Chapter 7. X-rays
The questions in this chapter cover a variety of appearances. In all questions interpretation of the X-ray will be needed. In many the probable diagnosis and a management plan will also be expected.
QUESTIONS
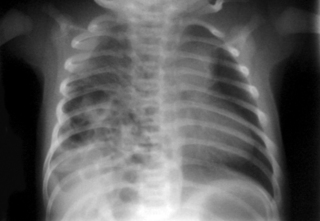
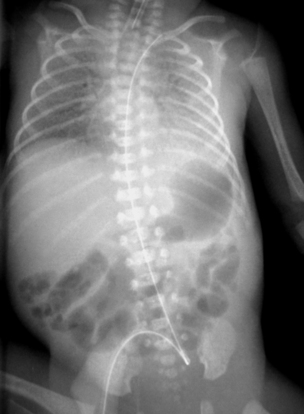
2. A 28 week baby is 10 days old. Abdominal distension has been noted and the following X-ray is obtained.
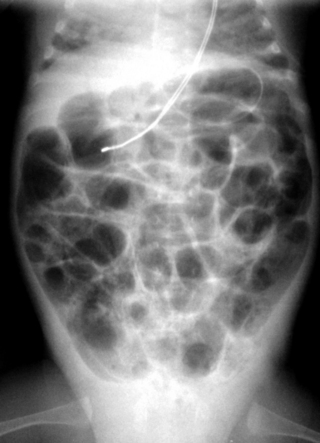 |
| Figure 7.2. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What is the diagnosis?
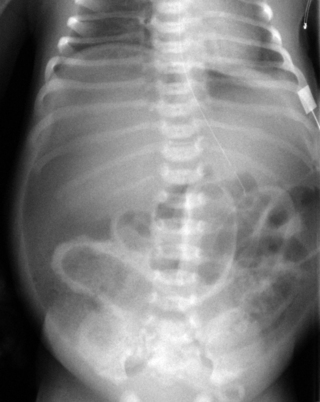
3. The same baby as in question 2 is reviewed a few hours later. His abdomen has become more distended and discoloured. The following abdominal X-ray is obtained.
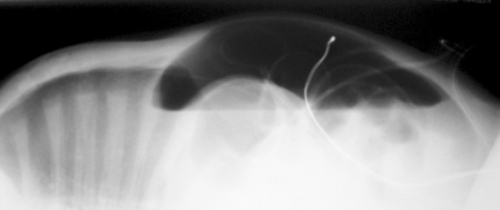 |
| Figure 7.3. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What is the diagnosis?
c. What is the management of this baby?
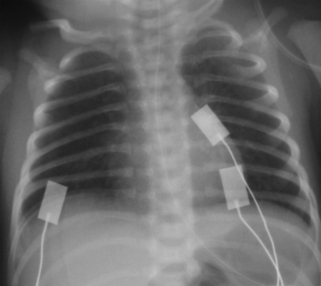
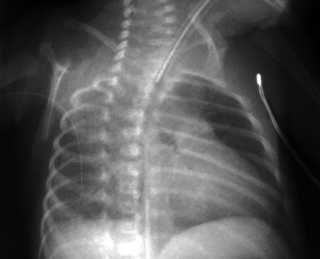
4. A 37 week gestation baby is noted to have frequent small vomits. At 24 hours of age he is noted to be tachypnoeic and he is admitted to the neonatal unit. A chest X-ray is obtained.
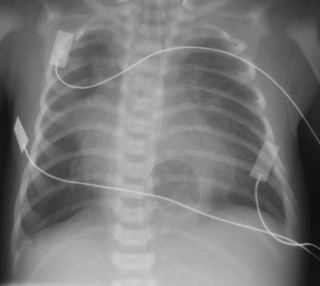 |
| Figure 7.4. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What are the diagnoses?
c. What is the management of the baby?
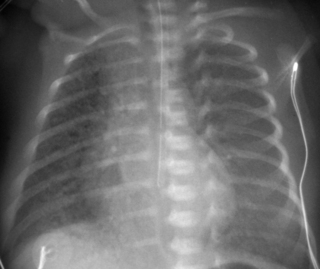
6. A 27 week infant is ventilated for RDS. Ventilatory requirements have increased over the last hour. A chest X-ray is obtained.
