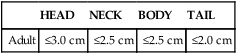
CHAPTER 9 opening in the duodenum for the entrance of the common bile duct. anomaly caused by the failure of a normal regression of the left ventral bud. multiple, persistent, or prolonged episodes of pancreatitis. the process of secreting outwardly through a duct to the surface of an organ. secondary secretory duct of the pancreas. primary secretory duct of the pancreas. controls the blood sugar level in the body. pertaining to the pancreas and duodenum. the joining of the portal, splenic, and superior mesenteric veins. • Highly digestive enzymes are secreted by the acinar cells and drain into the duodenum through the pancreatic ducts. • Chyme from the duodenum stimulates release of hormones that act on the pancreatic juices. a. cholecystokinin—produced in the duodenum to stimulate secretion of pancreatic enzymes and contraction of the gallbladder. b. gastrin—secreted by the stomach to stimulate secretion of gastric acids; stimulates growth of mucosa of the exocrine pancreas. c. secretin—produced in the duodenum to stimulate secretion of sodium bicarbonate. • Islet cells of Langerhans secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. a. alpha cells secrete glucagon (increases blood glucose). b. beta cells secrete insulin (decreases blood glucose) and move amino acid out of blood and into tissue cells. • Failure to produce sufficient amount of insulin leads to diabetes mellitus • An elongated organ lying transverse and obliquely in the epigastric and hypochondriac regions of the body. • Retroperitoneal organ located posterior to the lesser sac. • The pancreas is 12 to 18 cm long. • Divided into the tail, body, neck, head, and uncinate process. • Lies medial to the descending portion of the duodenum, lateral to the superior mesenteric vein, and anterior to the inferior vena cava. • Lies inferior and lateral to the main portal vein and hepatic artery. • Gastroduodenal artery lies in the anterolateral portion of the pancreatic head. • Common bile duct is situated in the posterolateral and inferior portion of the pancreatic head. • Failure of the normal fusion of the ducts of Wirsung and Santorini. • Duct of Wirsung is small and only drains the inferior portion of the pancreatic head. • Duct of Santorini drains the majority of the pancreas. • Nothing by mouth (NPO) 6 to 8 hours before examination for adults, 6 hours for children, and 4 hours for infants. • Emergency examinations may be performed without preparation. • Use the highest-frequency abdominal transducer possible to obtain optimal resolution for penetration depth. • Place gain settings to display the normal liver parenchyma as a medium shade of gray with adjustments to reduce echoes within the vessels. • Focal zone(s) at or below the place of interest. • Sufficient imaging depth to visualize structures immediately posterior to the region of interest. • Harmonic imaging and decreasing the compression (dynamic range) can be used to reduce artifactual echoes within anechoic structures and to improve prominence of posterior acoustic shadowing. • Spatial compounding can be used to improve visualization of structures posterior to a highly attenuating structure. • Begin with the patient in the supine position. • The pancreas lies obliquely in the abdomen and may be difficult to visualize. Use the liver as an acoustical window. • The entire pancreas and surrounding vascular landmarks must be examined and documented in two scanning planes from the level of the celiac axis to below the renal veins. • Varying patient position and imaging windows should aid in visualization. • Suspended inspiration, expiration, or Valsalva maneuver may optimize visualization. • Distending the stomach with water may aid in outlining the pancreas. • Documentation and measurement of any abnormality in two scanning planes with and without color Doppler should be included.
Pancreas
Pancreas physiology
Functions of the pancreas
Exocrine
Endocrine
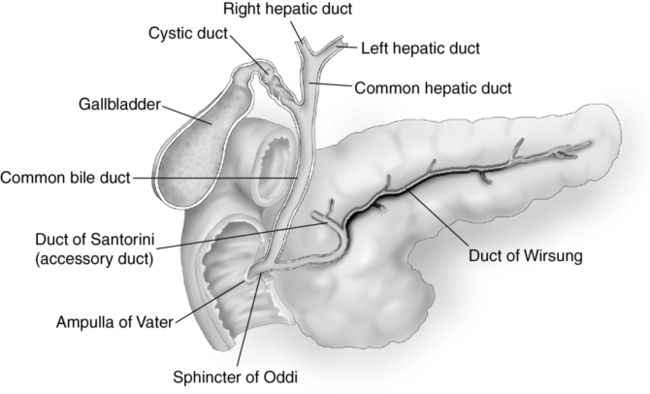
Pancreas anatomy (fig. 9-1)
Pancreas divisions and location
Head
Congenital anomalies
Pancreatic divisum
Technique
Preparation
Examination technique and image optimization
Obgyn Key
Fastest Obstetric, Gynecology and Pediatric Insight Engine