Abnormal Fetal Presentation
Roya Sohaey, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Occiput-Posterior
Complete Breech
Frank Breech
Footling Breech
Less Common
Transverse Lie
Incomplete Breech
Rare but Important
Funic Presentation
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Normal presentation at term
Vertex and occiput-anterior
Back of head faces pubis
43% vertex at 15-22 weeks
90% vertex at 31-35 weeks
3-4% of term fetuses are breech
87% deliver by cesarean section
External cephalic version
40% success in nulliparous women
60% success in multiparous women
Etiology of malpresentation
Idiopathic
Prematurity
Placenta previa
Uterine anomaly
Abnormal fetal movement
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Occiput-Posterior
Vertex + face to pubis
Vaginal delivery attempted
Labor typically longer
Complete Breech
Buttocks presenting
Flexed legs (feet down)
Frank Breech
Buttocks presenting
Extended legs (feet up)
Footling Breech
Foot or feet presenting
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Transverse Lie
Fetus is sideways
Head in one flank, bottom in other
Obligatory cesarean delivery
Incomplete Breech
Hybrid of complete and frank breech
One leg extended and one leg flexed
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Funic Presentation
Umbilical cord slips in front of fetus
More common with nonvertex presentation
Cord may prolapse into vagina
Emergency cesarean delivery
Other Essential Information
Twins
Presenting twin vertex for vaginal delivery
Second twin position less important
Image Gallery
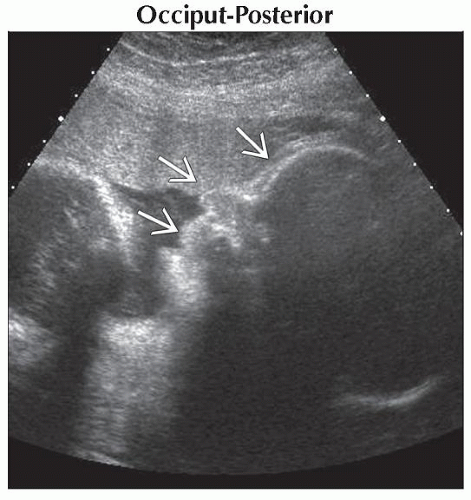 Sagittal ultrasound shows a late term fetus in a cephalic position; however, the face
 , not the occiput, is facing the anterior uterine wall. The finding may be relevant if the patient is in active labor. , not the occiput, is facing the anterior uterine wall. The finding may be relevant if the patient is in active labor.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|