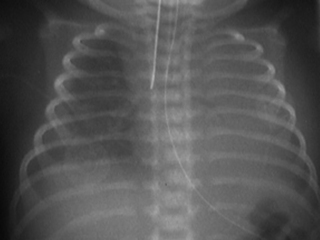 |
| Figure 7.6. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What is the management of the baby?
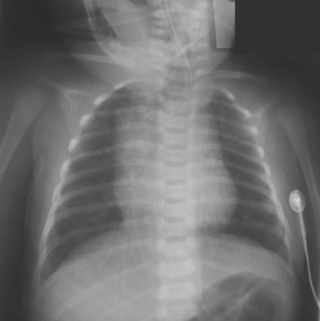
7. A term baby is noted to have a degree of frontal bossing, as does his mother. A chest X-ray is performed.
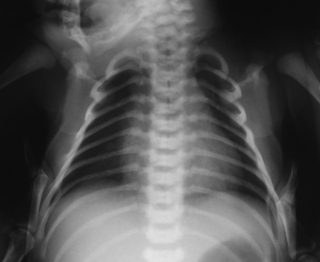 |
| Figure 7.7. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What is the diagnosis?
c. What is the inheritance of this condition?
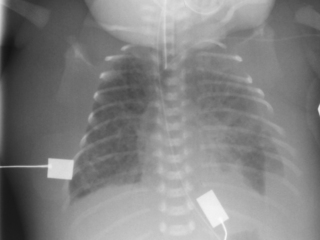
8. A 29 week gestation baby has been on CPAP for moderate respiratory distress and has been stable in 35% oxygen. He is active and has been noted to have quite marked intercostal recession on occasion. He suddenly deteriorates with persistent recession and an increase in oxygen requirements to 95%. A chest X-ray is taken.
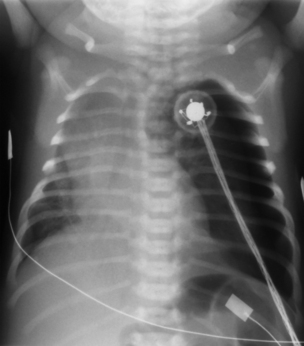 |
| Figure 7.8. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What is the management of the baby?
9. A 27 week gestation infant is ventilated for respiratory distress. Ventilation requirements have been moderately high and two doses of surfactant have been given. Oxygen requirements have steadily risen from 55% to 95%. In response to a profound bradycardia and desaturation he receives ventilation down his endotracheal tube using a resuscitation bag. He deteriorates further and a chest X-ray is obtained.
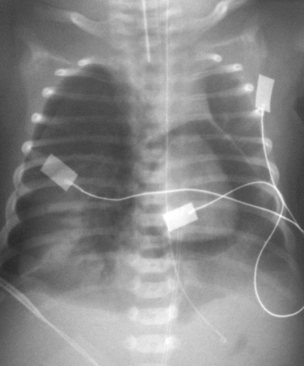 |
| Figure 7.9. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What is the management of the baby?
10. A 31 week gestation infant is admitted to the intensive care unit. Mother booked late and there has been minimal antenatal care. The baby needs resuscitation at delivery and is transferred to the unit ventilated. Ventilation proves very difficult and a chest X-ray is obtained.
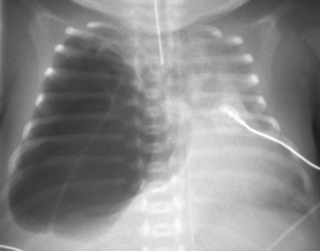 |
| Figure 7.10. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What is the differential diagnosis?
c. What is the management of the baby?
