Professor’s Pearls
Section IV: The Newborn Nursery
1 Case: You are seeing a 3-day-old infant in the nursery. She was born vaginally at term to a 21-year-old G1P0. Prenatal testing results were normal. Maternal and infant blood type is O Rh-positive. The infant is breastfeeding. Her birth weight was 3500 g, and her current weight is down 10%. She appears jaundiced to the nipple line. Otherwise her physical examination is normal. She is scheduled for discharge today. How do you proceed?
2 Case: You are called to the newborn nursery to evaluate a 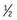 -hour-old female infant with respiratory distress. She was born at 36-
-hour-old female infant with respiratory distress. She was born at 36-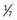 weeks’ gestation, by cesarean delivery for breech presentation to a 36-year-old G3P2002. Mother presented in labor, and the infant was found to be breech. Membranes were ruptured for 6 hours. Maternal laboratory test results were normal except group B streptococcus was positive. Mother was treated with one dose of clindamycin IV before the cesarean delivery. Apgar scores were 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Over the next 20 minutes the infant began to develop tachypnea, grunting, and retractions. At the time of your examination, temperature is 37.2°C heart rate, 150 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 75 breaths per minute. Pulse oximetry is 87% on room air. Her examination is significant for crackles bilaterally at the lung bases, as well as grunting, retractions, and nasal flaring. There are no murmurs. She is vigorous. What is your approach to this patient?
weeks’ gestation, by cesarean delivery for breech presentation to a 36-year-old G3P2002. Mother presented in labor, and the infant was found to be breech. Membranes were ruptured for 6 hours. Maternal laboratory test results were normal except group B streptococcus was positive. Mother was treated with one dose of clindamycin IV before the cesarean delivery. Apgar scores were 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Over the next 20 minutes the infant began to develop tachypnea, grunting, and retractions. At the time of your examination, temperature is 37.2°C heart rate, 150 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 75 breaths per minute. Pulse oximetry is 87% on room air. Her examination is significant for crackles bilaterally at the lung bases, as well as grunting, retractions, and nasal flaring. There are no murmurs. She is vigorous. What is your approach to this patient?
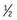 -hour-old female infant with respiratory distress. She was born at 36-
-hour-old female infant with respiratory distress. She was born at 36-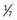 weeks’ gestation, by cesarean delivery for breech presentation to a 36-year-old G3P2002. Mother presented in labor, and the infant was found to be breech. Membranes were ruptured for 6 hours. Maternal laboratory test results were normal except group B streptococcus was positive. Mother was treated with one dose of clindamycin IV before the cesarean delivery. Apgar scores were 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Over the next 20 minutes the infant began to develop tachypnea, grunting, and retractions. At the time of your examination, temperature is 37.2°C heart rate, 150 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 75 breaths per minute. Pulse oximetry is 87% on room air. Her examination is significant for crackles bilaterally at the lung bases, as well as grunting, retractions, and nasal flaring. There are no murmurs. She is vigorous. What is your approach to this patient?
weeks’ gestation, by cesarean delivery for breech presentation to a 36-year-old G3P2002. Mother presented in labor, and the infant was found to be breech. Membranes were ruptured for 6 hours. Maternal laboratory test results were normal except group B streptococcus was positive. Mother was treated with one dose of clindamycin IV before the cesarean delivery. Apgar scores were 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Over the next 20 minutes the infant began to develop tachypnea, grunting, and retractions. At the time of your examination, temperature is 37.2°C heart rate, 150 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 75 breaths per minute. Pulse oximetry is 87% on room air. Her examination is significant for crackles bilaterally at the lung bases, as well as grunting, retractions, and nasal flaring. There are no murmurs. She is vigorous. What is your approach to this patient?3 Case: You are evaluating a male newborn in the nursery. As you review the maternal record, you note that a fetal ultrasound at 21 weeks of age showed left-sided hydronephrosis, with anteroposterior the diameter of the right renal pelvis at 5 mm, and the left at 8 mm. The infant is clinically well. His physical examination including the abdominal and genitourinary examination is normal. He has yet to void or pass stool. You are about to speak with the family. What should you tell them regarding this ultrasound abnormality? What studies will you order, and when should they be done?
4 Case: You are called to evaluate a 36-hour-old female in the nursery. This infant was born to a 16-year-old mother who received no prenatal care. The mother admits to using marijuana during pregnancy. The infant has not passed stool since birth. She was bottle feeding about 1 ounce every 3 hours. In the last two feedings, however, her mother has struggled to get her to take 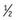 ounce. She has voided four times in the last 36 hours. Her birth weight was 2875 grams, and her weight now is 2600 grams, down 6% from birth weight. Her vital signs are stable. She is jaundiced to the neck and mildly icteric. She is fussy and has a mildly distended abdomen. Otherwise her examination is normal. How will you evaluate this patient?
ounce. She has voided four times in the last 36 hours. Her birth weight was 2875 grams, and her weight now is 2600 grams, down 6% from birth weight. Her vital signs are stable. She is jaundiced to the neck and mildly icteric. She is fussy and has a mildly distended abdomen. Otherwise her examination is normal. How will you evaluate this patient?
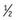 ounce. She has voided four times in the last 36 hours. Her birth weight was 2875 grams, and her weight now is 2600 grams, down 6% from birth weight. Her vital signs are stable. She is jaundiced to the neck and mildly icteric. She is fussy and has a mildly distended abdomen. Otherwise her examination is normal. How will you evaluate this patient?
ounce. She has voided four times in the last 36 hours. Her birth weight was 2875 grams, and her weight now is 2600 grams, down 6% from birth weight. Her vital signs are stable. She is jaundiced to the neck and mildly icteric. She is fussy and has a mildly distended abdomen. Otherwise her examination is normal. How will you evaluate this patient?5 Case: A female newborn is being discharged from the nursery. Her mother was on selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant therapy during pregnancy. Otherwise the prenatal and newborn nursery course has been uneventful. She has not passed her otoacoustic emissions (OAE) hearing screen. The nurses have attempted it three times, to no avail. What information and support can you offer to the family? What follow-up does this child require?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


