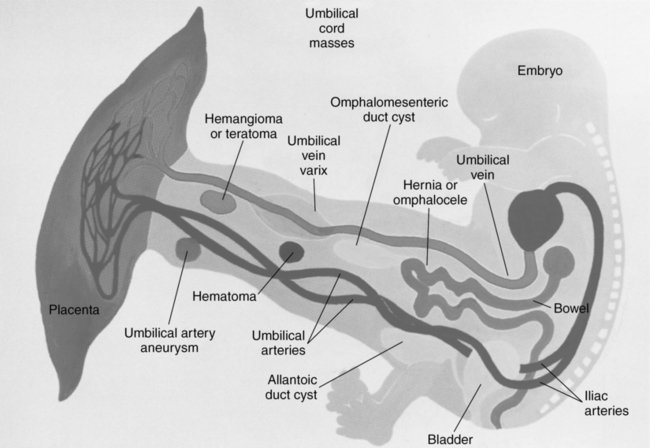
CHAPTER 28 premature detachment of the placenta from the maternal wall. elongated duct that contributes to the development of the umbilical cord. maternal surface of the placenta. cord insertion into the margin of the placenta. spontaneous uterine contraction occurring throughout pregnancy. the portion of the chorion that develops into the fetal portion of the placenta. chorion around the gestational sac on the opposite side of implantation. fetal surface of the placenta. vascular projections from the chorion at the implantation and placental site. a placental condition in which the chorionic plate of the placenta is smaller than the basal plate. occurs when the cord is completely wrapped around the fetal neck at a minimum of two times. abnormal proliferation of the trophoblastic cells in the first trimester. premature separation of the normally implanted placenta from the uterus. growth of the chorionic villi superficially into the myometrium. growth of the chorionic villi deep into the myometrium. growth of the chorionic villi through the myometrium. placenta completely covers the internal cervical os. area behind the placenta composed of the decidua, myometrium, and uteroplacental vessels. additional placenta tissue (lobes) connected to the body of the placenta by blood vessels. failure of the anterior abdominal wall to close completely at the level of the umbilicus. occurs when the intramembranous vessels course across the cervical os. mucoid connective tissue that surrounds the vessels within the umbilical cord. • Formed by the decidua basalis and decidua frondosum. • Separated from the uterine myometrium by the retroplacental complex. • Solid, homogeneous medium-gray structure. • Hyperechoic chorionic plate. • Cystic areas directly behind chorionic plate (fetal vessels). • Anechoic or hypoechoic sonolucent areas within placenta (placental lakes) are insignificant and commonly displayed after 25 weeks. • Hypoechoic retroplacental complex. • Myometrium appears as a thin hypoechoic layer posterior to the retroplacental complex. • Grading dependent on echogenicity attributed to calcium and fibrous deposition with advancing age. • Maternal hypertension, cigarette smoking, intrauterine growth restriction, and multifetal gestation may cause premature maturation. • Delayed maturation is most commonly associated with maternal diabetes mellitus. • Placental placement in front of the fetus relative to the birth canal. • Primary cause of painless vaginal bleeding in the third trimester. • Risk factors include advanced maternal age, multiparity, and previous cesarean section, therapeutic abortion, or closely spaced pregnancies. • Complications of placenta previa include premature delivery, life-threatening maternal hemorrhage, and increased risk of placenta accreta, stillbirth, and intrauterine growth restriction. • Only 5% of cases diagnosed with placenta previa in the second trimester remain at term, a result of placental migration.