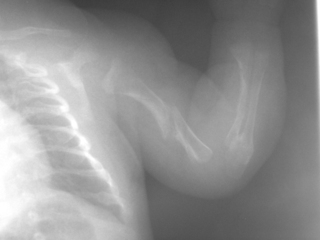
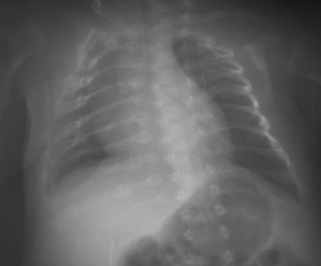
12. A term baby is thought to have an absent Moro reflex and limited movement of the arm. An X-ray is taken. In view of these changes a chest X-ray is then performed.
 |
| Figure 7.12a. |
 |
| Figure 7.12b. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the arm X-ray.
b. Describe the abnormalities on the chest X-ray.
c. What is the most likely diagnosis?
d. What management would you consider?
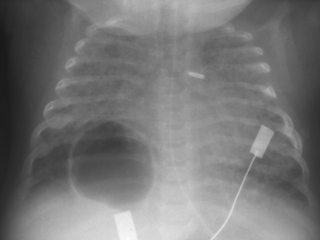
13. A 27 week gestation infant is now 4 weeks old. She needs 0.4 L/min supplementary oxygen but this has recently risen to 0.8 L/min. A chest X-ray is performed.
a. Describe the abnormalities on the X-ray.
b. What management has this baby had in the past that is clearly evident on the X-ray?
c. What management will you initiate in response to the abnormality on this chest X-ray?
 |
| Figure 7.13. |
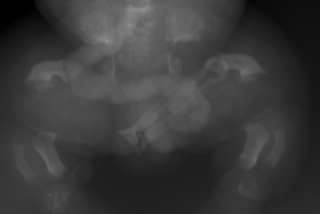
14. Antenatal ultrasounds have suggested a growth retarded fetus. At birth, the baby has obvious limb abnormalities and requires ventilation. Limb and chest X-rays are performed.
 |
| Figure 7.14a. |
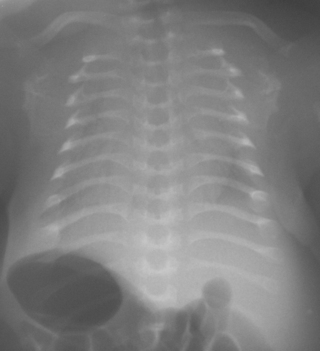 |
| Figure 7.14b. |
a. Describe the abnormalities on the limb X-ray.
b. Describe the abnormalities on the chest X-ray.
c. What is the most likely diagnosis?
d. What is the prognosis?
15. A baby is born at term and is noted to be cyanosed at rest. There is moderate recession. There is bilateral lower limb oedema. Femoral pulses are weak. The anterior fontanelle is bulging and a loud bruit can be heard when listening over it. A chest X-ray is performed.
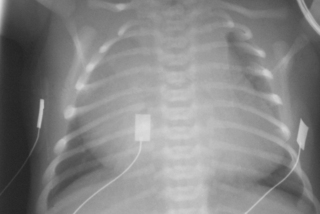 |
| Figure 7.15. |
a. What abnormalities are there?
b. What possible explanation do you have?
c. What initial further investigations would you consider?
16. A baby is born at 26 weeks and requires ventilation from birth. Surfactant was given on delivery suite. Ventilation has steadily increased and the baby is in 95% oxygen at pressures of 28/6 at 24 hours of age. Blood gases are poor. A chest X-ray is performed.
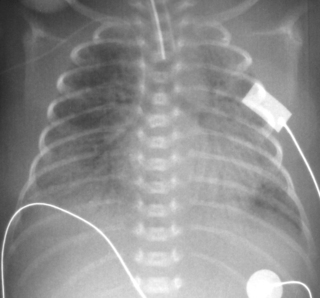 |
| Figure 7.16. |
a. What abnormalities are there?
b. What is the most likely diagnosis?
c. What treatment would you consider?
17. A term infant is born following a severe asphyxial insult. There is thick meconium present and the oro-pharynx and trachea are suctioned under direct vision and meconium is removed. Ventilation is required and requirements steadily increase. At 8 hours of age the pressures are 32/4 and 100% oxygen is required. The blood gas shows a pH of 7.01, PO 2 of 3.4 and PCO 2 of 7.2.
