Acyanotic Heart Disease With Normal Vascularity
Alexander J. Towbin, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Aortic Coarctation
Aortic Stenosis
Less Common
Interrupted Aortic Arch
Pulmonary Stenosis
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Obstructive lesions cause acyanotic heart disease with normal pulmonary vascularity
Patients with small, left-to-right shunts have normal vascularity
In neonates, increased pulmonary vascular resistance causes left-to-right shunt to have normal vascularity
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Aortic Coarctation
Stenosis in proximal descending aorta
Usually just beyond origin of left subclavian artery
5-8% of congenital heart defects (CHD)
2x more common in males
Associations: Turner syndrome, bicuspid aortic valve, ventricular septal defect
Severe coarct presents when ductus closes
Mild coarct presents with upper extremity hypertension and ↓ lower extremity pulses
Rib notching not usually seen on chest x-ray (CXR) until after age 6
Treatment options: Surgical repair, angioplasty, stent placement
Aortic Stenosis
Types: Supravalvular, valvular, or subaortic
Valvular aortic stenosis is most common
Accounts for 3-6% of CHD
4x more common in males
˜ 20% have associated cardiac anomaly
Severity related to degree of obstruction
CXR: Normal or with cardiomegaly, vascular congestion, and poststenotic dilation of ascending aorta
Subaortic stenosis can be discrete or diffuse
Supravalvular is least common
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Interrupted Aortic Arch
Discontinuity of aorta (1% of all CHD)
Associations: DiGeorge syndrome and 22q11 deletion
3 types: Isolated, simple, and complex
Isolated: No other cardiac anomalies
Simple: Associated with ventricular septal defect and patent ductus arteriosus
Complex: Associated with complex CHD
Pulmonary Stenosis
Types: Valvular, subvalvular, supravalvular, or in branch pulmonary arteries
Valvular stenosis is most common
7-9% of all CHD
Presents with asymptomatic murmur
CXR: Dilated main pulmonary artery
Treatment: Balloon valvuloplasty
Image Gallery
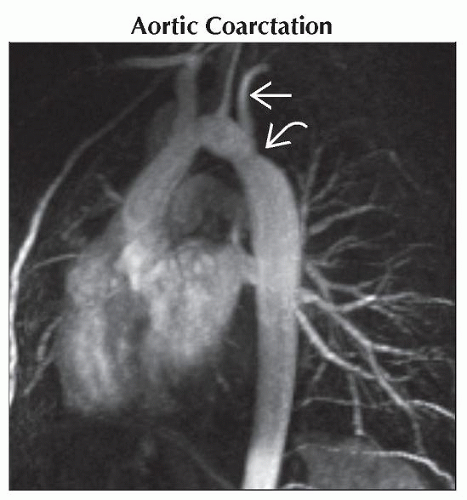 Sagittal MIP of T1 C+ subtraction MR shows a focal area of stenosis in the proximal descending aorta
 just distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery just distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|