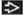Abnormal Fetal Posture/Movement
Janice L. B. Byrne, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
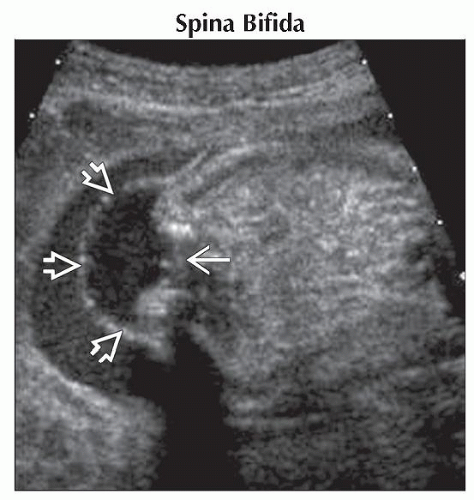
Spina Bifida
Trisomy 18
Arthrogryposis, Akinesia Sequence
Fetal Constraint
Less Common
Body Stalk Anomaly
Caudal Regression Sequence
Fetal Hypoxia/Severe Hypotonia
Amniotic Bands
Fetal Neck Masses
Joint Dislocation
Vertebral Segmentation Abnormalities
Rare but Important
Iniencephaly
Multiple Pterygium Syndrome
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Postural abnormalities
Is the abnormality fixed or does the position normalize with fetal movement?
Is the abnormal body posture associated with an obvious anomaly?
Fetal movement abnormalities
Is the movement abnormality progressive over time or an acute change?
Is there evidence of arthrogryposis?
Is there associated oligohydramnios, polyhydramnios, osteopenia or edema/hydrops?
Is the fetus normally grown?
Can normal movement be elicited by acoustic stimulation?
Normal sleep cycle vs. pathologic lack of movement
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Spina Bifida
Lack of movement of the lower extremities associated with clubfeet ± ventriculomegaly
Abnormal calvarium shape (“lemon” sign) with small abnormal posterior fossa (“banana” sign)
Trisomy 18
Arthrogryposis of multiple joints may be seen
Severe symmetrical growth restriction (IUGR) and multiple anomalies common
Arthrogryposis, Akinesia Sequence
Fixed contractures of multiple joints, often severe
Joint abnormalities due to fetal akinesia
Bilateral and symmetrical
Upper and lower extremities may be equally affected or discordant in severity
Associated polyhydramnios due to decreased swallowing
Skin edema, osteopenia, frank hydrops often late findings, especially in lethal cases
Fetal Constraint
Multiple gestation
Postural abnormalities due to crowding
True deformations may result (clubfeet, torticollis, plagiocephaly)
Fibroids
Large submucosal or multiple smaller fibroids
Uterine anomaly
Associated malposition common
Severe oligohydramnios
Premature rupture of membranes
Twin-twin transfusion donor twin
Severe IUGR, genitourinary anomalies
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Body Stalk Anomaly
Severe postural abnormalities
Rotary scoliosis with unusual angulation of extremities from the body axis
Lack of free floating umbilical cord
Large schisis defects of abdomen &/or thorax seen, often with adherence of defect to the placenta
Caudal Regression Sequence
Absent sacrum with hypoplastic lower extremities
Legs held in a fixed, “Buddha” or “crossed-legged tailor’s” posture
More common in poorly controlled diabetes
Fetal Hypoxia/Severe Hypotonia
Decreased or absent fetal breathing, tone and movement
Increased risk of fetal/neonatal birth asphyxia, neurologic injury, seizures
Chronic hypoxia from severe uteroplacental insufficiency
IUGR, oligohydramnios
Abnormal Dopplers with absent or reversed end diastolic flow, pulsatile ductus venosus
Causes of acute hypoxia
Abruptio placenta
Severe maternal hypoxemia (trauma, cardiopulmonary arrest, asphyxia)
Severe hypotonia: May be acute or chronic
Hyperextended or hyperflexed neck
Usually due to underlying neurologic abnormality
Amniotic Bands
Wide spectrum of disruptions, often associated with postural abnormalities
Fetus may appear tethered
Membrane strands may be visible in amniotic cavity
Fetal Neck Masses
Postural abnormality of neck may be progressive
Decreased fetal swallowing → development of polyhydramnios → increased risk of airway obstruction
Goiter
Neck hyperextension with large goiter
Sagittal view to evaluate position of head and neck; mode of delivery or airway at birth unlikely to be affected if normal neck flexion observed
Cystic hygroma (lymphangioma)
Large and asymmetrical masses lead to significant postural abnormality of head and neck
Joint Dislocation
More common in hips, knees
Vertebral Segmentation Abnormalities
Hemivertebrae, missing vertebral segments, abnormal ribs associated with scoliosis
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Iniencephaly
Persistent “stargazer” posture of head, neck due to fixed cervical hyperextension, cervical neural tube defect
Other malformations common
Multiple Pterygium Syndrome
Fixed joint contractures associated with abnormal posture
Pterygia may not be visualized on ultrasound
Cystic hygroma and hydrops in lethal type
Other Essential Information
Hydrops and polyhydramnios with arthrogryposis predict high risk for lethality
If decreased or absent fetal movement, search for evidence of acute or chronic condition
If acute, fetal hypoxia is likely and delivery may be life saving
If abnormal posture, evaluate for evidence of associated fetal or uterine abnormality to determine underlying cause
Image Gallery
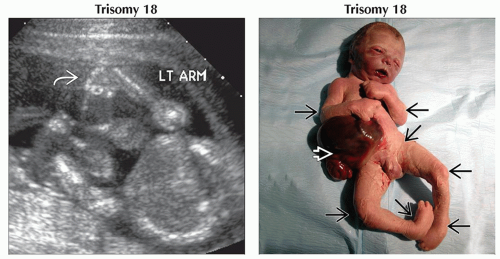 (Left) Transabdominal ultrasound shows a typical case of arthrogryposis associated with trisomy 18. The hand
 was persistently held in an abnormal orientation to the wrist. The legs were held in extension, and the left foot was clubbed. (Right) Clinical photograph shows a stillborn term infant with trisomy 18. Arthrogryposis with multiple joint contractures can be seen was persistently held in an abnormal orientation to the wrist. The legs were held in extension, and the left foot was clubbed. (Right) Clinical photograph shows a stillborn term infant with trisomy 18. Arthrogryposis with multiple joint contractures can be seen  . A large omphalocele is also apparent . A large omphalocele is also apparent  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|