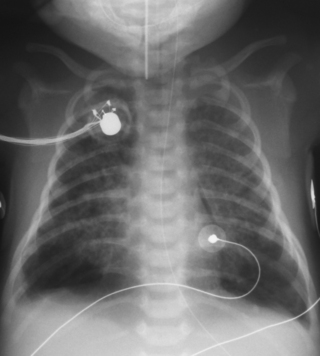 |
| Figure 7.17. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. What is the diagnosis and what complication may be present?
c. What action could be taken?
18. A 36 week gestation infant has mild respiratory distress at birth. He requires 30% oxygen and there is mild recession. As symptoms persist an X-ray is performed at 6 hours of age.
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. If this is the only problem with the baby, what is the most likely diagnosis?
c. If the baby is asymptomatic, what should you do?
d. If the baby is symptomatic, what would you consider?
e. What other investigations would be warranted?
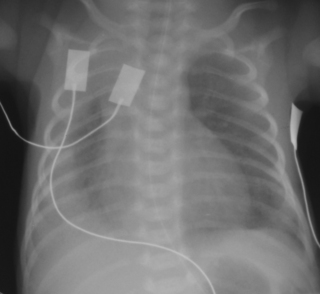 |
| Figure 7.18. |
19. A term infant is born by elective caesarean section because of previous caesarean sections. Shortly after birth the baby is noted to be mildly dusky and grunting and there is mild recession. A septic screen is performed and a chest X-ray obtained. Antibiotics are started.
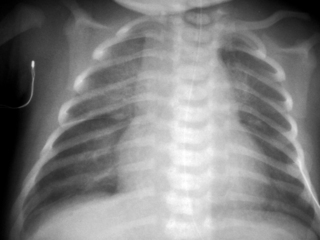 |
| Figure 7.19. |
a. What abnormality is seen on this X-ray?
b. What is the most likely diagnosis?
c. What management steps do you need to take?
d. What is the prognosis for the baby?
21. A 26 week infant is in 0.5 L/min of supplementary oxygen at 36 weeks corrected age. He has mild recession and capillary gases show a fully compensated respiratory acidosis. A chest X-ray is taken as part of a work-up for chronic lung disease.
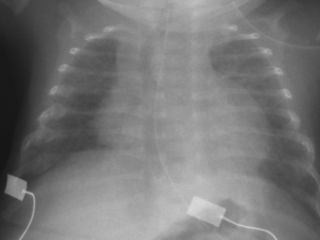 |
| Figure 7.21. |
a. Describe the X-ray.
b. What is the likely diagnosis?
22. A baby born at 24 weeks gestation is 2 weeks old. He has been stable on low ventilation pressures but has not tolerated CPAP. Attempts have been made to start nasogastric feeds on several occasions but he does not appear to tolerate them as there are reasonable volume gastric aspirates on most occasions. Over the last 48 hours the aspirates have become increasingly bilious and an abdominal X-ray is taken.
a. Describe the X-ray abnormalities.
b. What is the diagnosis?
c. What is this diagnosis commonly associated with?
d. What is your immediate management plan?
e. What is the likely outcome for this baby?
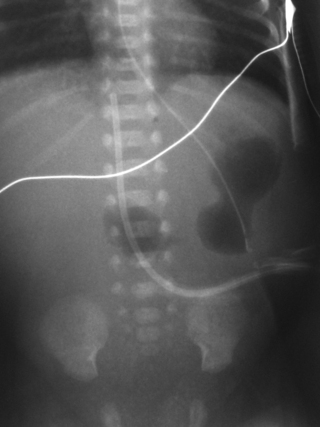 |
| Figure 7.22. |
23. A 26 week infant has been ventilated for RDS. He was weaned onto CPAP after 16 days and was initially stable. Six days after starting CPAP his oxygen requirements started to rise (from 35% to 65%) and he was commenced on a course of dexamethasone; 36 hours after starting dexamethasone he deteriorates substantially. An X-ray is taken.
 |
| Figure 7.23. |
a. What abnormalities are seen on this X-ray?
b. What is the diagnosis?
c. What is your management plan?
