Abnormal First Trimester Fetus
Anne Kennedy, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
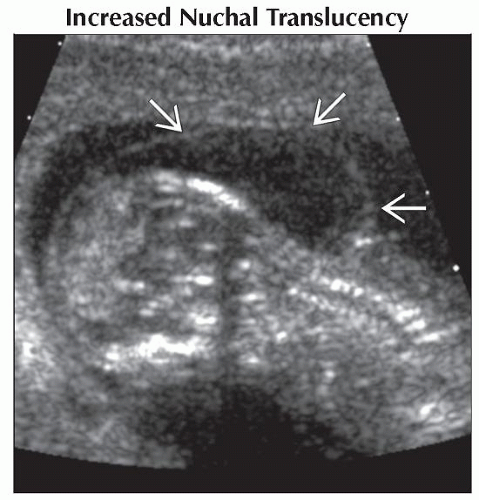
Increased Nuchal Translucency
Cystic Hygroma
Central Nervous System Anomalies, Severe
Congenital Heart Defects
Less Common
Absent Nasal Bone
Gastroschisis
Omphalocele
Conjoined Twins
Twin Reversed Arterial Perfusion
Rare but Important
Autosomal Recessive Syndromes
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Must know normal developmental anatomy to avoid erroneous diagnosis of anomaly
Brain: Infratentorial
Rhombencephalon = precursor of cerebellum and brain stem
Appears hypoechoic
Not to be mistaken for posterior fossa cyst
Brain: Supratentorial
Presence of complete falx excludes alobar/semilobar holoprosencephaly
Look for “butterfly” sign of choroids to exclude alobar/semilobar holoprosencephaly
Skull vault
Ossification visible by ∽ 12 weeks
Abdomen
Physiologic herniation of bowel is a normal embryological process
Bowel leaves peritoneum → base of umbilical cord → rotates 270° then re-enters abdominal cavity
Re-entry complete by 11.2 weeks gestational age
Never normal to see liver in base of cord
Limbs
Limb buds develop by 9 weeks
Femur can be measured by 13 weeks, visible earlier
Hands and feet fully formed by 13 weeks
Amniotic fluid
Produced by membranes in first trimester
Renal function does not account for majority of fluid volume until 16-17 weeks
Cannot exclude renal agenesis, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease on basis of normal fluid in first trimester
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Increased Nuchal Translucency
Check ductus venosus (DV) waveform
Abnormal DV waveform = ↑ risk of adverse outcome even if chromosomes normal
Trisomy 21
Look for associated absent nasal bone, atrioventricular septal defect
Cystic hygroma/skin edema in Down syndrome is truncal
Trisomy 18
Look for associated omphalocele, complex congenital heart disease
Trisomy 13
Look for associated alobar holoprosencephaly, cyclopia, proboscis
Turner syndrome
Fetuses often hydropic
Look for “domed” extremity edema, Down syndrome edema more truncal
Cystic Hygroma
Look for internal septations on axial images
Look for other stigmata of Down/Turner syndrome
Central Nervous System Anomalies, Severe
Exencephaly
No skull vault echo
Brain seen “too well” initially with eventual destruction
Look for amniotic bands as etiology
Anencephaly
Look for “frog eye” appearance
No skull or brain above orbits
Occipital encephalocele
Confirm defect from different scan planes to avoid confusion with cystic hygroma
Alobar holoprosencephaly
Butterfly sign of choroid will be absent
Look for monoventricle/fused thalami
Congenital Heart Defects
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Absent Nasal Bone
Midsagittal plane
Normal appearance is 2 bright echoes, one from skin, shorter, brighter echo from bone
Gastroschisis
Bowel loops free in amniotic fluid, no surrounding membrane
Cord inserted on abdominal wall, defect usually to the right
Omphalocele
Membrane bound defect
Cord inserted at apex of defect
Never normal to see liver involved in physiologic bowel herniation into base of cord
Conjoined Twins
Monochorionic monoamniotic gestation
Fixed relationship of embryos/fetuses with contiguous skin covering
Twin Reversed Arterial Perfusion
TRAP: One normal “pump” twin
One anomalous twin
Diffuse truncal edema
Often subcutaneous cysts in edematous tissues
Absent or rudimentary cranial vault
Always check direction of flow in umbilical artery of an anomalous twin
Will be toward the anomalous fetus in TRAP
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Autosomal Recessive Syndromes
25% recurrence risk, early diagnosis allows intervention for poor outcome conditions
Meckel Gruber Syndrome
Occipital encephalocele, renal cystic dysplasia, polydactyly
Achondrogenesis 1A, 1B
Severe micromelia, poor spine ossification, hydrops
Other Essential Information
NT measurement technique
Midsagittal scan plane
Neutral head position
Use (+) not (x) cursors
Show amnion separate from nuchal skin
Transvaginal ultrasound mandatory for adequate resolution of anomalies
Normal first trimester scan does not exclude all anomalies
Some entities change progressively over time
Coarctation/aortic stenosis may not have significant hemodynamic effects until third trimester
Aqueductal stenosis often presents as hydrocephalus in 3rd trimester
Image Gallery
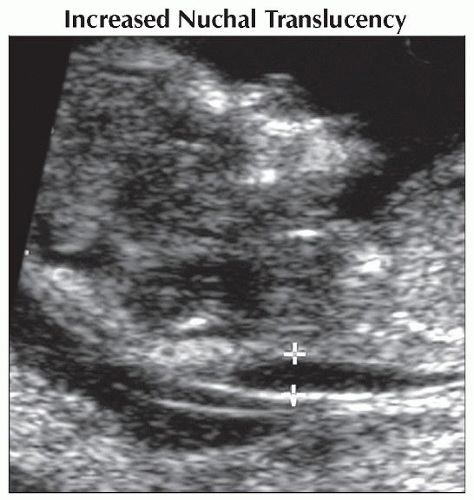 Sagittal ultrasound shows typical increased nuchal translucency (calipers) of 3 mm in a fetus with trisomy 21. In the second trimester nuchal fold skin thickening and brachycephaly developed. |
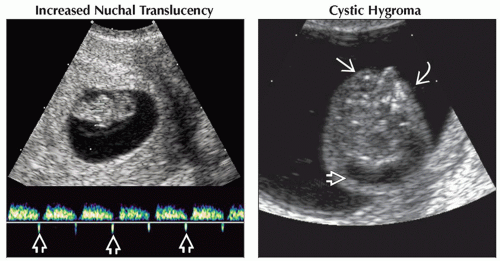 (Left) Pulsed Doppler ultrasound at 9 weeks shows abnormal ductus venosus flow with reversal during the A wave
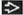 . Follow-up at 13 weeks showed ↑ nuchal translucency. At birth infant had a non-lethal, short-limbed, skeletal dysplasia. (Right) Axial transvaginal ultrasound in a fetus with cystic hygroma . Follow-up at 13 weeks showed ↑ nuchal translucency. At birth infant had a non-lethal, short-limbed, skeletal dysplasia. (Right) Axial transvaginal ultrasound in a fetus with cystic hygroma 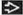 shows only right globe shows only right globe  & suggests hypoplastic left midface & suggests hypoplastic left midface 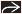 . The brain also looked abnormal. Pregnancy termination revealed both trisomy 21 & trisomy 9. . The brain also looked abnormal. Pregnancy termination revealed both trisomy 21 & trisomy 9.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|