Placenta and umbilical cord
Placenta
Anatomy (fig. 28-1)
Normal sonographic appearance
First trimester
Second and third trimesters
Placental maturity and grading
Placenta previa
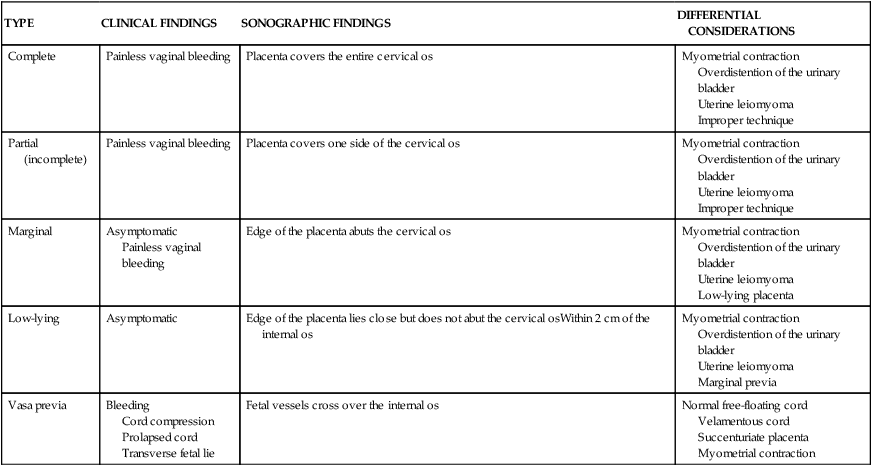
TYPE
CLINICAL FINDINGS
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Complete
Painless vaginal bleeding
Placenta covers the entire cervical os
Myometrial contraction
Overdistention of the urinary bladder
Uterine leiomyoma
Improper technique
Partial (incomplete)
Painless vaginal bleeding
Placenta covers one side of the cervical os
Myometrial contraction
Overdistention of the urinary bladder
Uterine leiomyoma
Improper technique
Marginal
Asymptomatic
Painless vaginal bleeding
Edge of the placenta abuts the cervical os
Myometrial contraction
Overdistention of the urinary bladder
Uterine leiomyoma
Low-lying placenta
Low-lying
Asymptomatic
Edge of the placenta lies close but does not abut the cervical osWithin 2 cm of the internal os
Myometrial contraction
Overdistention of the urinary bladder
Uterine leiomyoma
Marginal previa
Vasa previa
Bleeding
Cord compression
Prolapsed cord
Transverse fetal lie
Fetal vessels cross over the internal os
Normal free-floating cord
Velamentous cord
Succenturiate placenta
Myometrial contraction
ABNORMALITY
INFORMATION
SONOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
DIFFERENTIAL CONSIDERATIONS
Abruption
Premature placental detachment
Clinical findings include severe pelvic pain and vaginal bleeding
Risk factors include maternal hypertension, smoking, diabetes, trauma, placenta previa, and short umbilical cord
Hypoechoic retroplacental mass
Placental thickening
Well-defined margins
Elevation of placental edges
Subamniotic or preplacental locations are rare
Normal retroplacental complex
Amniochorionic separation
Myometrial contraction
Uterine leiomyoma
Accreta
Accreta
Chorionic villi of the placenta are in direct contact with the uterine myometrium
Attributed to complete or partial absence of the decidua basalis
Risk factors include multiparity, placenta previa, and previous cesarean section
Increta—placenta invades the uterine myometrium
Percreta—placental vessels invade the uterine serosa or urinary bladder
Accreta
Obscured or absent retroplacental complex
Numerous placental lakesIncreta
Extension of villi into the myometrium
Percreta
Extension of villi outside of the uterus
Adenomyosis
Myometrial contraction
Uterine leiomyoma
Amniochorionic separation
Amnion can be separated from the fetal surface of the placenta but cannot be separated from the umbilical insertion site
Chorion can be separated from the endometrial lining but cannot be separated from the placental edge
Localized fluid between the fetal side of the placenta and the amniotic membrane
Membrane may move
Placental abruption
Normal venous lakes
Battledore placenta
Cord inserts into the end margin of the placenta
Insertion of the cord into the end margin of the placenta
Normal cord lying adjacent to the placental margin
Velamentous cord
Calcifications
Sign of maturing placenta
Associated with maternal cigarette smoking or thrombotic disorders
Hyperechoic focus within the placental tissue
Posterior acoustic shadowing
Molar pregnancy
Circumvallate placenta
Abnormal placental shape in which the membranes insert away from the placental edge toward the center
Increases risk for abruption, intrauterine growth restriction, premature labor, and perinatal death
Rolled up placental edge
Irregular fold or thickening of the placenta
Upturned placental edge contains hypoechoic or cystic spaces
Thick placental cord insertion
Abruption
Amniotic shelf
Synechiae
Fibrin deposits
More commonly located along the subchorionic region of the placenta
Attributed to the regulation of intervillous circulation
Hypoechoic area beneath the chorionic plate of the placenta
Triangular or rectangle in shape
Venous lake
Subchorionic hematoma
Intervillous thrombosis
Presence of thrombus within the intervillous spaces
Occurs in one third of pregnancies
Little risk to fetus
Anechoic or hypoechoic intraplacental mass
Nonvascular
Chorioangioma
Placental lakes
Placental infarct
Result of ischemic necrosis
Occurs in 25% of pregnancies
No clinical risk when small
Hypoechoic focal placental mass
Calcification may occur
Intervillous thrombosis
Placental lake
Placental lakes
Also called venous lakes
Anechoic or hypoechoic area within the placenta
Internal blood flow
Intervillous thrombosis
Placental infarct
Placentomalacia
Small placenta
Intrauterine growth restriction
Intrauterine infection
Chromosomal abnormality![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access