaches
Presence of fractures of major importance
Consider osseous fragility syndromes including osteogenesis imperfecta and hypophosphatasia
Severity and number of in utero fractures may help distinguish lethal vs. non-lethal disorder
Rib fractures without long bone fractures seen in type IA achondrogenesis
Image Gallery
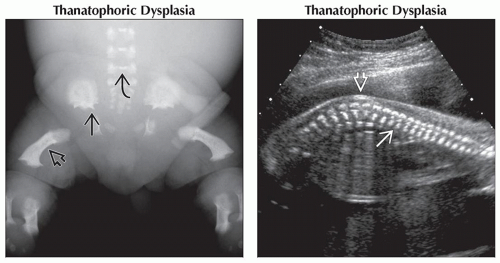 (Left) Anteroposterior radiograph shows the short curved femur
 typical of type I TD. Note also the spicules on the inferior iliac wing typical of type I TD. Note also the spicules on the inferior iliac wing  and the platyspondyly and the platyspondyly  involving the lumbar spine. (Right) Sagittal ultrasound shows lumbar lordosis involving the lumbar spine. (Right) Sagittal ultrasound shows lumbar lordosis  in a fetus with thanatophoric dysplasia. The platyspondyly in a fetus with thanatophoric dysplasia. The platyspondyly  is also prominent. is also prominent.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|