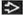Abnormal Foot
Janice L. B. Byrne, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Clubfoot
Rockerbottom Foot
Sandal Gap Foot
Edema of Feet and Extremities
Less Common
Amniotic Band Syndrome
Ectrodactyly
Abnormal Toes
Terminal Transverse Limb Defect
Rare but Important
Sirenomelia
Amelia, Micromelia
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Is the anomaly an isolated finding?
Are there multiple anomalies?
Bilateral vs. unilateral
Are hands similarly affected?
Is the finding associated with abnormal or lack of fetal movement?
Lack of movement within the amniotic cavity?
Does the fetus appear “stuck” to the placenta?
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Clubfoot
Plane of imaging important
Coronal view: Ankles should be straight
Lateral view: Bones of foot and tibia/fibula should not be seen in same plane
“Footprint” view: Clubfoot associated with abnormal shape/shortening
Bilateral vs. unilateral
Limitations to diagnosis
Gestational age: Clubfoot difficult to diagnose past 2nd trimester
Oligohydramnios
Crowding in multiple gestation
Footling breech position limits visualization of feet
Rockerbottom Foot
Prominent heel associated with rounded bottom of foot
Best seen in lateral view
May be associated with dorsiflexed great toe, short hallux
Look carefully for other anomalies associated with trisomy 18
Persistently clenched hands or overlapping digits
Sandal Gap Foot
Gap between great toe and 2nd toe
May be normal finding with fetal “flare” of toes while moving feet
Look for persistence of gap even when fetus at rest
Most often seen in normal fetuses but is a minor marker in trisomy 21
Edema of Feet and Extremities
Pattern of edema important for establishing differential diagnosis
Edema of extremities vs. body edema
Unilateral edema concerning for obstructive phenomenon such as amniotic bands or tumor
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Amniotic Band Syndrome
Amputations of digits or feet/hands
Usually asymmetrical
Associated disruptions of face, calvarium, body wall
Constriction rings of extremities
Adherence to placenta in severe cases
Extremity edema distal to constriction band is common
Ectrodactyly
Split hand-split foot malformation
Fusion of digits with deep median cleft (“lobster claw”)
May be unilateral or bilateral
May involve upper, lower, or both
Variable appearance between extremities
Abnormal Toes
Polydactyly
Often difficult to diagnose, especially in early gestation
Foot usually appears wider than normal
Look at hands for extra fingers
Post-axial more common than pre-axial except in diabetic embryopathy
Syndactyly
Usually not diagnosed prenatally
May be associated with abnormal shape of foot
Oligodactyly
Foot appears narrow
Often associated with abnormality of tibia or fibula
Abnormal position of foot common
Terminal Transverse Limb Defect
Varying degree of limb deficiency
May be seen with congenital varicella infection
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Sirenomelia
Legs may appear “stuck” together
Single femur or fewer than 4 lower extremity long bones valuable clues
Foot/feet may be absent, single, or a complex fusion of structures
Usually associated with bilateral renal agenesis
May be difficult to visualize due to oligohydramnios
Amelia, Micromelia
Extremities may be absent (amelia) vs. severely shortened (micromelia)
May be limited to upper or lower extremities
Digits may be present
Symmetrical micromelia associated with severe skeletal dysplasias
Other Essential Information
If multiple anomalies, consider aneuploidy syndromes
Trisomy 18
Rockerbottom feet classic finding
Hands with overlapping digits
Multiple other anomalies including cardiac, orofacial, extremity
Severe growth restriction the rule by late 2nd trimester
Trisomy 21
Extremity findings are often subtle “soft marker” findings
Extremity anomalies: “Sandal gap” foot & clinodactyly, short humeri & femora
Pattern of edema in hydrops rarely involves hands and feet
Increased nuchal thickening in 2nd trimester
Flat mid-face with hypoplastic nasal bone common
May see tongue thrusting behavior in 3rd trimester
Turner syndrome
Pattern of edema characteristic
Edema of the dorsum of hands & feet
Anasarca common
Often with large cystic hygroma
Female gender
Fetus with multiple anomalies: Transfer of care to a tertiary care center
Alternative Differential Approaches
Clubfoot with abnormal calvarium shape: Neural tube defect
Severe foot and extremity edema with cystic hygroma: Turner syndrome
Rockerbottom feet with other anomalies and growth restriction: Trisomy 18
Image Gallery