24. A term baby becomes cyanosed 6 hours after birth. Increasing the inspired oxygen concentration only partially treats this. On examination the chest is clear and there are no abnormal sounds. A chest X-ray is obtained.
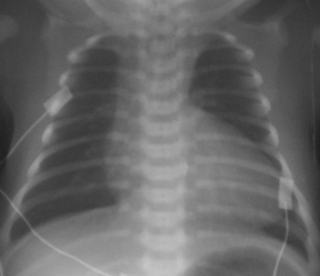 |
| Figure 7.24. |
a. Describe the chest X-ray.
b. What is your diagnosis?
c. What will you do next?
26. A term infant is born to a mother who is known to have insulin dependent diabetes. He is grunting from birth and oxygen saturations are poor. A chest X-ray is obtained.
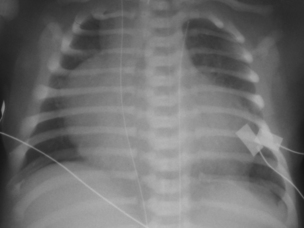 |
| Figure 7.26. |
a. Describe the X-ray.
b. What is your diagnosis?
c. What will you do next?
27. A 32 week gestation infant has been born. There has been a 10-week history of oligohydramnios. The baby has required ventilation from birth. Blood gases are poor at high ventilation pressures. A chest X-ray is taken at 3 hours of age.
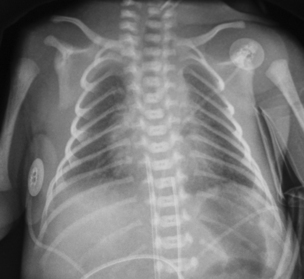 |
| Figure 7.27. |
a. Describe the X-ray.
b. What is your diagnosis?
30. A 28 week gestation infant has been ventilated for 12 days. He is now 6 weeks old and requires 0.6 L/min of oxygen. A chest X-ray is taken.
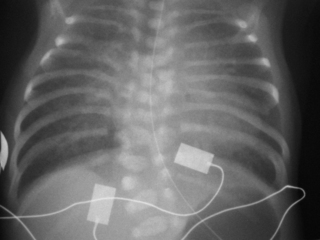 |
| Figure 7.30. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. What action will you take?
31. A 25 week gestation infant has been ventilated since birth and is now 9 days old. A chest X-ray is taken.
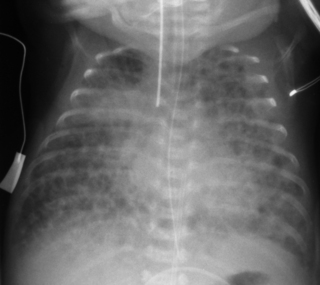 |
| Figure 7.31. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. What is responsible for these changes?
32. A 26 week gestation infant has received one dose of surfactant in the delivery room and a further dose 12 hours later. A chest X-ray is taken at 24 hours of age.
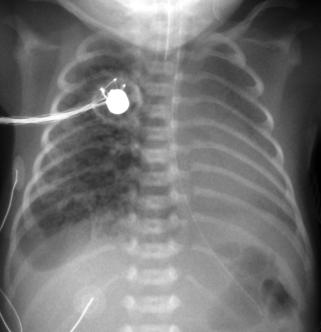 |
| Figure 7.32. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. What do you think has happened?
c. What will you do next?
33. A baby is born at 36 weeks to a mother with insulin dependent diabetes. He does not tolerate feeds and abdominal distension is noted. A chest and abdominal X-ray is taken at 36 hours of age.
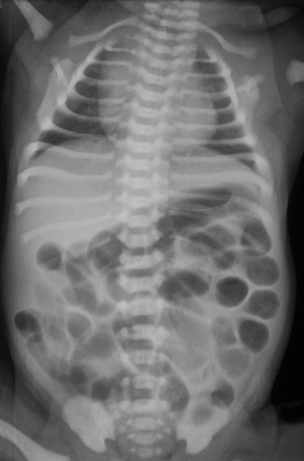 |
| Figure 7.33. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. What do you think has happened?
c. What will you do next?
