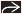Abnormal Spine Position
Anne Kennedy, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Positional
Spina Bifida
Body Stalk Anomaly
VACTERL Association
Vertebral Anomaly
Less Common
Amniotic Band Syndrome
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
Achondroplasia
Asphyxiating Thoracic Dysplasia
Rare but Important
Conjoined Twins
Iniencephaly
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Is fetal position fixed or variable?
If variable, less likely to be significant problem
If fixed, evaluate global fetal movement
Any evidence of arthrogryposis/akinesia sequence
Serial evaluation important as akinesis sequences may be progressive
Look at abdominal wall and cord insertion site to exclude body stalk anomaly
Scan through amniotic fluid looking for bands
Are bones of spine normal?
Use high frequency transducer for better resolution
Assess vertebral body height, mineralization, presence of 3 ossification centers at all levels
Is spine length normal?
Caudal regression sequence may cause spine position to look unusual as loss of normal sacral curvature
Make sure vertebra are present between the iliac wings
Scan through cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine systematically
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Positional
Most commonly idiopathic due to fetal stretching movements
Fetus seen to move extremities
Normal amniotic fluid
Change in position on follow-up scans
May be due to fetal crowding
Multiple gestations, late pregnancy
Associated with oligohydramnios
Renal agenesis/other bilateral renal anomalies
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome donor
Look for synechiae
Fetal parts oriented around large synechia
Large uterine fibroids may distort cavity → unusual fetal position
Müllerian duct anomalies may result in decreased cavity size/unusual fetal lie
Spina Bifida
Depending on level of neural tube defect (NTD) may see sharp kyphosis
Thoracic NTD most likely to result in abnormal spine position
Iniencephaly is high cervical NTD causing neck hyperextension due to shortening of cervical spine
Look for associated brain findings of Chiari II malformation
Ventriculomegaly, “banana” cerebellum, “lemon-shaped” head
Look for splayed/absent posterior elements
Look for associated myelomeningocele/myeloschisis
Body Stalk Anomaly
Result of embryologic maldevelopment with interruption of normal embryonic folding process
Open abdominal wall defect
Peritoneum in continuity with amnion therefore fetus fixed to placenta
Body stalk/yolk stalk fusion fails: Short or absent umbilical cord
Normal cord development allows fetus to move freely within amniotic sac
If no cord, fetus tethered to uterine wall
Extremities and cranium move
Spine growth/elongation → hyperextension about fixed point where abdominal cavity is open and adherent to placenta
VACTERL Association
Non-random association of seven core anomalies
Vertebral anomalies
Anal atresia
Cardiac anomalies
Tracheoesophageal atresia
Renal anomalies
Limb defects (radial ray)
Vertebral Anomaly
Look for hemivertebra/fused vertebrae at apex of scoliosis/kyphosis
Ask for history of maternal diabetes, alcohol use, drug exposure (e.g., valproate)
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
Lethal skeletal dysplasia with severe micromelia
“Telephone receiver” femur in type 1
Kleeblattschädel (cloverleaf) skull type 2
Distinctive spine appearance
Marked platyspondyly with intervertebral disc height > vertebral body height (normally equal)
Lumbar kyphosis
Achondroplasia
Thoracolumbar kyphosis
Narrowed interpedicular distance
Progressive rhizomelic limb shortening
Macrocephaly with frontal bossing
Trident hands
Asphyxiating Thoracic Dysplasia
Thoracic lordosis, lumbar kyphosis
Short, horizontal ribs with small thorax
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Conjoined Twins
Contiguous skin covering between twins
Spines hyperextended due to fixed anterior point of union
Bridging tissue may be pliable → orientation of twins can vary from scan to scan
Iniencephaly
Lethal extensive open neural tube defect
Defect in occiput and inion
Occipital encephalocele + spinal dysraphism
Fixed cervical hyperextension → “stargazer” fetus
Other Essential Information
Twin gestation
Determine chorionicity
Conjoined twins are monochorionic
Differential diagnosis for fixed scoliosis in one twin of dichorionic twins is as for singleton
Apparently isolated hemivertebra causing abnormal spine position may be “tip of the iceberg”
Perform formal fetal echocardiogram at 18-22 weeks
Look carefully for other stigmata of VACTERL association
Assess spinal cord with high resolution transducer if possible
Tethered cord
Lipoma
Diastematomyelia
Image Gallery
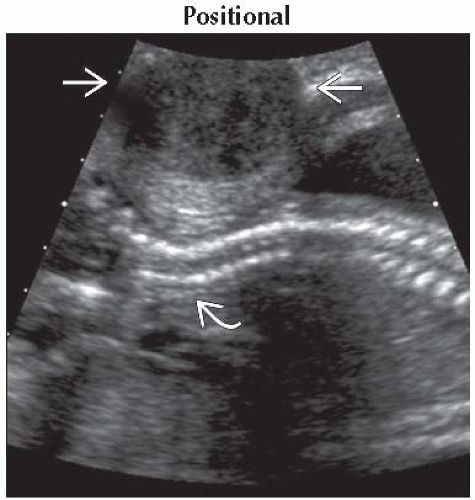
 Sagittal ultrasound shows prominent but transient thoracic kyphosis. This was a transient finding and is seen with normal fetal movement. |
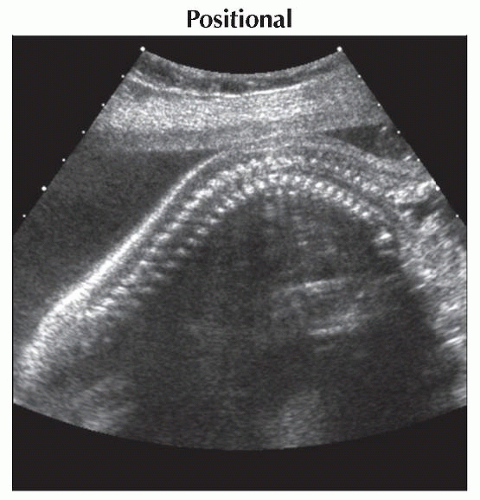
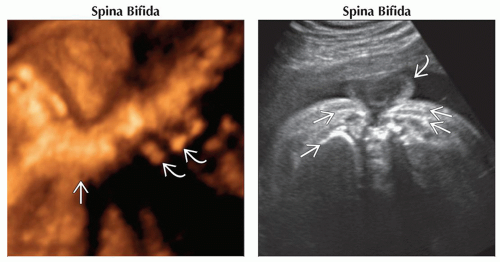 (Left) 3D ultrasound shows acute angulation
 of the thoracic spine in a fetus with a high thoracic neural tube defect. Origins of some of the upper ribs of the thoracic spine in a fetus with a high thoracic neural tube defect. Origins of some of the upper ribs 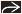 are seen; the rest of the torso was twisted out of plane. (Right) Axial oblique ultrasound in the same case as previous image shows the myelomeningocele sac are seen; the rest of the torso was twisted out of plane. (Right) Axial oblique ultrasound in the same case as previous image shows the myelomeningocele sac 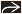 involving the thoracic spine. Several ribs involving the thoracic spine. Several ribs  are imaged due to the degree of twisting of the torso. are imaged due to the degree of twisting of the torso.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|