Chapter 50 Teaching Visual
Lumbar Puncture
Medical Knowledge
Before Starting the Procedure
Contraindications to performing an LP:
• Increased intracranial pressure (ICP): If there is clinical suspicion of increased ICP, LP should not be performed. Fundoscopic examination of the eye, as well as a CT scan of the head, may be required to rule out intracranial mass lesions. A negative CT scan of the head does not rule out increased ICP definitively, but it does help to rule out the risk for herniation.
• Thrombocytopenia: Most clinicians will not perform an LP if the patient’s platelet count is less <50,000.
• Unstable patient: For example, if the patient is unable to be safely positioned for the LP because of compromised respiratory status
If the above conditions have been excluded, it should be safe to proceed with the procedure.
Beginning the Procedure
Positioning the Patient
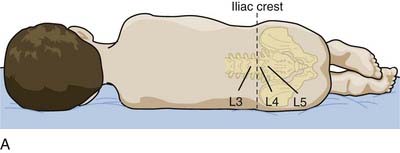
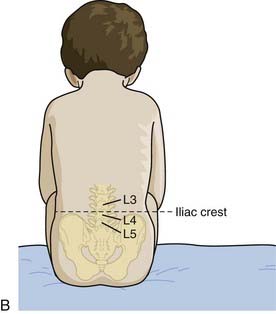
There are two ways of positioning patients for an LP (Figure 50-1):
• Lateral recumbent position
• An assistant helps by flexing the patient’s neck and drawing the patient’s knees to the patient’s chest.
An imaginary line between the iliac crests should intersect the midline just above the L4 vertebra (see Figure 50-1).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree