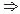Abnormal Calvarium
Anne Kennedy, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Abnormal Shape
Poor Scan Technique
Dolichocephaly
Brachycephaly
“Lemon-Shaped”
“Strawberry-Shaped”
Round
Spaulding Sign
Craniosynostosis
Calvarial Defect
Exencephaly, Anencephaly
Encephalocele
Amniotic Band Syndrome
Abnormal Size
Macrocephaly
Microcephaly
Less Common
Decreased Ossification
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Achondrogenesis
Hypophosphatasia
Scalp Masses
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Assess calvarial size, shape, and mineralization in all cases
Size
Is size concordant with gestational age and other biometric parameters?
Shape
Can you see standard scan plane anatomy?
If not, is it because of fetal position or maternal habitus?
Use transvaginal sonography for better resolution
3D ultrasound allows volume acquisition
Data manipulation allows reproduction of true axial plane
Mineralization
Skull is formed after 10 weeks; use EV sonography from 10-14 weeks for better resolution if questions
If brain seen “too well” consider conditions with poor mineralization
Transducer pressure cannot deform a normally ossified cranium
Is there a bony defect?
Essential to look at skull vault from several scan planes
Refraction of beam may create an apparent defect where none exists
Cystic hygroma may be mistaken for an occipital encephalocele
Must know normal anatomy: Do not mistake metopic suture for frontal encephalocele
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Poor Scan Technique
Make sure thalami and cavum septi pellucidi are visible
Dolichocephaly
Boat shaped: Long back-to-front, narrow side-to-side
Seen with breech presentation, oligohydramnios, myelomeningocele
Brachycephaly
Short back-to-front, wide side-to-side
Described in trisomy 21
“Lemon-Shaped”
Bifrontal concavity seen with Chiari II malformation
Resolves in third trimester in all cases
Occurs in various other conditions and 1% of normal fetuses
“Strawberry-Shaped”
Triangular configuration described in trisomy 18
Most fetuses with trisomy 18 have multiple other anomalies
Round
May be technical if measurement obtained in wrong scan plane
If normal anatomic markers are not identified and head shape appears round from multiple acoustic windows, underlying brain is usually abnormal
Look carefully for signs of aprosencephaly/holoprosencephaly spectrum
Spaulding Sign
Bones of skull vault overlap as brain collapses following demise
Craniosynostosis
Abnormal head shape secondary to premature closure of sutures
Look for features of associated conditions (e.g., Crouzon, Pfeiffer, Apert, skeletal dysplasia)
Exencephaly, Anencephaly
Exencephaly: Lack of cranial vault but brain tissue present
Anencephaly: Cranial vault absent, no brain tissue, skull base contains gelatinous angiomatous stroma
Encephalocele
Occipital: Herniation of intracranial structures through an occipital defect
Look for other anomalies/signs of aneuploidy
Frontal: Herniation of intracranial structures through an anterior skull defect
Look for associated hypertelorism, callosal dysgenesis, midline lipoma
Amniotic Band Syndrome
Look for linear echoes from bands in amniotic fluid
Look for associated extremity amputation or constriction defects
Macrocephaly
Enlarged head: Biparietal diameter (± head circumference) > 2 SD above mean
Look for underlying abnormalities (e.g., hydrocephalus, tumor, megalencephaly)
Microcephaly
Small head: Biparietal diameter (± head circumference) > 2 SD below mean
Seen with infection, ischemia, syndromes, malformations
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Associated with fractures in long bones, beaded ribs
Achondrogenesis
Hallmark is lack of vertebral ossification
Hypophosphatasia
Associated with micromelia and thin, bowed bones in perinatal lethal form
Scalp Masses
Calvarium normal
Mass (e.g., lymphangioma, hemangioma) arises from scalp
Other Essential Information
Technique very important in head measurement and evaluation of calvarial contour
Biparietal diameter (BPD)
Measure at level of thalami and cavum septi pellucidi
Cerebellar hemispheres should not be visible
Midline echoes in center of oval-shaped cross-section
Measure outer edge proximal skull to inner edge distal skull
Head circumference: Measure at outer edge of skull in same plane as BPD