34. A term infant shows minimal respiratory effort and requires ventilation. A chest X-ray is taken. On talking to the parents you notice that the mother shows little expression in her facial movements.
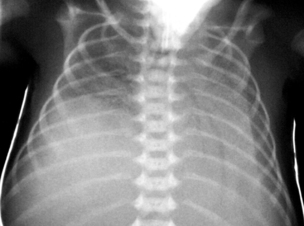 |
| Figure 7.34. |
a. Describe the X-ray?
b. What do you think may be the explanation for these appearances?
c. What will you do?
35. A 25 week gestation infant has been ventilated since birth. Three doses of surfactant have been given with little effect. A chest X-ray is taken at 48 hours of age.
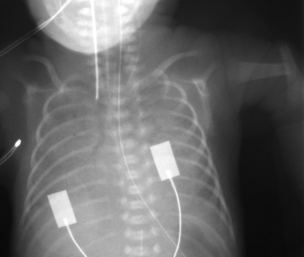 |
| Figure 7.35. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
37. A 24 week infant requires ventilation from birth and is now 4 weeks old. He is known to have duodenal atresia but the surgeons do not want to operate until he is a lot bigger. He has been to theatre for a surgical procedure. A chest X-ray is taken to check that the procedure has been performed correctly. The appearance of the right lung is as it has been since birth.
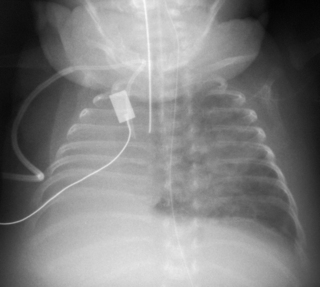 |
| Figure 7.37. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. What was the surgical procedure?
c. What is the explanation for the appearances of the right lung?
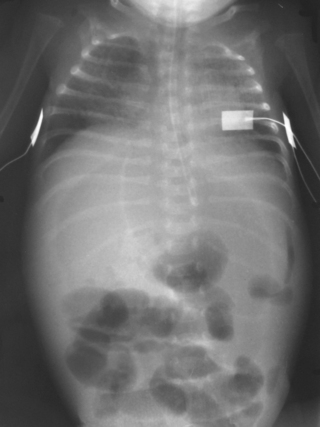
38. A 28 week gestation infant has been born and has needed relatively little ventilatory support. Feeds are introduced on day 3 and increased slowly. On day 5 he deteriorates and there is obvious abdominal distension. An X-ray is obtained.
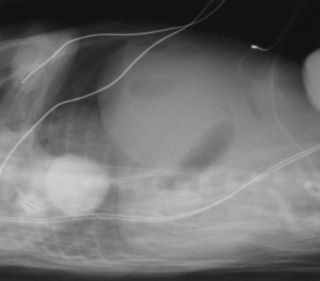 |
| Figure 7.38. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
b. What do you think has happened?
c. What will you do next?
39. A term infant is born in poor condition following an ante-partum haemorrhage. The infant takes a few deep gasps and then stops breathing. Heart rate is 57 bpm. Bag and mask ventilation is commenced. There is poor chest movement and there is little response to ventilation. Transillumination is performed and there is no difference between the two sides. An endotracheal tube is inserted and ventilation does not improve. A butterfly needle is inserted into the right chest. A few bubbles are seen but this then stops. An X-ray is taken.




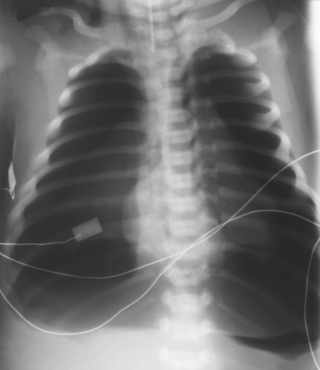 |
| Figure 7.39. |
a. What does the X-ray show?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree