Chapter 8. Scans
More recently, the availability of high quality magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has increased, and the detail possible with this technique may be invaluable in the assessment of infants with congenital neurological abnormalities or those who have suffered an episode of perinatal asphyxia.
This chapter contains ultrasound, CT and MRI scans along with relevant clinical histories. As with x-rays, interpretation is required as well as proposed management in some. In others you will be asked to comment upon the possible long-term significance of the abnormality that has been detected. There are many textbooks available for reference. 123 and 4
QUESTIONS
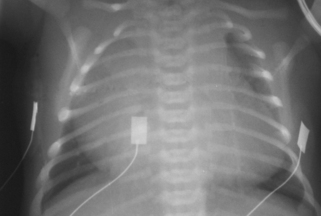
2. The same infant had the following chest x-ray taken.
a. Describe the chest x-ray.
b. What is the diagnosis from the chest x-ray?
c. How is this image linked with the MRI scan?
 |
| Figure 8.2. |
3. A term baby is born following a difficult vaginal delivery. No resuscitation is required and he is returned to his mother. Paediatricians are asked to review him at 18 hours of age as it is thought that he may have made some abnormal movements. He appears well on examination and an MRI scan is performed.
 |
| Figure 8.3. |
4. A preterm baby, born at 28 weeks’ gestation has a follow-up scan carried out at 34 weeks corrected gestational age.
 |
| Figure 8.4. |
a. What type of scan is this?
b. What does it show?
c. Why has this happened?
d. What is the outlook for this baby?
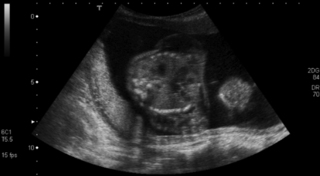
5. This scan was carried out on a 25 week gestation infant, who is now 72 hours old. He had a very stormy first two days, requiring maximal inotropic support and high ventilatory pressures. He is now requiring no blood pressure support and is on minimal ventilation.
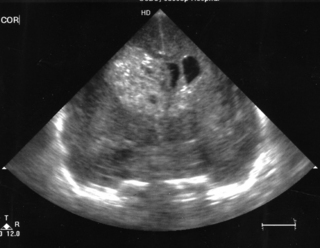 |
| Figure 8.5. |
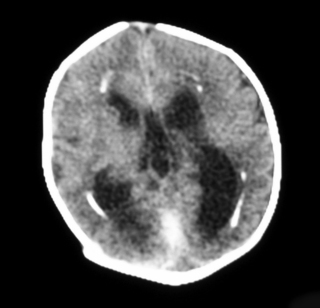
6. A 27 week gestation baby has a routine head scan performed at 2 days of age.
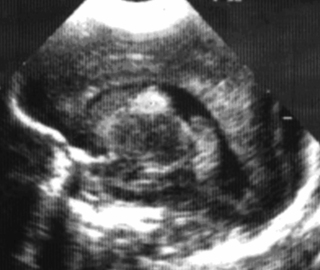 |
| Figure 8.6. |
a. Describe the scan.
b. Will this affect the baby’s long-term outcome?
7. A routine head scan is performed in a 29 week gestation infant. Parents want to know what it shows and whether it means that their baby is going to be normal or not.
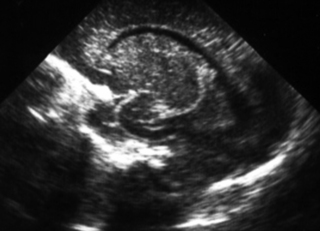 |
| Figure 8.7. |
a. Describe the scan.
b. What is the likely outcome for this baby?
9. This scan was carried out on day 7 in an ex-26 week gestation infant.
a. Describe the scan.
b. What is the most likely cause?
c. What is your management?
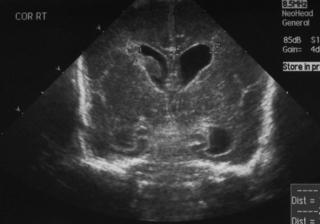 |
| Figure 8.9. |
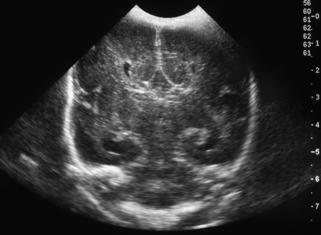
11. This is a routine scan carried out on a baby born at 30 weeks’ gestation who requires no ventilatory support and is tolerating full milk feeds by 5 days of life.
 |
| Figure 8.12. |
a. Describe the scan.
b. What is the diagnosis?
c. What is the outcome for this baby?
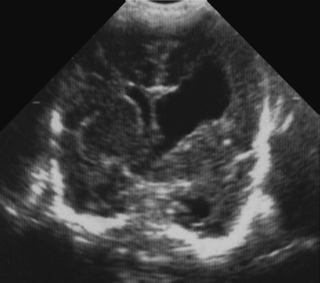
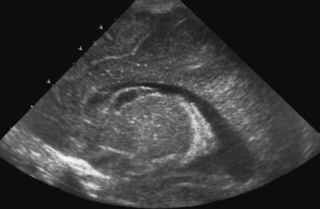
13. A 29 week infant has a routine cranial ultrasound scan performed.
 |
| Figure 8.14. |
a. Describe the scan.
b. Why has this happened?
c. What is the outlook for this baby?
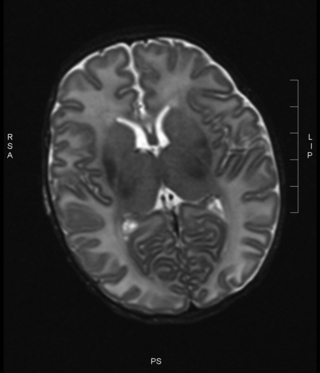
14. A baby is born at term through meconium-stained liquor and requires full resuscitation. She has seizures noted at 1 hour of age and is given a loading dose of phenobarbitone. She is ventilated for the first 12 hours and then copes without respiratory support. She has established feeding by day 7 and is discharged at day 10. An MRI is carried out the day before discharge.
 |
| Figure 8.15. |
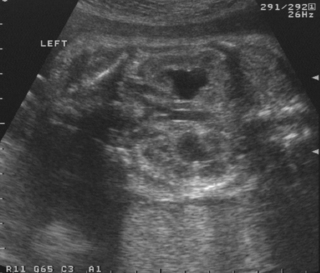
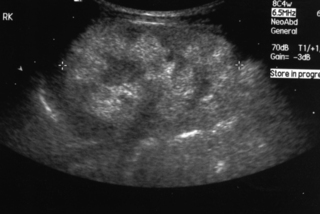
15. A baby girl is delivered by caesarean section for failure to progress. She has a large abdomen at birth with masses palpable bilaterally.
 |
| Figure 8.16. |
a. Describe the scan.
b. What is the likely diagnosis?
c. What problems might the baby have?
d. What are the known associations?
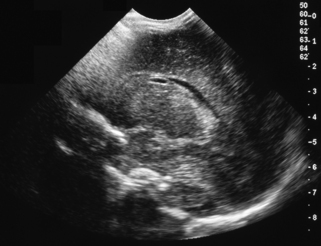
16. A routine cranial ultrasound scan is carried out on a 31 week gestation infant.
 |
| Figure 8.17. |
a. Describe the scan.
b. What is the diagnosis?
c. What is the outlook for this baby?
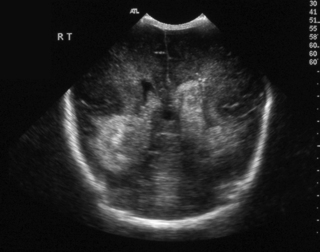
17. A baby born at 36 weeks gestation has severe RDS with a history of prolonged rupture of membranes for 5 days. He is treated with antibiotics and is transferred for high frequency oscillation ventilation. He was initially hypotensive requiring maximal inotropic support. A scan is carried out on day 3 after transfer.
a. Describe the scan.
 |
| Figure 8.18a. |
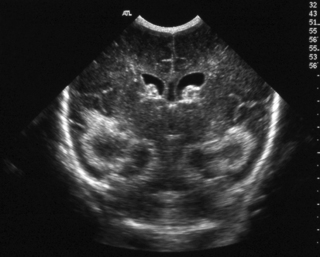
A few days later, a further scan was obtained.
b. Describe the changes.
 |
| Figure 8.18b. |
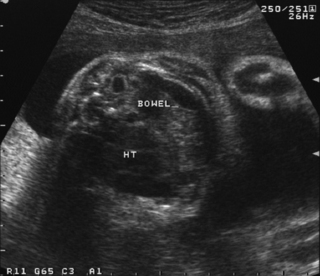
19. A woman is scanned antenatally at 30 weeks.
 |
| Figure 8.20. |
a. What does the scan show?
b. What will be your management of the baby at birth?
c. What are the baby’s chances of survival?
21. A woman is referred for a detailed fetal scan and has been found to have a raised alphafetoprotein.
a. What is the abnormality on this scan?
b. What other investigations would you carry out postnatally?
c. What conditions is this anomaly associated with?
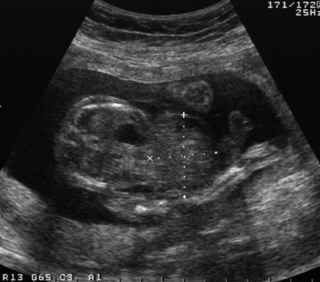 |
| Figure 8.22. |
22. A term infant is born vaginally following a rapid delivery. At 24 hours of age she is noted to be irritable and feeding is poor. A cranial ultrasound is performed and raises some concerns. Another investigation is performed.
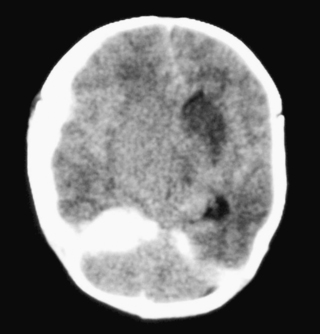 |
| Figure 8.23. |
23. An infant is noted on postnatal examination to have a large head circumference, with a bulging fontanelle. He is asymptomatic and feeding well by bottle. An MRI scan is performed.
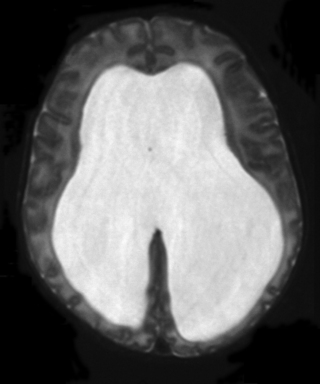 |
| Figure 8.24. |
a. Is this a T1 or T2 weighted MRI?
b. What does it show?
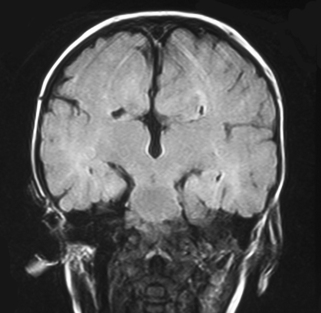
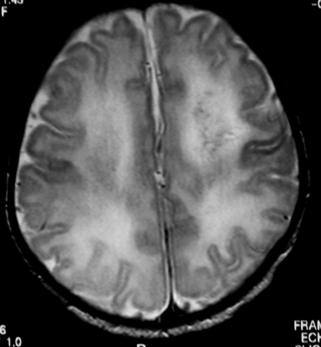
25. An MRI scan is carried out on a six month old infant.
a. Describe two abnormalities with this scan.
b. What is the likely cause?
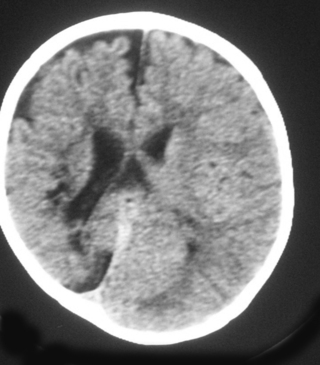 |
| Figure 8.26. |
27. A cranial ultrasound scan is carried out in a 25 week infant. She has been transferred in for intensive care from a level 2 unit. She seemed to be relatively stable for the first 24 hours after birth but at the age of 26 hours becomes acidotic and pale and required fluid resuscitation and increasing ventilation. A scan is carried out and is shown. Describe the scan.
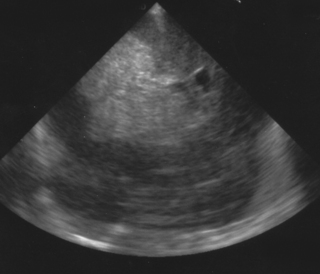 |
| Figure 8.28. |
ANSWERS
1.
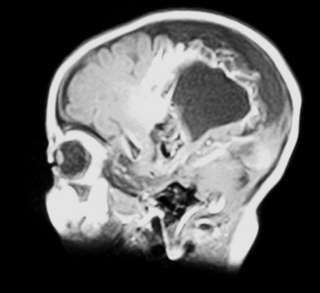
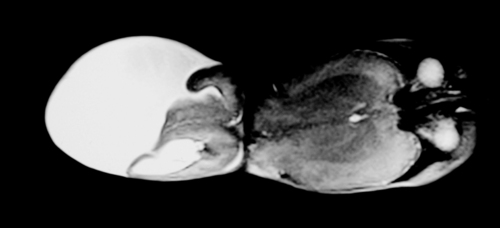
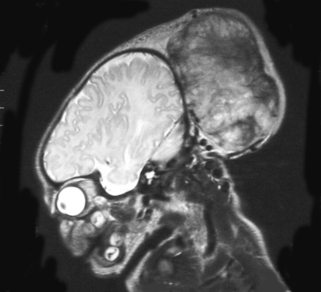
a. This is an MRI scan of the brain.
b. It shows a loss of cortex in the centre of the brain with an area filled with fluid. There is also increased extra-axial fluid around the brain. Blood vessels are tortuous and highlighted on the scan above the area filled with fluid.
2.




a. The chest x-ray shows a grossly enlarged heart with very little lung tissue visible.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree